Us asks australia increase defense spending 35 gdp – US asks Australia increase defense spending 35% of GDP sparks a crucial debate about regional security and economic priorities. This issue involves a complex interplay of historical alliances, geopolitical tensions in the Indo-Pacific, and Australia’s economic standing. Understanding the potential impacts on Australia’s military capabilities, economic stability, and international relations is paramount.
The request from the US raises critical questions about the future of Australia’s defense posture. Examining the historical context of defense spending, the current geopolitical landscape, and the potential economic consequences is essential for a comprehensive understanding of this significant development.
Background and Context
Australia’s defense spending has a long history intertwined with its strategic alliances and evolving regional security concerns. From the post-World War II era to the present, the nation’s military posture has been significantly shaped by its relationship with the United States, as well as the shifting dynamics in the Indo-Pacific region. The current geopolitical climate, characterized by rising tensions and a complex web of alliances, further underscores the need for careful consideration of Australia’s defense budget.The recent request for a substantial increase in defense spending, exceeding 35% of GDP, necessitates an understanding of the historical, geopolitical, and economic factors driving this decision.
This analysis delves into the historical trends, current challenges, and economic implications to provide a comprehensive perspective on Australia’s evolving security posture.
Historical Overview of Defense Spending
Australia’s defense spending has fluctuated throughout its history, reflecting its evolving security needs and international commitments. The nation’s participation in global conflicts, such as World War II and the Korean War, significantly influenced defense expenditure. Post-war, the relationship with the US, formalized through alliances like ANZUS, has been a cornerstone of Australia’s defense strategy. The Cold War era saw a consistent, albeit fluctuating, level of investment.
The end of the Cold War, however, brought about a period of relative peace, leading to reductions in defense spending. This trend reversed as the global security environment changed, highlighting the dynamic relationship between global events and national security priorities.
Current Geopolitical Landscape
The Indo-Pacific region is experiencing a period of significant geopolitical shifts. Rising powers, evolving alliances, and territorial disputes are reshaping the security landscape. The South China Sea disputes, the increasing assertiveness of certain nations, and the evolving nature of warfare all contribute to heightened concerns about regional stability. This complex environment requires a strategic and adaptive approach to defense.
Australia’s location in the Indo-Pacific makes it particularly vulnerable to regional tensions and requires a robust and forward-looking defense posture.
Factors Influencing Australia’s Strategic Priorities
Australia’s strategic priorities are influenced by its geographic location, its economic ties, and its international alliances. The country’s proximity to potential conflict zones, its dependence on maritime trade routes, and its close relationship with the United States shape its strategic outlook. Technological advancements and the evolving nature of warfare are also important considerations, requiring substantial investment in modern capabilities.
Economic Context of Australia’s GDP and Implications for Defense Spending
Australia’s GDP plays a crucial role in determining the nation’s capacity to fund its defense budget. A strong economy allows for increased investment in defense capabilities, while economic downturns can necessitate budgetary constraints. The relationship between GDP growth and defense spending is complex and requires careful consideration. The potential impact of economic fluctuations on defense investment needs to be assessed, given the importance of a robust defense posture for national security and economic stability.
Potential Motivations Behind the US Request
The US request for increased Australian defense spending is likely rooted in shared security concerns and the desire to maintain a robust military presence in the Indo-Pacific region. The US’s strategic interests in the region align with Australia’s, creating a mutually beneficial relationship in terms of defense and security. The US, as a key partner, is likely motivated to enhance its allies’ capabilities to deter potential threats and maintain regional stability.
Table: Australia’s Defense Spending Timeline
| Time Period | Event | Impact on Defense Spending |
|---|---|---|
| Post-WWII | Establishment of ANZUS alliance | Increased defense spending due to heightened security concerns |
| Cold War | Global tensions and arms race | Fluctuating spending, generally consistent investment in defense capabilities |
| Post-Cold War | Reduced global tensions | Decrease in defense spending due to perceived lower security risks |
| 21st Century | Rising tensions in Indo-Pacific, evolving threat landscape | Increasing defense spending to meet contemporary security challenges |
Economic Implications
A 35% increase in Australia’s defense spending, while potentially bolstering national security, carries significant economic implications that demand careful consideration. This substantial allocation of resources will undoubtedly reshape the nation’s economic landscape, impacting various sectors and potentially altering the budget’s trajectory. Understanding these effects is crucial for a comprehensive evaluation of the proposed policy change.
The US asking Australia to boost defense spending by 35% of GDP is a significant move, especially considering the current global climate. This pressure likely stems from a desire to bolster regional security, but also perhaps reflects the rapid advancements in military technology, like the recent Saab Helsing Pit AI-piloted warplane test against a real fighter pilot, demonstrating the potential for autonomous systems.
Ultimately, these developments could significantly influence future defense strategies, and thus the need for increased spending by Australia to stay competitive.
Potential Impact on GDP Growth
A surge in defense spending, while potentially stimulating economic activity in the short term through increased government contracts and job creation, may also divert resources from other sectors with potentially higher long-term growth potential. This redirection could result in a less-than-proportional increase in overall economic output, depending on the efficiency and effectiveness of the expenditure. The impact of such a shift in resources on long-term GDP growth warrants careful scrutiny.
Impact on Other Sectors
Increased defense spending could lead to a significant reallocation of resources. Industries like aerospace, manufacturing, and technology will likely experience a surge in demand, leading to job creation and potential growth in these sectors. However, this may come at the expense of investment in other sectors such as renewable energy, healthcare, or education, potentially hindering their growth. A thorough analysis of the “opportunity cost” of diverting resources from these sectors is essential.
Impact on the Budget Deficit/Surplus
A 35% increase in defense spending will undoubtedly strain government finances. The added expenditure will likely contribute to a larger budget deficit, potentially impacting the national debt and the country’s fiscal position. This increase will necessitate either cuts in other government spending or an increase in taxation, each with its own economic repercussions. Understanding the fiscal implications of this increase is paramount.
Defense Spending Scenarios and Economic Effects
The following table Artikels potential scenarios for defense spending and their corresponding economic outcomes:
| Defense Spending Scenario | GDP Growth Impact | Budget Deficit/Surplus | Impact on Other Sectors |
|---|---|---|---|
| 35% Increase (Scenario 1) | Potentially moderate, depending on investment efficiency | Likely larger budget deficit | Potential for reduced investment in other sectors, but increased demand in defense-related sectors |
| 35% Increase (Scenario 2 – with efficiency measures) | Potentially higher, with focus on strategic investment | Moderate budget deficit, or possibly reduced deficit compared to Scenario 1 | Targeted investment in defense-related sectors while still considering investment in other sectors. |
| 35% Increase (Scenario 3 – with cost-cutting in other sectors) | Potentially moderate to low, depending on efficiency of cuts in other sectors | Smaller budget deficit, or possibly surplus, dependent on cost-cutting measures | Significant impact on sectors experiencing cuts, potentially negatively impacting their growth. |
The table above provides a simplified illustration. A comprehensive analysis would require detailed modeling and forecasting of the specific effects of each scenario.
Job Creation and Job Losses
Increased defense spending is anticipated to generate jobs in the defense industry, but it’s also important to acknowledge the potential for job losses in other sectors due to the reallocation of resources. The magnitude of these effects will depend on the specific nature of the defense spending program, the efficiency of the government’s investment, and the availability of skilled labor in the defense industry.
The potential for job displacement in other sectors needs to be carefully assessed alongside the job creation in the defense sector.
Strategic Implications: Us Asks Australia Increase Defense Spending 35 Gdp
Australia’s planned 35% increase in defense spending carries significant strategic implications, potentially reshaping its military capabilities, regional security dynamics, and international relationships. This substantial investment promises to bolster Australia’s defense posture, but also necessitates careful consideration of the potential consequences for regional stability and global power balances. The decision underscores Australia’s evolving security priorities and its commitment to maintaining a robust defense presence in the Indo-Pacific region.
Potential Military Capabilities
The increased defense spending will likely translate into a range of enhancements to Australia’s military capabilities. This includes the acquisition of advanced weaponry, upgraded military infrastructure, and a potential expansion of personnel. The specifics of these acquisitions will depend on the government’s priorities, but it is anticipated that Australia will prioritize modernization efforts to maintain its technological edge.
Examples include procuring more sophisticated fighter jets, submarines, and naval vessels. The focus on modernization will likely involve substantial investment in research and development to maintain a leading-edge defense capability in the Indo-Pacific.
Implications for Regional Security and Power Dynamics
Australia’s increased defense spending will undoubtedly impact regional security and power dynamics in the Indo-Pacific. The heightened military presence and capabilities could potentially deter potential adversaries, and project a stronger sense of security to allies. This will affect how other regional powers perceive Australia’s influence and capacity for conflict response. The increase in defense spending will inevitably be scrutinized by neighboring nations, and its implications for regional stability will be closely watched.
Potential Alliances and Partnerships
Australia’s strategic alliances and partnerships will be crucial in shaping its response to evolving security challenges. Strengthening existing relationships with key allies like the United States, Japan, and the UK will be paramount. Potential new partnerships in the region will also need to be explored. The nature and extent of these partnerships will significantly influence Australia’s ability to address threats and maintain its strategic objectives.
The emphasis on partnerships could also be reflected in joint exercises, intelligence sharing, and combined operations.
Implications for International Relations
The increased defense spending will undoubtedly influence Australia’s international relations. Australia will need to navigate its relationships with both traditional allies and emerging powers. The implications of such a move will also be felt on a global stage, affecting how other countries perceive Australia’s role in global security architecture. The increased defense spending may necessitate adjustments in diplomatic efforts to ensure that Australia’s actions are perceived positively by international partners.
Potential for a Military Arms Race
An increase in defense spending by one country can sometimes trigger a response from neighboring nations. This could potentially lead to a military arms race in the region. However, the specifics will depend on the nature of the increased spending and the responses of other regional powers. The anticipated increase in defense spending will likely be met with varied reactions from other nations, and the regional implications will require careful consideration.
Projected Military Capabilities Based on Spending Levels
| Spending Level Increase (%) | Potential Acquisition | Impact on Regional Balance |
|---|---|---|
| 10-20% | Improved equipment and personnel training. | Maintain current regional influence. |
| 20-30% | Acquisition of advanced weaponry and technology. | Potential to exert greater influence, depending on other regional powers’ responses. |
| 30-40% | Significant expansion of military assets and modernization. | Potentially alter regional power dynamics significantly. |
Societal Implications
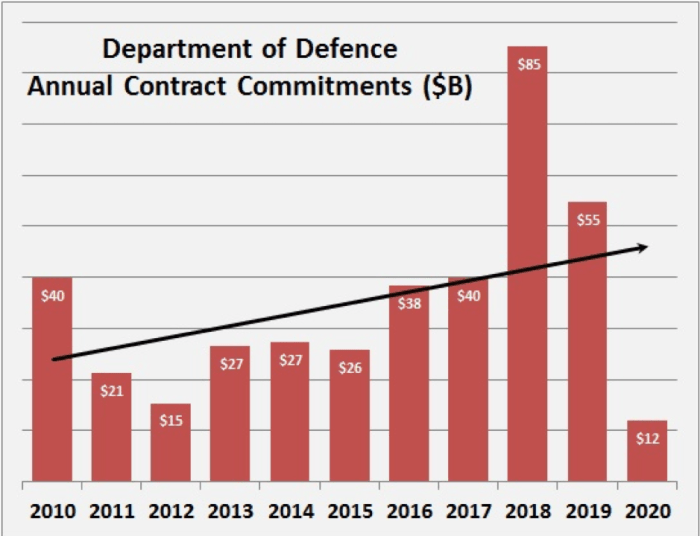
Australia’s proposed 35% increase in defense spending, while aimed at bolstering national security, will undoubtedly have profound societal repercussions. The allocation of substantial resources to the military sector inevitably influences other crucial aspects of the nation’s well-being, from public opinion and political discourse to domestic investment and social programs. Understanding these potential impacts is vital for a comprehensive assessment of the proposed policy.Increased defense spending, while potentially enhancing national security, might divert resources from other critical areas.
This could lead to a re-evaluation of priorities, both politically and socially, impacting how Australians perceive the nation’s future direction.
Potential Impact on Public Opinion
Public opinion regarding the proposed increase in defense spending will likely be multifaceted. Some segments of the population will likely support the move, viewing it as a necessary investment for national security and a demonstration of Australia’s commitment to its international obligations. Others may oppose it, concerned about the potential for reduced funding in areas like education, healthcare, or social welfare.
Impact on Political Discourse
The debate surrounding increased defense spending will undoubtedly shape political discourse, potentially becoming a focal point for differing policy priorities and values. The government will need to articulate a compelling justification for the increased spending, addressing concerns and potential trade-offs with other social priorities. Political parties and commentators will likely analyze the economic and social costs and benefits, further influencing the public discourse.
Impact on Domestic Investment and Social Programs
A substantial allocation of funds to defense will likely impact domestic investment and social programs. Reduced funding for these sectors could lead to delays in infrastructure projects, hindering economic growth, or limit the reach of crucial social programs aimed at supporting vulnerable populations. The opportunity cost of prioritizing defense over other areas is a critical aspect to consider.
Potential Public Support for the Increase
Support for the increase in defense spending will likely be influenced by a variety of factors, including perceived threats to national security, economic conditions, and prevailing political climate. Public perception of international events, perceived threats, and the perceived strength of Australia’s current security posture will play a significant role.
Potential Public Opposition and Counter-Arguments
Opposition to the increased defense spending will stem from concerns about the allocation of resources. Concerns about the economic implications of diverting funds from essential social programs and the potential impact on domestic investment will be significant. Alternative approaches to ensuring national security, such as diplomatic initiatives or strengthening international partnerships, may be proposed as viable alternatives.
Contrasting Perspectives on the Issue
| Perspective | Key Arguments | Potential Concerns |
|---|---|---|
| Supporters of Increased Spending | Enhanced national security, strategic advantage, demonstration of commitment to international alliances. | Potential diversion of resources from crucial social programs, negative impact on domestic investment. |
| Opponents of Increased Spending | Reduced funding for essential social programs, economic consequences of diverting funds, potential for alternative security strategies. | Potential for decreased national security in the long run if defense spending is not sufficient to counter threats. |
International Relations

Australia’s significant increase in defense spending, projected at 35% of GDP, will undoubtedly ripple through international relations. This substantial investment carries implications for regional security dynamics, potentially altering existing power balances and influencing alliances. The shift will undoubtedly prompt responses from both allies and adversaries, reshaping the geopolitical landscape.This heightened military expenditure will inevitably impact Australia’s relationships with its key partners, particularly the United States.
The potential for enhanced cooperation, but also possible areas of friction, must be considered. The increased defense budget could also prompt reassessments of military strategies and force postures among other nations in the region. Understanding these potential reactions is crucial for assessing the long-term effects on global security and economic stability.
Potential Impact on US-Australia Relations
The strengthened defense ties between Australia and the United States are likely to be further cemented. Shared strategic interests, particularly concerning the Indo-Pacific region, will likely drive closer collaboration. Joint military exercises and intelligence sharing could intensify, strengthening the existing alliance. However, potential points of contention could emerge if the increased Australian defense spending impacts the allocation of resources for joint projects.
The US is asking Australia to significantly boost its defense spending, aiming for a 35% GDP increase. This geopolitical maneuvering is certainly interesting, especially considering the global context and the rising tensions. Interestingly, the parallels between the tennis star Carlos Alcaraz’s impressive career and Rafael Nadal’s legendary legacy in the sport, as discussed in this fascinating article about destiny child alcaraz treasures nadal heritage , offer a unique perspective on the broader narrative of ambition and excellence.
Ultimately, the US’s pressure on Australia for a greater defense budget highlights the complex interplay of global power dynamics.
Differences in strategic priorities could also create slight strains on the relationship.
The US asking Australia to bump up defense spending by 35% of GDP is a pretty big deal, but it’s interesting to see how other legal battles are playing out. For example, a judge recently dismissed Justin Baldonis’s $400 million defamation lawsuit against Blake here. This legal action, while unrelated, highlights the complexities of high-stakes disputes, and perhaps, the ongoing tensions influencing these kinds of international financial requests.
It’s all connected in a way, isn’t it? Back to the initial point, the US request for increased defense spending from Australia still has some big questions to answer.
Potential Reactions from Other Nations in the Region
Several nations in the region will likely react to Australia’s increased defense spending. Some may view it as a positive sign of regional security, while others may interpret it as a provocation. For instance, countries like Indonesia and Malaysia may feel compelled to enhance their own defense capabilities to maintain a balance of power. China, a significant player in the region, may view the increased spending as a direct challenge to its influence and might respond with increased military activity.
Potential Implications for International Trade and Economic Cooperation
Increased defense spending could potentially divert resources away from other sectors, including infrastructure and economic development. This could negatively affect international trade if it impacts Australia’s economic competitiveness. However, the increased spending could also stimulate domestic industries, potentially creating new export opportunities and attracting foreign investment. The long-term economic impact will depend on how the additional spending is managed and integrated into the broader economy.
Analysis of Possible Impact on Existing International Agreements
Australia’s heightened defense spending might have subtle effects on existing international agreements. Agreements on arms control or regional security could be impacted, depending on the specific nature of the agreement and the interpretations by other parties. For example, if the increased spending is seen as destabilizing, it could lead to renegotiations or withdrawals from existing agreements. The implications will vary depending on the specific agreements in question.
Comparison of Different Approaches and Reactions from Various International Actors, Us asks australia increase defense spending 35 gdp
The responses to Australia’s defense spending will vary greatly among international actors. The United States, as a close ally, may welcome the increased cooperation and share in the potential benefits. China, however, may view the increased spending as a challenge and respond accordingly. Other nations in the region may adopt a cautious approach, seeking to balance their own security concerns with the need for regional stability.
Potential Responses from Different Nations
| Nation | Potential Response |
|---|---|
| United States | Increased cooperation and potentially more joint military exercises |
| China | Potential increase in military activity and assertiveness in the region |
| Indonesia | Increased defense spending and/or strengthening of military ties with other regional actors |
| Malaysia | Potential adjustments to defense posture and increased military spending to maintain regional balance |
| India | Potential for increased military cooperation with Australia and other allies |
Potential Scenarios and Outcomes
Australia’s request to increase defense spending by 35% of GDP presents a complex array of potential outcomes, ranging from enhanced national security to significant economic strain. Analyzing these scenarios requires considering the interplay of domestic economic factors, regional strategic dynamics, and international relations. Understanding the potential benefits and drawbacks, as well as the diverse responses Australia could make, is crucial for a comprehensive evaluation.
Hypothetical Scenarios
The potential outcomes of this substantial defense spending increase can be categorized into several scenarios, each with unique implications. These scenarios are not mutually exclusive and real-world outcomes may present a combination of these features.
Potential Benefits of Increased Spending
A significant increase in defense spending could bolster Australia’s military capabilities, potentially deterring potential adversaries and enhancing its regional influence. This could translate into improved national security, allowing for more effective response to threats and greater protection of Australian interests. Furthermore, a substantial investment could stimulate the domestic economy through job creation in the defense sector and related industries.
For instance, increased demand for equipment and personnel could lead to the expansion of manufacturing facilities and technological advancements in Australia.
Potential Drawbacks of Increased Spending
Conversely, a substantial increase in defense spending carries significant economic implications. Increased government debt and potentially higher taxes could impact the broader economy, potentially slowing economic growth. A substantial shift in resources away from other critical sectors like education, healthcare, and infrastructure could negatively impact societal well-being. Furthermore, an overemphasis on military solutions could neglect non-military approaches to security and international relations, which are equally important.
Possible Responses from Australia
Australia’s response to the request for increased defense spending will likely depend on the political climate and public perception. The government might implement the full 35% increase, or opt for a phased approach, gradually increasing spending over time. An alternative approach could involve prioritizing certain areas of defense expenditure, focusing resources on specific capabilities or technologies.
Consequences of Not Increasing Spending
Failure to increase defense spending could result in a weakening of Australia’s military capabilities, potentially jeopardizing its national security interests. This could lead to a reduced ability to respond to emerging threats and protect Australian interests in the region. It could also impact Australia’s standing in the international community, possibly leading to reduced cooperation and alliances.
Long-Term Outcomes
The long-term outcomes of the spending decision will be influenced by the specific scenario and the chosen response. Sustained investment could lead to a more secure and influential Australia on the world stage. However, a misallocation of resources or an overly aggressive military approach could have negative consequences, potentially impacting Australia’s international relations and economic prosperity.
Table of Potential Scenarios and Outcomes
| Scenario | Potential Outcomes | Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scenario 1: Gradual Increase | Phased increase in spending over several years. | Reduced economic impact, allows for adjustment and assessment. | Potential for a slower response to emerging threats, less immediate strengthening of capabilities. |
| Scenario 2: Full Increase | Immediate and full implementation of the 35% increase. | Rapid enhancement of military capabilities, stronger deterrence. | Significant economic strain, potential for inflation and higher taxes. |
| Scenario 3: Targeted Increase | Focus on specific defense capabilities and technologies. | Efficient allocation of resources, potential for breakthroughs in specific areas. | Potential gaps in other defense areas, possible over-reliance on certain technologies. |
| Scenario 4: No Increase | Maintenance of current defense spending levels. | Preservation of current economic stability. | Weakening of military capabilities, potential for increased security risks. |
Alternative Solutions
A 35% increase in Australia’s defense spending, while seemingly a strong response to regional security concerns, presents significant economic burdens. Exploring alternative solutions that bolster national security without such a drastic budgetary shift is crucial. These alternatives require careful consideration of their effectiveness, feasibility, and potential implications across various sectors.Alternative approaches to strengthening Australia’s defense capabilities can range from enhanced diplomatic initiatives to improved intelligence gathering and strategic partnerships.
These solutions aim to achieve a similar outcome – deterring potential threats and ensuring regional stability – without the substantial economic strain of a massive defense budget increase.
Enhanced Diplomatic Initiatives
Australia’s influence in the region can be significantly enhanced through proactive diplomacy. This involves strengthening existing alliances and forging new partnerships with key regional players. Improved communication and collaboration on security issues can foster a more cohesive and unified approach to regional challenges. For example, Australia could play a leading role in mediating disputes between nations, facilitating dialogue, and promoting shared security interests.
- Increased engagement with regional organizations like ASEAN can provide platforms for cooperation and information sharing. This collaborative approach can lead to a more coordinated response to emerging security threats. The economic implication is a potential reduction in military expenditure as resources are allocated towards diplomatic initiatives.
- Deepening relationships with key allies like the United States and other nations sharing similar security concerns can bolster Australia’s standing and leverage in the region. This can enhance strategic depth and provide additional support in times of crisis. Economically, this can lead to joint ventures and shared security initiatives, potentially reducing individual nation’s defense burden.
Improved Intelligence Gathering and Analysis
A robust intelligence gathering and analysis capability is paramount for effective defense strategy. Investing in advanced technologies and personnel training can significantly improve Australia’s ability to anticipate and respond to threats. This approach can reduce the need for large-scale military deployments by allowing for proactive measures and targeted responses.
- Modernizing intelligence gathering techniques can help predict potential conflicts or crises, enabling preemptive actions to mitigate risks. This approach can save substantial financial resources that would otherwise be spent on reactive military operations.
- Developing advanced surveillance systems and employing sophisticated analytical tools to interpret data from various sources can provide valuable insights into emerging threats. The economic implications are focused on technology investments and personnel training, which may be less expensive than a large-scale military build-up.
Strategic Partnerships and Collaborative Defense
Instead of solely relying on its own defense forces, Australia can leverage partnerships with other nations to bolster its security posture. Joint exercises, combined operations, and intelligence sharing can create a more formidable deterrent. This approach also allows for a sharing of defense costs and resources, making it economically sustainable.
- Establishing and strengthening security partnerships with nations in the region can lead to joint defense initiatives and shared resources. Economically, this allows for cost-sharing and resource pooling, which can result in more cost-effective defense strategies.
- Joint exercises and training programs with key allies can enhance interoperability and improve response times to potential threats. This approach may be more effective and less costly than a significant increase in Australia’s individual defense spending.
Table: Alternative Solutions – Pros & Cons
| Alternative Solution | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Enhanced Diplomatic Initiatives | Reduced defense spending, increased regional cooperation | Potentially slower response times, dependence on other nations’ actions |
| Improved Intelligence Gathering and Analysis | Proactive threat assessment, reduced military deployments | Requires significant investment in technology and personnel |
| Strategic Partnerships and Collaborative Defense | Shared costs, increased deterrence | Potential conflicts of interest, reliance on partner nations’ capabilities |
Last Recap
In conclusion, the US’s request for a substantial increase in Australia’s defense spending presents a complex set of challenges and opportunities. From potential military gains and regional security implications to the economic and societal repercussions, this issue requires careful consideration. Exploring alternative solutions and assessing the various potential outcomes will be vital for Australia’s decision-making process. The ultimate response will undoubtedly shape the nation’s future trajectory.

