Tariffs stock market Trump sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into the complex interplay between trade policies, market fluctuations, and public opinion during the Trump administration. We’ll explore the historical context of tariffs implemented by the Trump administration, examining the various types of tariffs, their specific targets, and their potential economic consequences. We’ll delve into the correlation between tariff announcements and stock market responses, analyzing the short-term and long-term impacts on performance.
Finally, we’ll discuss the rationale behind Trump’s approach, the global responses, and the diverse perspectives on tariffs.
This analysis will not only present factual data but also offer insights into the underlying motivations and consequences of these policies. Tables and visual representations will help illustrate the key impacts and relationships, making the information easily digestible. The discussion will consider both domestic and international perspectives, allowing readers to grasp the multifaceted nature of this crucial period in economic history.
Tariffs and their Economic Impact
The Trump administration’s trade policies, heavily reliant on tariffs, significantly impacted global trade and domestic markets. These policies aimed to protect American industries and jobs, but their economic effects were complex and multifaceted. Understanding these effects requires examining the specific tariffs imposed, their targets, and the subsequent ripple effects across various sectors.
Historical Overview of Trump-Era Tariffs
The Trump administration implemented a series of tariffs on various imported goods, primarily targeting China. These tariffs were often initiated in response to perceived unfair trade practices, such as intellectual property theft or alleged subsidies to Chinese companies. The actions were often met with retaliatory tariffs from other countries.
Types of Tariffs and Targets
The Trump administration imposed different types of tariffs, including ad valorem tariffs (a percentage of the imported good’s value) and countervailing duties (imposed to offset subsidies). These tariffs were applied to a broad range of goods, encompassing consumer products, industrial materials, and agricultural products. Significant targets included steel, aluminum, solar panels, and, most notably, a wide range of Chinese goods.
Economic Consequences on Various Sectors
Tariffs imposed by the Trump administration had substantial impacts on various sectors. Manufacturing industries faced increased costs due to higher import prices for raw materials and intermediate goods. Agriculture was particularly affected, with farmers experiencing reduced export opportunities and higher input costs. Consumer goods prices also rose, impacting household budgets. The effects were not uniform across all sectors or regions.
Ripple Effects on Global Trade Relationships
The imposition of tariffs by the Trump administration led to retaliatory tariffs from other countries, disrupting global supply chains and trade relationships. These actions fostered uncertainty and instability in the international market. The retaliatory measures often impacted industries in other countries, causing disruptions and job losses.
Comparison of Domestic and International Market Effects
Tariffs imposed on imports impacted both domestic and international markets. Domestically, consumers faced higher prices, while industries dependent on imported inputs experienced increased production costs. Internationally, retaliatory tariffs led to trade disputes and reduced trade volumes, potentially hindering economic growth in other countries.
Impact on Specific Industries
| Industry | Import Impact | Export Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Steel | Increased prices for steel used in manufacturing | Reduced exports of American steel due to retaliatory tariffs |
| Aluminum | Increased prices for aluminum used in manufacturing | Reduced exports of American aluminum due to retaliatory tariffs |
| Solar Panels | Increased prices for solar panels | Reduced exports of American solar panels due to retaliatory tariffs |
| Agricultural Products (e.g., soybeans) | Reduced export markets for soybeans due to Chinese tariffs | Reduced revenue for farmers who exported to China |
| Consumer Electronics (e.g., from China) | Increased prices for consumer electronics | Reduced demand for American consumer electronics from Chinese market |
The table illustrates the import/export impacts of tariffs on selected industries. It highlights the complexities of tariff policies, demonstrating how they can influence different sectors and markets. The table represents a snapshot of the situation during the period, and effects could vary depending on the specific goods and circumstances.
Trump’s tariffs on imported goods sparked a lot of debate about their impact on the stock market. It’s a classic example of when policymakers ignore economists’ warnings about unintended consequences, like the potential for trade wars to destabilize the economy. This often leads to unpredictable results, as seen in the fluctuating stock market during that period. To learn more about the pitfalls of ignoring expert advice in policymaking, check out this insightful article on when policymakers ignore economists warnings.
Ultimately, the tariffs’ effect on the stock market remained a complex and controversial issue.
Tariffs and Stock Market Fluctuations: Tariffs Stock Market Trump

Tariffs, imposed by governments to influence trade, often have a ripple effect across various economic sectors, including the stock market. The imposition of tariffs can create uncertainty, impact supply chains, and alter consumer behavior, all of which can significantly influence investor sentiment and stock market performance. Understanding the correlation between tariff announcements and stock market responses is crucial for investors and policymakers alike.The stock market, a complex ecosystem of investor decisions, is sensitive to news events and economic signals.
Tariff announcements, as a form of economic policy, often trigger reactions in the market. These reactions can be immediate and dramatic, or they can unfold gradually over time, depending on the specifics of the tariff, the affected industries, and the overall economic climate. The impact of tariffs on the stock market is not always straightforward, and can vary depending on the nature and magnitude of the tariff.
Correlation between Tariff Announcements and Stock Market Responses
Tariff announcements frequently precede stock market fluctuations. The market often reacts negatively to the announcement of tariffs, as investors anticipate potential economic disruption, trade wars, and reduced profitability for companies involved in international trade. This reaction can be immediate, with stock prices dropping following the announcement, or more gradual, as investors process the implications of the tariff policy.
Conversely, in some cases, if the tariff is perceived as beneficial to certain sectors, or if the overall economic outlook is robust, the market may not react as dramatically.
Short-Term and Long-Term Impacts of Tariffs on Stock Market Performance
The short-term impact of tariffs on stock market performance is often characterized by volatility and uncertainty. Investors may react quickly to news of tariff increases, potentially triggering a sell-off as they assess the potential consequences. This volatility can be amplified by speculation and market sentiment. The long-term impact of tariffs is more complex, potentially affecting profitability, supply chains, and consumer confidence over an extended period.
For example, sustained tariffs on critical components can increase manufacturing costs, affecting companies’ bottom lines and impacting investor confidence in the long term.
Comparison of Stock Market Performance During Periods with and without Tariffs
Comparing stock market performance during periods with and without tariffs is a complex task, requiring careful analysis of various economic indicators. Generally, periods marked by tariff announcements or implementation are associated with increased market volatility. A comparison of the S&P 500 during periods of no tariffs versus periods of tariff implementation can reveal potential trends in market reaction.
However, a comprehensive analysis should consider factors beyond tariffs, including interest rates, inflation, and overall economic growth.
Investor Reactions to Tariff Policies
Investors respond to tariff policies in diverse ways, often depending on their individual risk tolerance and investment strategies. Some investors may be more sensitive to the short-term fluctuations in stock prices triggered by tariff announcements, while others may focus on the long-term implications of the policy. A company’s exposure to international trade can also influence investor reactions. Companies heavily reliant on international supply chains may see their stock prices more negatively impacted by tariff announcements.
Role of Uncertainty and Speculation in the Stock Market’s Response to Tariffs
Uncertainty surrounding tariff policies plays a significant role in the stock market’s response. The potential for further tariffs, retaliatory measures, or the duration of the tariffs creates an atmosphere of uncertainty. Speculation, based on interpretations of the tariff policy’s potential impact, can also significantly influence investor behavior. This can lead to significant fluctuations in stock prices that may not necessarily reflect the actual economic impact of the tariff.
Examples include the 2018-2020 US-China trade war, where the constant uncertainty regarding future tariffs impacted market confidence.
Trump’s tariffs and their impact on the stock market are definitely a hot topic, but recent developments like Trump’s big beautiful bill stumbling in the Senate as Musk steps up efforts to block it are making things even more complicated. This could have a ripple effect on the whole economy, and it’s interesting to see how the stock market reacts to these political maneuvers.
Looking ahead, the future of tariffs under the new administration could significantly influence the stock market’s trajectory.
S&P 500 Performance Before, During, and After Significant Tariff Announcements (Illustrative Table)
| Period | S&P 500 Performance | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-Tariff Announcement (e.g., 2017) | Steady Growth | Stable economic climate, low tariff activity. |
| During Tariff Announcement (e.g., 2018) | Fluctuating (Negative) | Announcement of tariffs triggers negative reactions, with volatility in the market. |
| Post-Tariff Announcement (e.g., 2019) | Mixed (Negative/Positive) | Market response is influenced by the policy’s duration and any retaliatory measures. |
Note: This table is illustrative and should not be considered an exhaustive analysis of all tariff periods.
Trump’s Trade Policies and Public Opinion
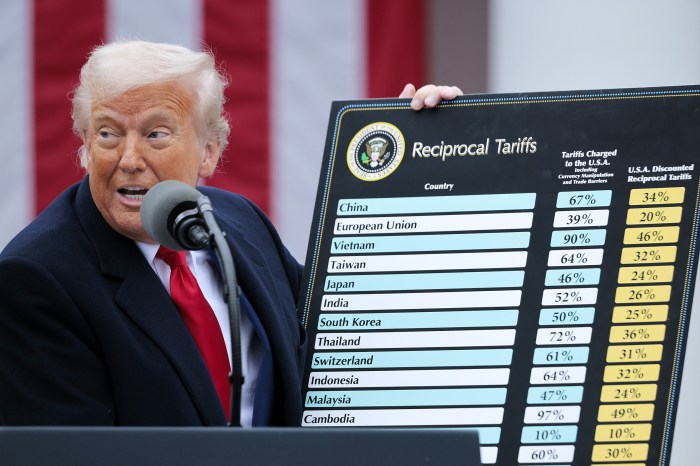
Donald Trump’s approach to international trade, characterized by a significant emphasis on tariffs, generated considerable debate and diverse reactions. His policies aimed to reshape global trade relationships, but their impact extended far beyond economic considerations, profoundly affecting public opinion and political dynamics both domestically and internationally. This analysis delves into the rationale behind these policies, examines public perceptions, and explores the political ramifications.Trump’s trade policies were largely driven by a belief that existing international trade agreements were disadvantageous to the United States.
He argued that these agreements led to job losses and a trade deficit, necessitating a more protectionist stance to safeguard American industries and workers. This viewpoint, often framed as “America First,” was central to his rationale for imposing tariffs on goods from various countries, particularly China.
Rationale Behind Trump’s Approach to Tariffs
Trump’s administration justified tariffs as a means to level the playing field in international trade. They contended that tariffs would reduce the trade deficit, encourage domestic production, and protect American industries from unfair competition. Advocates argued that tariffs would pressure foreign governments to negotiate fairer trade deals, ultimately benefiting the United States. A key element was the belief that tariffs would strengthen American manufacturing and revitalize struggling sectors.
Public Perception of Trump’s Trade Policies
Domestically, public opinion on Trump’s tariffs was sharply divided. Supporters viewed them as a necessary measure to protect American jobs and industries. Critics, however, argued that tariffs imposed significant costs on consumers through higher prices and hindered economic growth. The impact on specific industries and regions varied significantly, with some sectors experiencing job losses while others saw increased production.Internationally, Trump’s tariffs were met with a mix of concern and opposition.
Many countries viewed the tariffs as protectionist and retaliatory, leading to trade wars and disruptions in global supply chains. This often resulted in negative impacts on international trade relationships and led to concerns about a global economic downturn. International organizations like the WTO voiced concerns about the potential for widespread trade disruptions.
Trump’s tariffs definitely had an impact on the stock market, didn’t they? It’s fascinating how economic policies ripple through everything, even seemingly unrelated areas like music videos. Speaking of which, have you seen the top 10 music videos of all time according to AI? the top 10 music videos of all time according to ai It’s pretty interesting how a machine can have such a refined taste! Ultimately, though, the complexities of tariffs and their effects on the stock market remain a complex subject.
Political Implications on Trump’s Support Base, Tariffs stock market trump
Trump’s trade policies had significant political implications for his support base. Supporters in the manufacturing sector and rural communities often viewed the tariffs as beneficial, boosting their economic prospects. Conversely, sectors reliant on international trade or import-dependent consumers experienced economic headwinds, potentially alienating certain segments of the electorate. The political implications of these policies varied greatly depending on the specific constituency.
Arguments For and Against Tariffs
- Arguments in Favor of Tariffs: Proponents argued that tariffs could protect domestic industries, increase domestic employment, and reduce the trade deficit. They believed that tariffs would force foreign countries to negotiate fairer trade agreements. The argument that tariffs would strengthen the American manufacturing sector was frequently emphasized.
- Arguments Against Tariffs: Critics argued that tariffs increased consumer prices, reduced economic growth, and led to retaliatory measures from other countries. They highlighted the potential for trade wars and disruptions in global supply chains. The potential for negative impacts on specific industries and regions was also a major concern.
Role of Trade Negotiations and Agreements in Shaping Public Opinion
Trade negotiations and agreements significantly influenced public opinion on Trump’s policies. The outcomes of these negotiations, particularly those resulting in trade disputes and tariffs, directly shaped public perceptions. The perception of fairness and reciprocity in trade agreements played a crucial role in shaping public opinion, with differing interpretations on whether existing agreements were advantageous or detrimental to the United States.
Summary of Arguments for and Against Tariffs
| Argument | Perspective | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Tariffs protect domestic industries | Pro-tariff | Various industry lobby groups |
| Tariffs increase domestic employment | Pro-tariff | Congressional testimony |
| Tariffs reduce trade deficit | Pro-tariff | Government trade reports |
| Tariffs lead to higher consumer prices | Anti-tariff | Economic analyses |
| Tariffs hinder economic growth | Anti-tariff | International economic organizations |
| Tariffs lead to trade wars | Anti-tariff | World Trade Organization reports |
Global Responses to Trump’s Tariffs
Trump’s imposition of tariffs sparked a wave of retaliatory measures from other countries, significantly impacting global trade and international relations. The ensuing trade conflicts had far-reaching consequences, affecting not only specific industries but also the broader economic landscape and geopolitical dynamics. The responses varied considerably, reflecting the unique economic and political contexts of each nation.
Retaliatory Actions by Other Nations
Various countries responded to Trump’s tariffs with retaliatory measures of their own, targeting American exports in sectors like agriculture, manufacturing, and technology. These actions were often coordinated among affected nations, demonstrating a collective resistance to what they perceived as unfair trade practices. The scale and scope of these responses varied, ranging from limited counter-tariffs to broader trade restrictions.
- China, arguably the most significant responder, implemented tariffs on numerous American goods, including agricultural products like soybeans and manufactured items. These retaliatory measures aimed to counter the economic damage inflicted by Trump’s tariffs and protect their domestic industries.
- The European Union (EU) imposed tariffs on American products, particularly agricultural goods and steel, as a direct response to the US tariffs. This action underscored the EU’s commitment to protecting its own industries and farmers from the negative effects of the trade war.
- Canada and Mexico, key trading partners of the US, also implemented tariffs on American goods as part of their retaliatory actions. These actions highlight the interconnectedness of global trade and the ripple effects of protectionist policies.
Impact on International Relations
Trump’s tariffs significantly strained international relations. The trade conflicts created friction between the US and its trading partners, leading to a decline in trust and cooperation. The uncertainty and unpredictability surrounding the trade policies negatively impacted investment and economic growth globally. The conflicts also raised questions about the future of the global trading system.
- The trade wars undermined the foundations of the existing multilateral trading system, raising concerns about the future of international cooperation on trade issues.
- The disputes frequently escalated into diplomatic tensions, leading to strained relationships between the US and its trading partners. The political ramifications of the trade conflicts were substantial.
Responses from International Organizations
International organizations like the World Trade Organization (WTO) played a crucial role in addressing the trade disputes arising from Trump’s tariffs. The WTO’s role in mediating trade disagreements and upholding international trade rules became even more critical during this period.
- The WTO issued rulings and recommendations in response to the trade disputes, aiming to resolve the conflicts and restore a more predictable trading environment.
- The WTO’s actions often faced criticism and challenges, as countries sought to protect their national interests and resist international pressure to comply with established trade rules.
Comparison of Trade Policies
Comparing the trade policies of other major world economies during this period reveals a complex picture. While some nations adopted more protectionist measures in response to Trump’s tariffs, others maintained more open and free trade policies. The varying approaches reflected the diverse economic and political priorities of different countries.
Table: Global Responses to Trump’s Tariffs
| Country | Retaliatory Measures | Overall Impact |
|---|---|---|
| China | Tariffs on US agricultural products, manufactured goods | Significant impact on bilateral trade, strained relations |
| EU | Tariffs on US agricultural goods, steel | Increased trade tensions with the US, impact on European industries |
| Canada | Tariffs on US goods, particularly agricultural products | Negative impact on bilateral trade, strained relations |
| Mexico | Tariffs on US goods, particularly agricultural products | Significant impact on bilateral trade, strained relations |
| Others | Varied, including tariffs, sanctions, and trade restrictions | Varied impacts depending on the specific trade relationships and industries affected |
Economic Models and Tariff Impact Predictions
Predicting the precise economic effects of tariffs is notoriously difficult. Numerous economic models attempt to simulate the consequences, but these models are never perfect representations of the complex global economy. Their outputs should be viewed as estimations rather than definitive forecasts. Understanding the strengths and limitations of these models is crucial for interpreting their results.Economic models, when applied to tariffs, try to capture the interplay of supply, demand, prices, and trade flows.
These models often consider factors like consumer behavior, producer responses, and the impact on international trade relationships. While no model perfectly mirrors reality, they provide valuable insights into potential outcomes and offer a structured way to think about the various channels through which tariffs might influence the economy.
Economic Models Used to Predict Tariff Effects
Various economic models are employed to simulate the effects of tariffs. These models differ in their complexity and the assumptions they make. Some common models include computable general equilibrium (CGE) models, partial equilibrium models, and econometric models. CGE models are designed to capture the broad macroeconomic effects, while partial equilibrium models focus on specific sectors or markets.
Econometric models utilize historical data to identify correlations between tariffs and economic variables.
Examples of Models Used to Estimate the Cost of Tariffs
The US International Trade Commission (ITC) frequently utilizes CGE models to assess the potential impact of tariffs on domestic industries and consumers. For instance, in their analysis of tariffs on imported steel, they considered the impact on steel prices, the demand for steel products, and the profitability of steel-producing companies. Other models, like those used by the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), focus on the broader global implications of tariffs.
Limitations and Assumptions of Economic Models
Economic models rely on assumptions about consumer behavior, firm responses, and the behavior of other countries in the international marketplace. These assumptions often simplify complex realities. For example, a model might assume that firms adjust their production immediately after a tariff is implemented, or that consumers will not alter their purchasing habits in response to price changes. These simplifications limit the model’s accuracy.
The models also struggle to capture unexpected events like changes in global demand or supply chains.
Challenges in Accurately Predicting Tariff Effects
Predicting the effects of tariffs is challenging because of the multitude of interacting factors. Changes in global supply chains, shifts in consumer preferences, and political developments can all influence the actual outcomes. Furthermore, the impact of tariffs can vary depending on the specific industry, the size of the tariff, and the overall economic conditions.
Economic Factors Influencing Tariff Effectiveness
Tariff effectiveness is not solely determined by the tariff rate. Factors such as the elasticity of demand for the affected goods, the availability of substitute goods, and the ability of domestic producers to adapt to the new market conditions all play a significant role. Tariffs might be more effective in markets with inelastic demand, meaning consumers are less responsive to price changes.
If producers lack alternatives, the tariff’s impact on prices and market share is likely to be greater.
Key Variables in a Tariff Impact Model
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Tariff Rate | Percentage increase in import price |
| Import Demand | Quantity of imported goods demanded |
| Domestic Supply | Quantity of domestically produced goods supplied |
| Consumer Prices | Prices paid by consumers for goods |
| Producer Prices | Prices received by domestic producers |
| Exchange Rates | Value of domestic currency relative to foreign currencies |
| Global Economic Conditions | Overall state of the global economy |
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, tariffs stock market Trump paints a complex picture of economic and political interactions. The analysis revealed a significant correlation between tariff announcements and stock market fluctuations, highlighting the uncertainty and speculation inherent in these policies. Furthermore, the global responses and diverse public opinions underscore the far-reaching implications of trade conflicts. The intricate interplay of economic models, market reactions, and political considerations creates a dynamic environment, demonstrating the need for careful analysis and consideration of various perspectives.

