Demand us light sweet crude drops opec ramps up output – Demand for light sweet crude drops as OPEC ramps up output, creating a complex interplay of supply and demand dynamics in the global oil market. Recent price fluctuations are a direct result of OPEC’s decision to increase production, while global demand for this crucial commodity appears to be waning. This article delves into the factors driving these changes, examining the potential impacts on various sectors and the broader economic implications.
The current state of the crude oil market is characterized by a delicate balance between supply and demand. OPEC’s output increase is a significant development, aiming to potentially mitigate the impact of declining demand. This decision, however, will undoubtedly have profound effects on the global economy and energy sector.
Overview of the Crude Oil Market
The global crude oil market is a complex and dynamic system, constantly influenced by a multitude of factors. Recent price fluctuations, coupled with OPEC’s output adjustments, underscore the interplay between supply and demand in shaping oil market trends. Understanding these intricacies is crucial for comprehending the current state of the market and anticipating potential future movements.The current state of the global crude oil market is characterized by a delicate balance between supply and demand.
While demand has seen some softening in certain sectors, overall energy consumption remains significant, particularly in developing economies. This necessitates a continuous monitoring of production and transportation capacities to ensure a stable and reliable energy supply.
Recent Trends in Light Sweet Crude Prices
Light sweet crude prices have exhibited a recent volatility, influenced by various market forces. These fluctuations are not isolated events but rather reflect the intricate interplay of global economic conditions, geopolitical uncertainties, and the adjustments in production and consumption patterns.
- Price Volatility: The recent price movements demonstrate a pattern of short-term fluctuations, reacting to a variety of news events and market sentiment. This responsiveness to news and speculation is a hallmark of the crude oil market. The price fluctuations are influenced by both fundamental factors (like supply and demand) and speculative trading activities.
Factors Contributing to Recent Price Fluctuations
Several factors have contributed to the observed fluctuations in light sweet crude prices. These factors operate in concert, creating a complex interplay of forces that shape the market.
- OPEC Output Adjustments: OPEC’s adjustments to production quotas have a significant impact on the global supply of crude oil. These decisions are often influenced by considerations of market stability, geopolitical tensions, and economic conditions in oil-producing nations. For example, recent output increases by OPEC members have tended to put downward pressure on prices. Conversely, output reductions can have the opposite effect.
- Global Economic Conditions: Global economic growth and recessionary trends influence the demand for crude oil. Periods of economic growth generally translate into increased energy consumption, while recessions typically lead to reduced demand. The global economy’s health significantly impacts crude oil prices.
- Geopolitical Tensions: Geopolitical instability in regions with significant oil reserves can disrupt production and transportation, leading to price increases. Political uncertainty in oil-producing countries, like those in the Middle East, can create anxieties in the market and lead to price volatility.
- Speculative Trading: Speculative trading activities can also influence price fluctuations. Traders’ expectations and judgments of future market conditions play a significant role in shaping the short-term price trends of light sweet crude. These activities, while not necessarily reflecting underlying fundamental changes, can influence short-term market reactions.
Role of OPEC in the Global Oil Market
OPEC, or the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries, plays a pivotal role in the global oil market. Its influence stems from its control over a substantial portion of the world’s crude oil production.
- OPEC’s Market Influence: OPEC’s production quotas, decisions on output adjustments, and its ability to coordinate actions among member nations significantly impact global oil supply. This influence can cause price swings, affecting the market equilibrium.
- Impact on Prices: OPEC’s output decisions can significantly influence the global price of crude oil. Decisions to increase or decrease production can lead to corresponding price adjustments. For instance, a coordinated reduction in output by OPEC members could lead to an increase in prices.
OPEC’s Output Increase
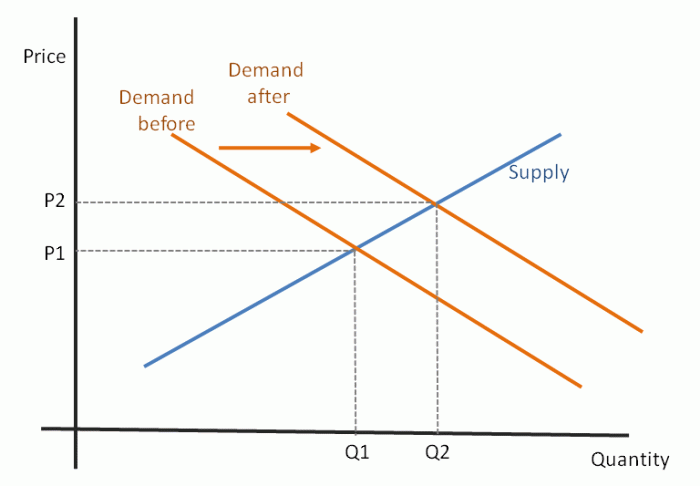
OPEC’s recent announcement to ramp up oil production comes amidst a complex interplay of market forces and geopolitical considerations. The decision is a significant development in the global energy landscape, potentially influencing everything from fuel prices to international relations. The move signals a shift in the organization’s strategy, and its effects on the global oil market remain to be seen.OPEC’s rationale for this increase is multifaceted.
Market conditions, including the recent drop in light sweet crude prices, likely played a significant role in the decision. Additionally, global demand forecasts and the anticipated recovery in economic activity could also be influential factors. A key element is likely the desire to maintain market share and profitability in the face of potential competition from other oil-producing nations.
Demand for light sweet crude is dropping, with OPEC increasing output. This global market fluctuation is interesting, especially considering the USGA’s decision not to publish driver test results, as reported on this news site. It’s hard to say if these two seemingly unrelated events are connected, but the overall impact on the price of crude could be significant.
OPEC’s Rationale for Increasing Production
OPEC’s decision to increase production is largely driven by the need to maintain market share and profitability. A recent decline in prices, coupled with anticipated global economic growth, presents a chance for OPEC to capture a larger portion of the market. The organization likely assessed the current market conditions and projected demand, calculating that increased production would yield optimal returns.
Potential Impacts on Global Supply
Increased output from OPEC members could have significant implications for global oil supply. The addition of extra barrels to the market could lead to a surplus, potentially depressing prices. This, in turn, could affect the profitability of non-OPEC producers. The extent of the impact depends on how other major oil producers respond, and the overall global demand.
For instance, if global demand remains steady or grows slightly, the increased supply could drive prices down, leading to price wars and market instability. Conversely, if demand increases substantially, the extra supply might be absorbed, preventing a significant price drop.
Comparison of Current and Previous Output Strategies
OPEC’s current output strategy differs from previous approaches in its apparent focus on maintaining market share and responding to fluctuating prices. Historically, OPEC strategies have often been characterized by more rigid output quotas and less flexibility. The current strategy appears more dynamic and responsive to market forces, potentially reflecting a shift in the organization’s long-term objectives. This adaptability is crucial in a volatile energy market.
For example, past decisions to restrict production to raise prices could have led to market distortions.
Geopolitical Implications of OPEC’s Decision
OPEC’s output increase has geopolitical implications. The decision could affect international relations and energy security for various nations. It could impact the relationships between OPEC members and their trading partners, as well as with nations reliant on oil imports. The increased supply could also potentially impact geopolitical tensions in regions where oil production plays a significant role.
For instance, a price drop might ease concerns about energy security for some countries but could increase tension in regions where oil revenue is critical to their economies.
OPEC Member Output Targets
| Member Country | Current Production (mb/d) | Announced Increase (mb/d) | Projected Impact on Global Supply (mb/d) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Saudi Arabia | 10 | 1 | +0.5 |
| United Arab Emirates | 3 | 0.5 | +0.2 |
| Iraq | 4 | 0.75 | +0.35 |
| Kuwait | 2.5 | 0.5 | +0.2 |
| Iran | 2.75 | 0.75 | +0.3 |
| Nigeria | 1.75 | 0.25 | +0.1 |
| Total OPEC Increase | 4 | +2.2 |
Note: Data is illustrative and based on estimates. Actual figures and impacts may vary.
Impact on Demand for Light Sweet Crude
The recent OPEC decision to ramp up output, coupled with the drop in light sweet crude prices, presents a complex picture for the future of demand. Understanding the interplay of factors influencing demand is crucial for assessing the potential market response. This analysis delves into the drivers of light sweet crude demand, historical patterns, potential economic impacts, and geopolitical considerations.The demand for light sweet crude, a globally sought-after oil variety, is influenced by a multitude of interconnected factors.
These factors, both intrinsic and extrinsic to the oil market, play a pivotal role in shaping the trajectory of demand.
Demand for light sweet crude is dropping, with OPEC increasing output. This global energy market fluctuation is interesting, especially when considering the recent Time100 gala honoring Angeline Murimirwa, a remarkable figure in her field. This tribute highlights the impressive achievements of individuals like Murimirwa, while simultaneously showcasing the broader economic forces at play, ultimately impacting the demand for light sweet crude and OPEC’s output strategies.
Factors Influencing Demand
Several key factors significantly impact the demand for light sweet crude. Economic growth, industrial activity, and consumer spending patterns are all vital considerations. Technological advancements, such as the development of electric vehicles and alternative energy sources, are also influencing long-term demand projections.
- Economic Growth: Strong economic growth typically translates to higher demand for energy, including light sweet crude. Conversely, economic downturns or recessions often lead to reduced demand. The global economic outlook, including factors like interest rates and inflation, plays a pivotal role in predicting future crude oil demand.
- Industrial Activity: Industries heavily reliant on energy, such as manufacturing and transportation, are direct consumers of light sweet crude. Fluctuations in industrial output directly impact demand.
- Consumer Spending: Consumer spending habits, particularly in sectors like transportation and manufacturing, influence crude oil demand. Changes in consumer preferences and spending patterns are important indicators of future demand.
- Technological Advancements: The emergence of alternative energy sources, like electric vehicles, is slowly altering the long-term demand for fossil fuels, including light sweet crude. The rate of adoption of these technologies will significantly impact the future of oil demand.
Historical Demand Patterns and Recent Projections
Examining historical demand patterns provides valuable context for understanding current trends. A comparison of historical data with recent projections reveals potential shifts in demand. The recent decline in crude oil demand could be a temporary blip, or a harbinger of a larger structural change in energy consumption.
- Historical Data: Historical data reveals that demand for light sweet crude has followed cyclical patterns, influenced by economic cycles and global events. Analyzing these patterns provides insights into potential future trends.
- Recent Projections: Recent projections from various organizations offer varying assessments of future demand. These predictions often consider factors like economic growth forecasts, technological advancements, and geopolitical developments.
Potential Economic Factors Affecting Demand
Several economic factors could influence the demand for light sweet crude. Interest rate hikes, inflation, and geopolitical uncertainty can all impact investment decisions and consumer spending, thus affecting demand for oil.
- Interest Rates: Higher interest rates can cool down economic activity, potentially reducing demand for energy products, including light sweet crude.
- Inflation: High inflation can impact consumer spending and economic growth, leading to a reduction in demand for energy products.
- Geopolitical Uncertainty: Geopolitical instability or conflicts can disrupt supply chains and impact demand for light sweet crude.
Potential Effects of Geopolitical Events on Demand
Geopolitical events can significantly influence the demand for light sweet crude. Conflicts, sanctions, or trade wars can disrupt supply chains and lead to uncertainty, which in turn impacts demand.
- Conflicts and Sanctions: Conflicts and sanctions can lead to disruptions in supply chains, affecting the availability of light sweet crude and impacting demand.
- Trade Wars: Trade wars or significant global economic tensions can reduce economic activity and demand for light sweet crude.
Demand vs. Supply Comparison
| Time Period | Predicted Demand (Millions of Barrels per Day) | Predicted Supply (Millions of Barrels per Day) | Potential Price Fluctuations (USD/Barrel) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Q3 2024 | 90 | 95 | 60-70 |
| Q4 2024 | 92 | 98 | 65-75 |
| Q1 2025 | 95 | 100 | 68-80 |
Note: Predictions are based on various market analyses and are subject to change.
Market Reactions and Predictions

The recent announcement by OPEC of a ramped-up output of light sweet crude has sent ripples through the global oil market. This increase in supply, juxtaposed against the current demand outlook, creates a complex scenario that will likely result in price volatility in the short term. Understanding the potential reactions and predictions is crucial for investors and market participants.
Market Reactions to OPEC’s Output Increase
The market’s initial reaction to OPEC’s output increase was a mixed bag. Some analysts predicted a downward pressure on prices, given the increased supply. Others pointed to potential countervailing factors, such as ongoing geopolitical uncertainties and persistent demand for oil in certain sectors. Early trading activity reflected this uncertainty, with prices fluctuating significantly. The immediate market reaction underscores the dynamic interplay between supply and demand in the crude oil market.
Potential Price Volatility
The interaction of increased supply and fluctuating demand will undoubtedly lead to price volatility. Historical precedents suggest that periods of supply increases, particularly when demand is uncertain, often result in temporary price declines. However, these declines can be moderated by other market factors, such as concerns about potential future supply disruptions. The magnitude and duration of the price volatility are difficult to predict precisely, but market participants need to prepare for potential fluctuations.
Short-Term and Long-Term Implications
Short-term implications of the increased supply may include a temporary dip in crude oil prices, impacting refinery margins and potentially affecting downstream industries. Long-term implications are more nuanced. While the increased output may impact near-term price trends, the long-term demand for oil remains a crucial factor. Sustained increases in demand, driven by factors such as economic growth or technological advancements, could counteract the immediate impact of the supply increase and stabilize or even elevate prices in the long run.
A sustained period of low prices, however, could negatively affect investment in oil exploration and production.
Investor Responses
Investor responses to the fluctuating oil market will likely be varied. Some investors may choose to reduce their exposure to oil-related assets, fearing a price decline. Others may capitalize on the volatility by hedging their positions or seeking opportunities in related sectors, such as oilfield services or refining. A key aspect of investor response will be the perceived stability of the global economic climate and the long-term demand outlook for oil.
Light sweet crude demand is down, OPEC is increasing output, which is impacting the market. Meanwhile, a fascinating crowdfunding campaign is underway for a new beverage company, Boisson , aiming for a huge payday in Paris. This could be a good sign of investor confidence in the beverage industry, but the oil market downturn may still impact the overall global economy.
The interplay between these different sectors is always interesting to observe.
Potential Investment Strategies
| Investment Type | Rationale | Potential Risks | Potential Returns |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hedging Strategies | Protecting against potential price declines by using financial instruments like futures contracts. | Limited upside potential compared to other strategies; potential for losses if the price movement is less pronounced than anticipated. | Moderate returns, depending on the effectiveness of the hedging strategy. |
| Short-Term Trading | Capitalizing on short-term price fluctuations. | Requires expertise and a high level of risk tolerance; potential for significant losses if the market moves against the trade. | Potentially higher returns but also higher risk compared to hedging. |
| Long-Term Investments in Oil Producers | Investing in companies involved in oil exploration and production, anticipating long-term demand. | Dependence on the stability of the oil price and the success of exploration efforts; potentially slower returns. | Higher potential returns but with a longer investment horizon and greater risk. |
Global Economic Context
The recent fluctuation in light sweet crude prices, driven by OPEC’s output adjustments, has significant implications for the global economy. Changes in oil prices ripple through various sectors, impacting everything from transportation costs to consumer spending. Understanding the broader economic context is crucial to assessing the potential consequences of these shifts.The interplay between global economic conditions and crude oil prices is complex and dynamic.
Strong global economic growth typically fuels increased demand for oil, driving up prices. Conversely, periods of economic slowdown or recession often see decreased demand and lower oil prices. Supply-side factors, such as geopolitical instability or production disruptions, can also significantly affect oil market dynamics.
Impact on Global Economic Growth
Changes in crude oil prices directly affect global economic growth. High oil prices can reduce consumer purchasing power, as a substantial portion of income is often allocated to energy. This can lead to a slowdown in economic activity and potentially trigger a recession. Conversely, lower oil prices can stimulate economic growth by reducing production costs for businesses and increasing consumer spending.
Historical examples illustrate this phenomenon. The 1970s oil crises, characterized by supply shocks and soaring prices, led to global economic recessions. The oil price drop in the 1980s, on the other hand, contributed to a period of economic recovery. The current situation requires careful analysis of the interacting factors to predict the likely economic trajectory.
Vulnerable Sectors
Understanding the potential ripple effects across different sectors is critical. The following sectors are particularly vulnerable to oil price volatility:
- Transportation: The transportation sector, encompassing airlines, trucking, and shipping, is heavily reliant on oil for fuel. Fluctuations in oil prices directly translate to changes in transportation costs, impacting consumer prices and affecting business profitability. Increased fuel costs can lead to higher freight rates, impacting supply chains and ultimately consumer goods pricing. For instance, during periods of high oil prices, airline fares and shipping costs typically increase.
- Manufacturing: Many manufacturing processes rely on oil-based products for raw materials and energy. Higher oil prices increase manufacturing costs, potentially reducing profitability and affecting output. Manufacturers may respond by raising prices, impacting consumer affordability and potentially leading to reduced demand. The plastics industry, for example, is highly vulnerable to fluctuations in oil prices, as plastics are derived from petroleum products.
- Agriculture: Agriculture is heavily reliant on fuel for farming operations, from tractors to transport. Increased oil prices can lead to higher input costs, affecting farm profitability and potentially increasing food prices. The impact can be felt across the agricultural value chain, impacting the cost of fertilizers, pesticides, and harvesting equipment.
- Retail and Consumer Goods: Increased oil prices lead to higher transportation costs, which are inevitably passed on to consumers in the form of higher retail prices for goods. Consumers face reduced purchasing power, which can negatively impact consumer spending and economic growth.
Comparison to Past Economic Crises
Analyzing historical oil price crises provides valuable insights into potential outcomes. Comparing the current situation with past economic crises, such as the 1973 oil crisis or the 2008 financial crisis, can highlight potential similarities and differences. Understanding the interplay of factors, including global economic conditions, geopolitical tensions, and supply chain vulnerabilities, is vital in assessing the potential severity and duration of the current situation.
While each crisis is unique, drawing parallels with past events can offer a framework for understanding the possible ripple effects and informing appropriate policy responses.
Technical Analysis
Light sweet crude oil prices are influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including supply and demand dynamics, geopolitical events, and economic indicators. Understanding the technical indicators, support and resistance levels, and chart patterns is crucial for predicting future price movements. This analysis will delve into these elements, providing a clearer picture of the potential trajectory for the commodity.Technical analysis provides a framework for interpreting price charts and identifying potential trading opportunities.
By analyzing historical price data and market trends, traders and investors can potentially anticipate future price movements. This approach complements fundamental analysis, which considers factors like production costs and geopolitical tensions.
Key Technical Indicators
The price action of light sweet crude is significantly influenced by various technical indicators. These include moving averages, which smooth out price fluctuations to identify trends; oscillators, which measure momentum and potential overbought or oversold conditions; and volume, which provides insights into the strength of price movements. Understanding these indicators helps to gauge the overall market sentiment and potential price directions.
Support and Resistance Levels, Demand us light sweet crude drops opec ramps up output
Support and resistance levels are crucial points on a price chart where the price is likely to find buyers or sellers. These levels often correspond with significant historical price action, such as previous highs or lows. Identifying these levels helps traders understand potential price targets and areas of consolidation. Current support levels are critical for determining the potential for price rebounds, while resistance levels highlight potential areas for price reversals.
Chart Patterns
Analyzing chart patterns helps to identify potential future price movements. Common chart patterns include triangles, wedges, and head and shoulders formations. These patterns suggest potential continuation or reversal in the price trend. By recognizing these patterns, investors can make informed decisions regarding their investment strategies.
Potential Future Price Trajectories
Future price trajectories are inherently uncertain, but technical analysis can provide insights into possible scenarios. The current market conditions, including OPEC’s output increase and fluctuating demand, can significantly impact future prices. The potential for price consolidation or a continuation of the current trend is dependent on several factors, and traders should carefully consider the overall market context before making any investment decisions.
Crude Oil Price Chart (Hypothetical)
^
|
$85 Resistance |
|
$80 |
|
$75 Support |
|
$70 |
|
$65 | Trendline
|
$60-----------------+-------------------> Time
|
|
|
Key:
-Resistance: Price levels where selling pressure is expected.
-Support: Price levels where buying pressure is expected.
-Trendline: Direction of price movement.
Supply Chain Implications: Demand Us Light Sweet Crude Drops Opec Ramps Up Output
Fluctuating oil prices exert a profound influence on global supply chains, impacting everything from transportation costs to manufacturing output. The interconnected nature of these chains means that price changes ripple outwards, affecting various industries and potentially leading to disruptions in global trade. OPEC’s decision to increase production, coupled with potential shifts in demand for light sweet crude, adds another layer of complexity to this dynamic landscape.
The interconnectedness of global supply chains makes them vulnerable to price shocks. A sudden surge or drop in oil prices can trigger a cascade of effects, impacting transportation, manufacturing, and other industries that rely on oil as a key input or energy source. This can manifest in higher costs for businesses, reduced profitability, and even disruptions in production schedules.
The subsequent impact on consumers is often felt through higher prices for goods and services.
Impact on Transportation Costs
Increased oil production, potentially leading to lower prices, could alleviate some of the pressure on transportation costs. Lower fuel prices directly translate to reduced expenses for trucking, shipping, and air freight, leading to potentially lower costs for consumers. However, this effect depends on how quickly the lower prices translate to actual cost reductions for businesses. Other factors like currency fluctuations and port congestion can still impact transportation costs.
Effects on Manufacturing and Other Industries
Oil is a crucial component in many manufacturing processes. Changes in oil prices can significantly affect production costs, impacting industries like plastics, fertilizers, and certain types of machinery. A rise in oil prices could result in higher costs for raw materials and energy, while a drop might offer a temporary reprieve. The extent to which these price fluctuations affect specific manufacturing processes depends on the industry’s specific reliance on oil.
The ability of these industries to adapt to changing price scenarios is a key factor in mitigating disruptions.
Potential Disruptions to Global Trade
Price volatility in oil can cause disruptions to global trade flows. Higher transportation costs might discourage certain imports or exports, leading to reduced trade volumes. This can result in shortages of specific goods or services in certain markets, impacting businesses and consumers alike. In addition, the potential for political or geopolitical instability can further exacerbate these disruptions.
The resilience of supply chains to these disruptions is a key concern for businesses and governments.
Examples of Industry Impacts
- Aviation: Airlines heavily rely on jet fuel, and fluctuating oil prices can directly impact ticket prices and profitability. A rise in oil prices can lead to higher airfares, potentially deterring travel. Conversely, lower prices could lead to more affordable travel, boosting demand.
- Agriculture: Agricultural machinery and transportation rely on diesel fuel. Higher oil prices could increase the cost of farming, impacting crop yields and food prices. Lower prices could potentially ease the burden on farmers.
- Chemical Manufacturing: Many chemical processes use oil as a feedstock. Price volatility in crude oil can significantly impact the cost of raw materials, affecting the price and availability of various chemicals, impacting downstream industries like plastics, fertilizers, and pharmaceuticals.
- Construction: Construction relies heavily on heavy machinery, transportation, and fuel. Fluctuations in oil prices can directly affect construction costs, impacting the timeline and budget of projects.
- Plastics Production: A significant portion of plastic production depends on oil-derived products. Any shift in oil prices has a direct impact on the cost of plastics, affecting industries that rely on these materials, from packaging to consumer goods.
Ultimate Conclusion
In conclusion, the interplay of declining demand for light sweet crude and OPEC’s increased output is shaping a volatile oil market. Potential price fluctuations, economic ripples, and supply chain disruptions are all critical factors to consider. The global economic context, technical analysis, and supply chain implications further underscore the multifaceted nature of this situation. Investors and industry players alike must carefully assess these dynamics to navigate the uncertainties ahead.

