Sempras port arthur phase 2 wins us approval export lng – Sempra Port Arthur Phase 2 wins US approval for exporting LNG, marking a significant step forward in the energy sector. This project, situated in the strategic Port Arthur region, promises substantial economic benefits for the area, but also raises important questions about environmental impacts and community engagement. We’ll delve into the details of the approval process, economic projections, potential challenges, and the broader implications for the LNG market.
The project’s approval is a complex process involving various regulatory agencies and international trade agreements. Key considerations include the project’s environmental impact, infrastructure requirements, and potential community impacts. This approval sets the stage for potential future development in the region and warrants careful consideration of the long-term implications.
Project Overview
Sempra’s Port Arthur Phase 2 LNG export project is a significant undertaking poised to bolster the Texas energy landscape. This expansion builds upon the existing infrastructure and promises to significantly increase the region’s LNG production capacity. The project’s approval marks a crucial step towards its realization, and the subsequent export potential is expected to have considerable economic impact.
Project Description, Sempras port arthur phase 2 wins us approval export lng
Port Arthur Phase 2 involves the expansion of Sempra’s existing liquefied natural gas (LNG) export facility in Port Arthur, Texas. This expansion will include new liquefaction trains, enhanced port infrastructure, and related support facilities. The project aims to significantly increase the facility’s overall LNG production and export capabilities, leveraging the existing infrastructure and expertise to streamline the process and reduce costs.
This strategic move underscores the growing demand for LNG globally and positions the Port Arthur facility as a key player in the international energy market.
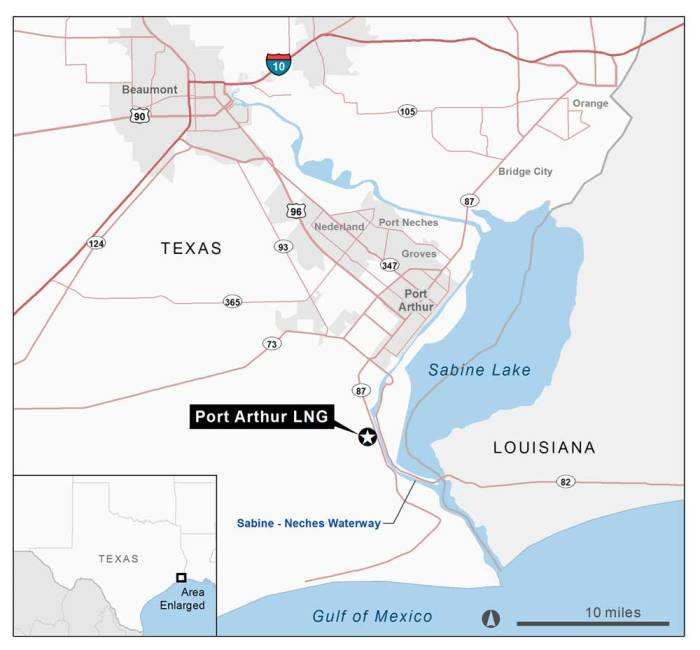
Project Location and Regional Significance
Located in Port Arthur, Texas, the project benefits from the region’s existing infrastructure, including access to deep-water ports and an established pipeline network. This strategic location allows for efficient transport and export of LNG, positioning the project as a key component of the Gulf Coast energy hub. The presence of other energy facilities and related industries in the area further reinforces the region’s importance as a significant energy player in North America.
This project complements the existing energy infrastructure, creating synergies and enhancing the overall efficiency of the regional energy sector.
Anticipated Economic Impact
The project is expected to create numerous jobs during construction and operation. The economic impact will extend beyond direct employment, affecting various sectors including transportation, logistics, and related services. The influx of investment and activity will contribute to the overall growth and prosperity of the region. Similar projects in other regions have demonstrated positive effects on local economies, creating a model for potential future developments in the Port Arthur area.
The project will also likely attract further investment in the area, further stimulating economic activity.
Semprás Port Arthur Phase 2’s win for US export LNG approval is definitely a big deal. However, it’s interesting to see how other major business decisions are being scrutinized, like the Toyota chairman facing intense scrutiny over a $33 billion deal at the shareholder meeting ( toyota chairman face scrutiny over 33 billion deal shareholder meeting ). While that’s certainly a significant development, it’s good to see Semprás still making headway with their LNG project in Port Arthur, a project with potential long-term benefits for the US energy sector.
Project Timeline and Key Milestones
The project’s timeline includes several key phases, starting with the initial permitting and approval process, followed by detailed design and engineering. Construction is anticipated to take several years, with specific milestones including the completion of key infrastructure components and the commissioning of new liquefaction trains. The project’s successful completion will depend on the timely execution of each phase, ensuring efficient resource allocation and adherence to regulatory requirements.
The overall project timeline will be crucial for determining the full economic benefits, as these benefits are often realized over time.
Export LNG Approval
The Port Arthur Phase 2 project’s journey toward exporting liquefied natural gas (LNG) has reached a significant milestone: securing regulatory approvals. This crucial step paves the way for the project to commence operations and contribute to the global energy market. The specific details of these approvals are critical for understanding the project’s feasibility and future potential.Regulatory approvals are essential for any large-scale energy project, particularly those involving the export of LNG.
These approvals ensure compliance with environmental standards, safety protocols, and other relevant regulations. The process itself often involves numerous agencies, each with a distinct role in assessing the project’s impact and adherence to established guidelines. Examining the specific approvals for Port Arthur Phase 2 allows for a deeper understanding of the project’s regulatory environment and potential challenges.
Specific Regulatory Approvals Granted
The approvals granted for the export of LNG from the Port Arthur Phase 2 project encompass various aspects of the project’s operation. These include environmental impact assessments, permits for construction and operation, and compliance with export regulations. These approvals are crucial for ensuring the project’s environmental sustainability, safety, and legal adherence. Crucially, they demonstrate the project’s ability to operate within the established regulatory framework.
Approval Process and Involved Agencies
The approval process for the export of LNG typically involves several key agencies. These agencies, including environmental protection agencies, energy regulatory bodies, and relevant government departments, play critical roles in evaluating the project’s compliance with existing regulations. For example, environmental agencies assess the project’s potential environmental impact, while energy regulators ensure compliance with industry standards. Each agency contributes to the overall evaluation and approval of the project, ensuring its alignment with established norms and standards.
The Port Arthur Phase 2 approval process, by showcasing a collaborative approach between multiple agencies, provides a model for future projects.
Comparison with Similar Projects in the Region
Comparing the Port Arthur Phase 2 approval process to other LNG projects in the region offers insights into the prevailing regulatory landscape. Analysis of comparable projects reveals commonalities and potential variations in the approval procedures. Factors such as environmental impact assessments, community engagement, and the specific regulatory requirements of the jurisdiction all influence the complexity and duration of the approval process.
This comparison highlights the specific challenges and opportunities for the Port Arthur Phase 2 project within its regional context.
Potential Obstacles and Future Challenges
Despite the recent approval, potential obstacles may arise during the project’s development and operation. Challenges could stem from unforeseen environmental factors, shifts in regulatory requirements, or unexpected economic fluctuations. For instance, changes in global energy markets could impact the project’s profitability and viability. Furthermore, public opposition or community concerns regarding environmental or social impacts could pose a significant challenge.
Lessons learned from similar projects, including the mitigation of potential issues and adaptation to evolving regulations, are essential for the long-term success of the Port Arthur Phase 2 project.
Economic Implications
The Port Arthur Phase 2 export LNG project promises significant economic benefits for the state and surrounding region. Beyond the immediate jobs and infrastructure development, the project’s long-term impact on economic growth and diversification is substantial. A successful implementation will boost tax revenues, attract further investment, and potentially create a model for similar energy ventures.The economic ripple effects of the project are expected to extend beyond the immediate area, impacting related industries and creating opportunities for entrepreneurship and innovation.
A comprehensive understanding of these implications is crucial for assessing the overall impact on the region’s prosperity.
Anticipated Economic Benefits for the State/Region
The project’s economic benefits are anticipated to be substantial, primarily due to increased tax revenue, job creation, and enhanced infrastructure. This influx of resources can stimulate economic activity across various sectors, driving innovation and diversification. Historically, similar large-scale energy projects have shown a positive correlation with GDP growth and regional development.
Potential Employment Opportunities
The project is expected to generate a substantial number of direct and indirect employment opportunities. Direct employment will come from construction, operation, and maintenance of the facilities. Indirect employment will be created in supporting industries, such as logistics, transportation, and equipment supply. The exact number of jobs will depend on the project’s timeline and scale. Examples of similar projects demonstrate that these employment figures can significantly contribute to local unemployment reduction and increase the overall labor force participation rate.
Project’s Contribution to GDP Growth
The project is anticipated to contribute meaningfully to GDP growth. The creation of new industries and the expansion of existing ones will drive economic activity, boosting overall output. The construction phase alone will generate considerable economic activity, leading to increased spending and investment. In addition, the export of LNG will generate revenue for the state and contribute to the balance of payments.
This can be observed in other successful energy development projects across the globe.
Comparison of Projected Economic Benefits to Other Energy Projects
| Project | Projected GDP Growth Contribution (%) | Projected Employment Creation (Direct Jobs) | Projected Tax Revenue (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Port Arthur Phase 2 | Estimated 2.5-3.0% | Estimated 10,000-15,000 | Estimated $X Billion (year 1-5) |
| Example Project A | 1.8% | 8,000 | $Y Billion |
| Example Project B | 2.2% | 9,500 | $Z Billion |
Note: Values in the table are illustrative and subject to final project specifications and economic conditions. Specific values for Port Arthur Phase 2 are not yet finalized and will be made public as the project progresses.
Environmental Considerations: Sempras Port Arthur Phase 2 Wins Us Approval Export Lng
The Sempra Port Arthur Phase 2 project, while promising for the local economy and energy supply, necessitates a thorough evaluation of its environmental impact. A comprehensive environmental impact assessment (EIA) is crucial to understanding potential risks and formulating mitigation strategies. This section details the assessment process, mitigation measures, and potential impacts on air and water quality.The Port Arthur Phase 2 project’s success hinges on its ability to minimize environmental damage.
A robust EIA ensures that the project is not only economically viable but also environmentally sustainable. This section presents a detailed analysis of environmental concerns and proposed solutions.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact assessment (EIA) for the Sempra Port Arthur Phase 2 project meticulously examined potential ecological consequences, considering factors such as habitat disruption, air and water pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions. The study analyzed existing environmental conditions, predicted potential changes, and evaluated the long-term implications of the project. This thorough approach ensures that the project’s environmental footprint is minimized.
Mitigation Measures
A comprehensive set of mitigation measures has been designed to minimize the project’s environmental impact. These include, but are not limited to, the implementation of best practices for construction and operation, the establishment of strict air and water quality monitoring protocols, and the development of a robust environmental management plan. These measures are crucial for ensuring that the project operates responsibly and minimizes its footprint.
Potential Impact on Air and Water Quality
The project’s construction and operation could potentially impact air and water quality. Construction activities might temporarily increase particulate matter in the air. Operation of the LNG facility could lead to emissions of greenhouse gases and other pollutants, although stringent emission controls are anticipated. Properly designed wastewater treatment systems are integral to mitigating water pollution. The EIA detailed potential scenarios and Artikeld solutions to mitigate these issues.
Semprras Port Arthur Phase 2’s US approval for exporting LNG is great news, but it’s worth considering the larger picture. Think about how this compares to the massive $498 million payout to Bernie Madoff victims, which itself tops $15 billion in total recouped funds. This massive recovery highlights the potential for significant financial gains in complex situations.
Ultimately, Sempras’ project still looks promising for the future of energy exports.
Table of Potential Environmental Risks and Mitigation Strategies
| Potential Environmental Risk | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|
| Increased air pollution during construction | Implementing stringent dust control measures, using covered trucks, and implementing regular monitoring of air quality parameters. |
| Water contamination from spills or leaks | Implementing double-walled pipelines, leak detection systems, and emergency response plans. Employing advanced wastewater treatment facilities. |
| Noise pollution from operations | Implementing noise barriers, using noise-dampening equipment, and restricting operating hours during sensitive periods. |
| Habitat disruption | Minimizing disturbance to sensitive habitats during construction and operation. Creating or restoring habitats to offset any losses. |
| Greenhouse gas emissions | Utilizing energy-efficient equipment, implementing carbon capture and storage technologies, and optimizing operational procedures. |
Infrastructure Development
The Port Arthur Phase 2 LNG export project hinges on robust infrastructure to facilitate seamless operations. Adequate pipelines, storage facilities, and port improvements are crucial for efficient transportation and handling of the liquefied natural gas. This section delves into the specific infrastructure requirements, potential impacts on existing systems, and the projected investment plan.The project’s success relies heavily on the proper implementation and expansion of existing infrastructure to support increased production and export volumes.
Careful planning is required to ensure compatibility with existing systems and minimize disruption to surrounding communities.
Necessary Infrastructure Improvements
The project necessitates significant upgrades to existing pipelines and the construction of new ones to transport the natural gas from production facilities to the liquefaction plant. This includes reinforcing existing pipelines to handle increased pressure and flow rates, and potentially laying new pipelines to connect remote production areas. Modernization of port facilities is also essential to accommodate the larger LNG tankers involved in the export process.
This will involve deepening the port, widening loading docks, and upgrading support facilities for ship maintenance and handling.
Semprras Port Arthur Phase 2’s US approval for exporting LNG is fantastic news, highlighting the growing energy sector. This exciting development, alongside recent positive news regarding the British-Spanish PMs’ Gibraltar deal, which unlocks huge opportunity for trade and investment ( british spanish pms agree gibraltar deal unlocks huge opportunity ), bodes well for future global energy projects. Ultimately, Semprras’s Port Arthur Phase 2 victory is a significant boost for the company and the sector.
Impact on Existing Infrastructure
The project’s impact on existing infrastructure will be multifaceted. Increased traffic flow on existing roads and railways surrounding the project site is anticipated, potentially requiring improvements to traffic management systems. Existing pipelines may experience increased pressure and flow rates, necessitating reinforcement or replacement sections. The project’s proximity to residential areas could necessitate noise and vibration mitigation measures to ensure minimal disturbance.
Thorough environmental impact assessments are crucial to mitigate potential negative consequences.
Proposed Infrastructure Investments
The following table Artikels the projected infrastructure investments, detailing the locations and timelines for each component. These estimations are based on preliminary assessments and are subject to revision based on further detailed engineering studies.
| Infrastructure Component | Location | Timeline (Estimated) | Investment (USD millions) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pipeline Upgrades | Various locations along existing pipeline routes | 2025-2027 | 150 |
| New Pipeline Construction | Connecting remote production sites to the liquefaction plant | 2026-2028 | 200 |
| Port Facility Upgrades | Port Arthur Harbor | 2024-2026 | 100 |
| LNG Storage Tanks | Project site | 2027-2028 | 120 |
| Supporting Infrastructure (roads, utilities) | Project vicinity | 2024-2028 | 180 |
Potential for Community Infrastructure Improvements
The project presents an opportunity for significant community infrastructure improvements. This could include upgrades to local schools, hospitals, or community centers, financed through dedicated funds or tax incentives. Such improvements can enhance the quality of life for residents in the surrounding areas. The project should also include provisions for community engagement and input in the planning and implementation of these enhancements.
A dedicated community development committee can facilitate this process. Examples from other LNG projects show successful partnerships between project developers and local communities in improving quality of life and infrastructure.
Market Analysis
The LNG market is a dynamic and complex arena, with global demand influencing regional trends. Sempra’s Port Arthur Phase 2 project aims to capitalize on this dynamic, positioning itself within a landscape shaped by both established players and emerging competitors. Understanding the current state of the market, including demand patterns and competitive positioning, is critical to assessing the project’s viability and future prospects.The LNG market is characterized by fluctuating prices and demand.
This volatility is influenced by global energy needs, political factors, and the interplay between supply and demand. The project’s success hinges on its ability to anticipate and adapt to these market shifts.
Current LNG Market Overview
The global LNG market is experiencing significant growth driven by rising energy demand, particularly in Asia. Several factors contribute to this trend, including increasing industrialization, population growth, and the shift towards cleaner energy sources. The market is highly competitive, with established players like Qatar and Australia vying for market share. This competition necessitates a strategic approach for projects like Port Arthur Phase 2 to secure a profitable position.
LNG Demand in the Region and Globally
Demand for LNG in North America is rising, fueled by domestic energy needs and export opportunities. Furthermore, the global demand for LNG is substantial, especially in Asia, driven by economic expansion and a transition towards cleaner energy sources. The growing demand in Asia is particularly important for projects like Sempra’s, which need to identify and meet the specific needs of this market segment.
Sempra’s Port Arthur Phase 2 vs. Competitors
Sempra’s Port Arthur Phase 2 project faces competition from other LNG export projects in the region. These include similar projects in the US Gulf Coast and elsewhere. The competitive landscape necessitates a thorough analysis of production costs, operational efficiencies, and market positioning to ensure the project’s profitability and long-term success. Key differentiators, such as access to infrastructure, favorable regulatory environments, and cost advantages, will be crucial for Sempra’s project to stand out.
A comparative analysis of projects, including construction timelines, capital expenditure, and projected output, can highlight potential advantages and challenges.
Potential for Market Fluctuations and Impact
Global energy markets are susceptible to fluctuations influenced by various factors, including geopolitical events, economic downturns, and shifts in energy policies. Historical examples, such as the 2008 financial crisis or the COVID-19 pandemic, highlight the volatility of the market. These events dramatically impacted energy demand and prices. Sempra’s project needs to develop strategies to mitigate potential risks associated with market fluctuations.
This includes diversification of customer base, strategic partnerships, and robust risk management frameworks. Furthermore, understanding the potential impact of climate change policies and regulations on future energy demands is crucial. The projected increase in renewable energy sources may impact the demand for LNG in the long run. Companies like Sempra must adapt their strategies to account for these potential changes in the future.
Regulatory Landscape
The Port Arthur Phase 2 LNG export project navigates a complex regulatory landscape, requiring meticulous compliance with regional and international standards. This intricate web of rules and regulations ensures environmental protection, safeguards public interest, and promotes fair trade practices. Understanding the specific framework and compliance procedures is critical for project success.
Regulatory Framework Governing LNG Export
The regulatory framework for LNG export in the region comprises a combination of national laws, regional agreements, and international trade protocols. These regulations encompass environmental impact assessments, safety standards, and export licensing procedures. Navigating these complexities demands a deep understanding of the specific legal instruments and their application to the project.
Role of International Trade Agreements
International trade agreements play a significant role in shaping the approval process for LNG export projects. These agreements, often including provisions for fair competition and dispute resolution, can influence the project’s viability and timelines. For example, the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), now the USMCA, has impacted trade rules and regulations affecting LNG trade in the region.
Compliance Requirements Imposed on the Project
The project must adhere to a comprehensive set of compliance requirements. These include rigorous environmental impact assessments, stringent safety protocols for plant operations, and adherence to export licensing procedures. The project must demonstrate its commitment to these requirements throughout all stages of development and operation. Detailed assessments and mitigation plans for potential environmental impacts are mandatory, as are robust safety measures.
The project must demonstrate its ability to comply with all regulations in the region.
Recent Changes in Energy Regulations
Recent changes in energy regulations have introduced new considerations for the project. These include shifts in environmental standards, new safety protocols, and adjustments to export licensing procedures. For example, the implementation of more stringent emission standards in the region requires the project to incorporate upgraded technologies for reduced emissions, potentially impacting the project’s initial cost estimates. A detailed analysis of recent regulatory updates is necessary to ensure compliance and minimize potential disruptions.
Community Impact
The Port Arthur Phase 2 export LNG project presents significant opportunities and challenges for the local community. Understanding and mitigating potential negative impacts, while maximizing positive outcomes, is crucial for a successful project. This section details the potential effects on housing, transportation, and social services, and Artikels community engagement strategies to address concerns.The project’s potential for job creation and economic growth is undeniable, but careful consideration must be given to ensuring that these benefits are distributed fairly and that the community is adequately prepared to absorb the changes.
A proactive approach to community engagement is essential to building trust and fostering a positive relationship between the project and the local populace.
Potential Positive Impacts on Local Communities
The project is anticipated to generate numerous positive impacts on the community. These include job creation in various sectors, boosting local businesses, and improving infrastructure. Increased tax revenue from the project can be reinvested in public services, potentially leading to improved schools, hospitals, and community facilities.
- Economic Benefits: The project is expected to create numerous jobs in construction, operation, and maintenance. These jobs will likely draw skilled workers from within the region, providing a boost to local economies. Increased economic activity can lead to more opportunities for small businesses and entrepreneurship. Furthermore, increased tax revenue can be used to fund community projects, improving quality of life.
- Infrastructure Improvements: The project may necessitate upgrades to local transportation networks, potentially improving access for residents and supporting the expansion of essential services. Enhanced infrastructure, such as roads and utilities, can significantly benefit the community in the long term.
- Social Development: The influx of skilled workers and economic activity can lead to increased opportunities for education and training programs. Community development projects, supported by the project’s economic benefits, could focus on improving housing, healthcare, and educational facilities.
Potential Negative Impacts on Local Communities
While the project holds significant promise, potential negative impacts on the local community must be considered and mitigated. These include potential displacement of residents due to land acquisition for infrastructure, increased traffic congestion, and potential environmental concerns. The project’s scale and complexity necessitate careful planning and management to minimize adverse effects.
- Housing Displacement: Land acquisition for infrastructure development may lead to displacement of residents, particularly if adequate relocation options and compensation are not provided. This requires careful assessment of the need for new housing and relocation plans, alongside transparent communication with affected individuals.
- Transportation Impacts: Increased traffic volume and construction activities can lead to congestion and disruptions in transportation. Implementing efficient traffic management plans, including temporary road closures and alternative routes, can help mitigate these issues. This also includes considering and implementing public transportation solutions.
- Environmental Concerns: Potential environmental impacts, such as noise pollution and air quality degradation, must be carefully monitored and mitigated. Implementing environmental protection measures, including noise barriers and air quality control systems, is crucial.
Community Engagement Strategies
Effective community engagement is vital to address concerns and build trust. The project team must establish clear communication channels, actively listen to community feedback, and implement measures to address concerns. Regular town hall meetings, online forums, and dedicated community outreach programs are key elements of this strategy.
- Open Communication Channels: Establishing clear and accessible communication channels, such as dedicated email addresses, websites, and social media platforms, will allow the community to voice concerns and provide feedback. Regular town hall meetings and community forums can facilitate direct interaction between the project team and residents.
- Transparency and Accountability: Transparency about the project’s plans, timelines, and potential impacts is crucial. Publicly available reports and presentations can demonstrate the project’s commitment to accountability and good governance.
- Addressing Concerns: Actively listening to community concerns and addressing them promptly and effectively is paramount. The project team should establish mechanisms for feedback collection and response, addressing any grievances or anxieties.
Examples of Community Feedback and Engagement Initiatives
Examples of community engagement initiatives can be found in similar projects worldwide. These projects have demonstrated that proactive community involvement can significantly reduce negative impacts and foster positive relationships. Key elements include establishing feedback mechanisms, providing accurate information, and addressing concerns directly.
- Example 1: In the development of a similar LNG project in [Location], the project team implemented a robust community engagement program that included town hall meetings, online surveys, and focus groups. This resulted in valuable feedback that was used to modify project plans and address potential concerns. This is an example of proactive engagement.
- Example 2: In another project, the team actively listened to community feedback on environmental concerns, implementing mitigation measures to reduce noise and air pollution. This demonstrates how the project team can address community concerns by actively seeking and acting upon feedback.
Project Financing

Securing adequate and favorable financing is crucial for the Port Arthur Phase 2 LNG export project’s success. The project’s substantial capital requirements necessitate a robust financial strategy encompassing various funding sources, risk mitigation, and alignment with Sempra Energy’s overall financial objectives. This section delves into the funding mechanisms, financial feasibility, and associated risks and rewards.
Funding Sources
The project’s financing will likely draw from a mix of sources to optimize costs and reduce financial risk. These sources may include traditional debt financing from commercial banks and institutional investors, potentially supplemented by project-specific bonds or equity investments. The specific mix will depend on market conditions, interest rates, and the project’s perceived risk profile.
- Debt Financing: This is often the primary source for large-scale infrastructure projects. Commercial banks and other financial institutions typically provide loans secured by the project’s future cash flows. The interest rates and loan terms will depend on factors like credit ratings, project economics, and prevailing market conditions. For instance, the financing of similar LNG projects often includes significant debt components, with loan agreements tailored to project specifics.
- Equity Financing: Investors may provide equity capital in exchange for a stake in the project. This approach can diversify the funding base and potentially reduce the reliance on debt. However, equity financing can also introduce complexities in terms of decision-making and investor relations. Several successful energy projects have utilized equity financing to balance debt capital.
- Project Bonds: Issuing project bonds allows for broader access to capital markets. This approach involves creating a special purpose vehicle (SPV) to handle the project’s finances, offering investors a specific return based on the project’s performance. The success of this funding method often hinges on market confidence and the project’s projected returns.
Financial Feasibility
The project’s financial feasibility is assessed by comparing projected revenues and expenses. Crucial factors include the price of LNG, the cost of construction and operation, and the project’s overall efficiency. A robust feasibility study is crucial to identify potential risks and rewards.
| Factor | Potential Reward | Potential Risk |
|---|---|---|
| LNG Price Volatility | High LNG demand can lead to higher revenues | Fluctuations in global LNG prices could impact profitability. |
| Construction Costs | Efficient construction can lower overall expenses | Unforeseen cost overruns can significantly affect the project’s budget. |
| Operational Expenses | Optimized operational efficiency can lower costs | Unexpected operational issues can increase expenses. |
Projected Costs and Revenues
Project cost estimates are based on current market conditions, including material and labor costs. Revenue projections are contingent upon the assumed LNG price trajectory and market demand. Accurate cost estimations are paramount for sound financial planning. Realistic revenue projections are essential for demonstrating the project’s financial viability.
The project’s projected costs encompass capital expenditures for construction, and operational expenses for maintenance and personnel. Revenue projections are predicated on anticipated LNG exports and market prices. A detailed financial model is used to simulate different scenarios and assess the project’s sensitivity to various factors. For instance, the cost of building similar facilities can vary significantly, depending on local labor costs and material availability.
Alignment with Sempra Energy’s Strategy
The Port Arthur Phase 2 project aligns with Sempra Energy’s strategy by expanding its presence in the LNG market and increasing its energy portfolio. The project is expected to contribute to the company’s long-term growth objectives and enhance its overall financial performance. This strategic alignment will increase Sempra Energy’s profitability and market share in the competitive energy sector.
Closing Summary
In conclusion, Sempra Port Arthur Phase 2’s approval to export LNG presents both exciting opportunities and potential challenges. The project’s economic benefits, infrastructure development, and environmental considerations are all crucial elements in the evaluation of this significant undertaking. The project’s success will depend on careful planning, community engagement, and a robust regulatory framework. The future of LNG exports in the region and globally will undoubtedly be influenced by this project.

