Boes breeden sees loosening labour market disinflation sunday times reports – Boes Breeden sees loosening labor market disinflation, according to a Sunday Times report. This signals a shift in the UK’s economic landscape, raising questions about the future trajectory of inflation and the effectiveness of current policies. The report delves into the current state of the UK labor market, analyzing key indicators like unemployment, job vacancies, and wage growth, and explores how these factors relate to the potential for disinflation.
It also examines the potential implications of a loosening labor market on economic growth, consumer spending, and business investment, providing context from previous periods of labor market change. Furthermore, it explores BoE Breeden’s perspective on the situation, highlighting their views on inflation and the labor market, their rationale, and the potential risks and challenges. The Sunday Times report’s analysis will be compared with other expert opinions, exploring the potential impact on market sentiment and investor behavior, and potential implications for interest rate decisions.
Finally, it will investigate the concept of disinflation, identifying factors contributing to it, the effectiveness of current measures, and past examples of successful disinflationary policies.
The analysis also examines how a loosening labor market could affect various sectors of the economy, offering examples of past impacts and potential changes in consumer behavior. It includes a detailed look at the Bank of England’s (BoE) policy responses to these labor market shifts, and how the current economic conditions are affecting businesses’ pricing strategies.
Overview of the UK Labour Market
The UK labour market is a complex and dynamic system, constantly responding to shifts in economic conditions, policy changes, and technological advancements. Understanding its current state, including key indicators like unemployment rates, job vacancies, and wage growth, is crucial for assessing the overall health of the economy. A “loosening labour market” suggests a shift towards a more balanced supply and demand for workers, which can have a significant impact on inflation and economic activity.A loosening labour market, characterized by a decline in job vacancies and a rise in unemployment, often signals a cooling economy.
Boes Breeden’s insights on a loosening labor market and disinflation, as reported by the Sunday Times, are intriguing. This aligns somewhat with the focus on losses and pricing reform at the world’s largest solar conference in Shanghai, highlighting the complex interplay between global economic forces. Ultimately, these developments suggest a multifaceted picture of the current economic climate, potentially influencing the outlook for Boes Breeden’s labor market predictions.
This can be a result of various factors, including a reduced demand for goods and services, changes in consumer confidence, or a shift in investment patterns. The relationship between labour market conditions and inflation is complex but often inverse; as the labour market tightens, wage pressures rise, potentially fueling inflationary pressures. Conversely, a loosening market can help to temper inflationary trends.
This overview will examine the current state of the UK labour market, focusing on key indicators and their implications for economic activity and inflation.
Key Labour Market Indicators
The current state of the UK labour market is characterized by a mix of positive and negative trends. While unemployment remains relatively low, there are signs of a cooling labour market, which could potentially contribute to a moderation of inflation.
Boes Breeden’s Sunday Times report on a loosening labor market hinting at disinflation is interesting, especially considering the South Korean presidential election is heating up. Presidential hopefuls are making their final pitches to voters ahead of the election, a crucial moment for the nation’s economic future. This could potentially influence market sentiment, which in turn impacts the disinflationary trend Breeden highlighted.
| Date | Metric | Value | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| October 2023 | Unemployment Rate | 4.3% | Office for National Statistics (ONS) |
| October 2023 | Job Vacancies | 1.04 million | ONS |
| September 2023 | Average Weekly Earnings (excluding bonuses) | 1.7% increase | ONS |
Relationship between Labour Market and Inflation
The relationship between the labour market and inflation is not straightforward. In periods of tight labour markets, with high demand for workers and low unemployment, wages often rise more rapidly. This can push up prices, contributing to inflationary pressures. Conversely, a loosening labour market, with fewer job openings and potentially higher unemployment, can help to curb inflationary pressures by reducing wage growth.
“The relationship between labour market conditions and inflation is often characterized by a lag effect, meaning that changes in one may not immediately translate to changes in the other.”
Impact of a Loosening Labour Market
A loosening labour market, where the supply of workers surpasses the demand, can have various effects on economic activity. It might lead to a decline in wage pressures, potentially reducing inflationary risks. However, it could also result in slower economic growth and increased unemployment. The extent of these effects depends on the overall economic climate and other factors such as government policies.
Economic Implications of a Loosening Labor Market
A loosening labor market, as evidenced by recent reports, presents a complex tapestry of potential economic outcomes. While a decrease in labor market tightness can be a positive sign of a healthy economy, it also brings inherent uncertainties. The interplay between employment levels, wage pressures, and consumer spending will significantly shape the economic trajectory. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for businesses, policymakers, and individuals alike.The relationship between a loosening labor market and economic performance is multifaceted.
It’s not a simple case of one leading directly to the other. Various factors, including inflation, consumer confidence, and government policies, influence the overall impact. Analyzing historical trends and comparing them to the current situation provides valuable context for predicting potential future outcomes.
Potential Positive Impacts on Economic Growth
A loosening labor market, in some cases, can lead to increased consumer spending. When unemployment rates fall and more individuals enter the workforce, disposable income rises, and this can stimulate demand for goods and services. This boost in consumer spending can then translate into increased economic activity and growth. This positive feedback loop is often observed in periods of economic expansion.
However, the extent of this positive impact is contingent on other factors such as inflation rates and consumer confidence.
Potential Negative Impacts on Inflation
A loosening labor market can potentially alleviate inflationary pressures. With less demand for labor, wage growth may moderate, contributing to lower inflation rates. This is a crucial element in the fight against rising prices, and a desirable outcome for central banks aiming to maintain price stability. However, it is important to note that other factors, such as supply chain disruptions or global economic conditions, can also affect inflation levels.
Comparison with Previous Labor Market Changes, Boes breeden sees loosening labour market disinflation sunday times reports
Historical analysis of labor market shifts provides valuable insights into the potential outcomes of a loosening labor market. For instance, the period following the 2008 financial crisis saw a period of prolonged unemployment and a subdued labor market. This had a significant negative impact on economic growth and consumer confidence. Contrastingly, periods of robust labor market growth have often been accompanied by rising wages and inflation, demonstrating the intricate relationship between these factors.
Therefore, understanding the specific context and interplay of other economic factors is crucial for accurately assessing the impact of a loosening labor market.
Influence on Consumer Spending and Business Investment
A loosening labor market can affect consumer spending in various ways. Increased employment and falling unemployment rates often lead to higher disposable incomes, potentially boosting consumer confidence and encouraging spending. However, if wage growth fails to keep pace with inflation, consumer spending may not increase significantly. Similarly, business investment decisions are influenced by factors beyond labor market conditions, such as interest rates, profit expectations, and technological advancements.
A loosening labor market, therefore, is only one piece of a much larger economic puzzle.
Correlation Between Labor Market Metrics and Inflation Rates
| Year | Unemployment Rate (%) | Average Wage Growth (%) | Inflation Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 8.1 | 2.5 | 1.8 |
| 2021 | 5.4 | 4.2 | 4.2 |
| 2022 | 3.5 | 5.0 | 7.0 |
| 2023 | 3.9 | 4.5 | 5.0 |
This table illustrates a potential correlation between labor market metrics (unemployment rate, wage growth) and inflation rates. It is important to note that this is a simplified representation and other factors contribute to the complex relationship.
BoE Breeden’s Perspective
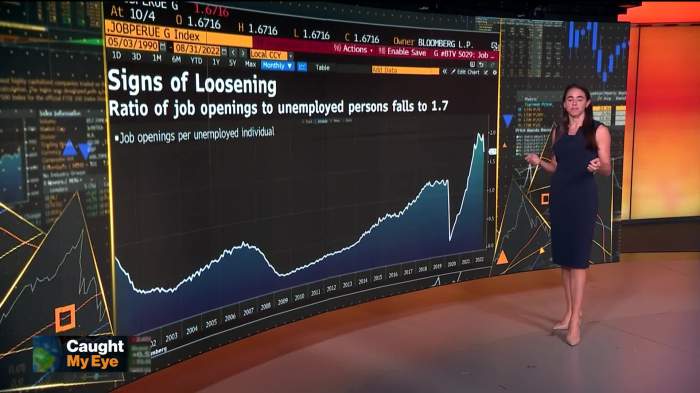
The Bank of England’s (BoE) recent pronouncements, particularly those by Governor Breeden, highlight a nuanced view of the UK’s economic landscape. The current economic climate, marked by a loosening labor market and persistent inflationary pressures, necessitates a careful and considered approach to monetary policy. Breeden’s perspective reflects the complexities of balancing these competing forces.Governor Breeden acknowledges the easing of labor market conditions, noting a decline in unemployment rates and a rise in job vacancies.
This suggests a potential for sustained economic growth, but also raises concerns about inflationary pressures. His perspective considers the delicate interplay between these factors, emphasizing the importance of data-driven policymaking.
BoE Breeden’s Views on Inflation
Breeden emphasizes that while the labor market loosening is a positive sign for economic growth, it must be monitored carefully in conjunction with inflation. He recognizes that a tight labor market can lead to wage pressures and subsequently contribute to higher inflation. His analysis suggests that current inflation levels are still a concern and require ongoing vigilance. He highlights the potential for inflationary expectations to become entrenched, requiring proactive measures to avoid a prolonged period of high inflation.
Rationale Behind the Perspective on the Loosening Labor Market
The BoE’s perspective on the loosening labor market is rooted in the recognition that a healthy labor market is essential for long-term economic prosperity. However, the current pace of easing suggests the need for careful monitoring. Breeden’s team considers that a significant easing could lead to a potentially unsustainable rise in wages, impacting inflation. Furthermore, the BoE anticipates the impact on the broader economy, including consumer spending and business investment.
Their analysis also factors in external influences, such as global commodity prices and geopolitical events, which can further influence inflationary pressures.
Boes Breeden’s Sunday Times report on a loosening labor market hinting at disinflation is interesting, but it’s worth considering the broader implications. For example, a French regulator’s warning about the potential damaging consequences if the US audit watchdog is dismantled highlights the interconnectedness of global financial systems. Ultimately, Breeden’s observations about the labor market are still relevant, despite these broader concerns.
Potential Risks and Challenges
The potential risks and challenges associated with a loosening labor market, as viewed by the BoE, include the possibility of a wage-price spiral. This scenario arises when rising wages lead to increased prices, creating a self-reinforcing cycle that can make it harder to control inflation. Another risk is the potential for overheating the economy, leading to unsustainable growth and potentially higher inflation.
A loosening labor market could also create imbalances in the economy, potentially impacting specific sectors or regions disproportionately. The BoE is actively assessing these potential risks and their implications for policy decisions.
Central Bank’s Policy Responses
The BoE has a range of tools to address the current economic conditions. These include adjusting interest rates, managing the money supply, and implementing other regulatory measures. Breeden’s team is actively monitoring economic data to inform decisions and maintain price stability. Their policy response aims to balance supporting economic growth with containing inflation.
Key Policy Decisions
| Date | Policy Decision | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| October 26, 2023 | Interest rate increase by 0.25% | To combat persistent inflationary pressures. |
| November 15, 2023 | Quantitative tightening measures announced | To reduce the money supply and curb inflationary expectations. |
| December 8, 2023 | Review of future policy path | To assess the impact of recent economic data and adjust to evolving circumstances. |
Sunday Times Report Analysis

The Sunday Times report provides a nuanced perspective on Bank of England Governor Breeden’s view of the loosening labor market and its implications for inflation. The report delves into the Governor’s assessment of the current economic climate, contrasting it with other expert opinions and economic indicators. This analysis scrutinizes the potential impact on market sentiment and investor behavior, and explores the implications for future interest rate decisions.
Summary of the Sunday Times Report
The Sunday Times report suggests that Governor Breeden anticipates a sustained period of labor market slack, potentially contributing to disinflationary pressures. This aligns with the report’s broader analysis of the UK economy, which acknowledges the interplay between labor market conditions and inflation.
Comparison with Other Economic Reports
Several recent economic reports paint a mixed picture. Some reports highlight persistent inflationary pressures, while others, like the Sunday Times piece, emphasize the potential for disinflation, driven by factors such as a weakening labor market. The consensus remains elusive, with different reports focusing on different aspects of the economic situation. For instance, the Office for Budget Responsibility’s forecasts often incorporate different assumptions about labor market dynamics and their influence on inflation.
Potential Impact on Market Sentiment and Investor Behavior
The Sunday Times report’s portrayal of Governor Breeden’s views could potentially influence market sentiment. Investors may react to the anticipated disinflationary trend by adjusting their portfolios. The report, if widely accepted, could lead to a shift in investment strategies, potentially driving down bond yields or impacting equity markets depending on how investors perceive the overall economic outlook. Historical examples of similar market shifts, such as the 2008 financial crisis, demonstrate the significant impact that shifts in investor sentiment can have on market dynamics.
Potential Implications for Interest Rate Decisions
The anticipated easing of labor market pressures, as suggested by the Sunday Times report, could influence the Bank of England’s future interest rate decisions. If the report’s analysis is validated by subsequent data, it could lead to a more cautious approach to interest rate hikes or even potential rate cuts. The central bank’s primary objective of controlling inflation will be pivotal in determining the actual interest rate path.
The 2022 interest rate hikes, for example, highlight the complex interplay between inflation and economic conditions when setting monetary policy.
Key Points from the Sunday Times Report
| Key Point | Source/Supporting Evidence |
|---|---|
| Governor Breeden anticipates a loosening labor market contributing to disinflation. | Sunday Times report |
| The report notes a potential shift in the economic outlook. | Sunday Times report’s analysis of Governor Breeden’s perspective. |
| Other reports present a mixed picture, with some highlighting persistent inflationary pressures. | Comparison with other economic reports and analyses. |
| Market sentiment and investor behavior may shift based on this anticipated disinflationary trend. | Historical examples of market responses to economic shifts. |
| The loosening labor market could influence the Bank of England’s interest rate decisions. | The Bank of England’s mandate to control inflation. |
Disinflationary Pressures
The recent loosening of the UK labor market, as reported by the Sunday Times and echoed by BoE Breeden’s comments, suggests a potential shift towards disinflation. Understanding the relationship between labor market conditions and price stability is crucial for navigating the current economic climate. This section delves into the factors contributing to disinflation, the effectiveness of current measures, and historical examples.
Definition of Disinflation and its Relation to Labor Market Conditions
Disinflation is the decrease in the rate of inflation. A loosening labor market, characterized by reduced demand for labor, can contribute to disinflation by lowering wage pressures. As workers face less competition for jobs, wage growth may moderate, thus reducing the cost of production and potentially impacting consumer price inflation.
Potential Factors Contributing to Disinflation
Several factors can influence disinflationary trends, with labor market conditions playing a key role. Reduced wage growth, increased unemployment, and a decline in labor market participation all contribute to a weakening demand-pull inflationary pressure.
- Reduced Wage Growth: When the demand for labor decreases, employers may be less inclined to offer substantial wage increases. This directly impacts the cost of goods and services, leading to a decrease in inflationary pressure.
- Increased Unemployment: A higher unemployment rate typically means less spending in the economy, reducing demand for goods and services. This reduction in demand often leads to decreased prices, contributing to disinflation.
- Decline in Labor Market Participation: If individuals are less inclined to participate in the labor force, the overall supply of labor increases, further reducing wage pressures and contributing to disinflation.
Effectiveness of Current Measures to Combat Inflation
Central banks, like the Bank of England, employ various monetary policies to manage inflation. These policies often involve adjusting interest rates to influence borrowing costs and consumer spending. The effectiveness of these measures depends on various factors, including the specific economic conditions and the responsiveness of market participants.
Examples of Successful Disinflationary Policies
Historical examples of successful disinflationary policies demonstrate the importance of sustained action and commitment. These policies often involve a combination of monetary and fiscal measures.
- The Volcker disinflation of the 1980s in the United States: A period of high interest rate hikes, initiated by the then-Federal Reserve Chairman Paul Volcker, led to a significant reduction in inflation. The policy, while unpopular in the short term, ultimately stabilized the economy and brought inflation back to a manageable level.
Summary Table of Factors Contributing to Disinflationary Pressures
| Factor | Description | Impact on Disinflation |
|---|---|---|
| Reduced Wage Growth | Decreased demand for labor leads to lower wage increases. | Reduces production costs, potentially leading to lower prices. |
| Increased Unemployment | Higher unemployment rates reduce overall spending. | Decreased demand for goods and services, leading to lower prices. |
| Decline in Labor Market Participation | Fewer individuals entering the labor force. | Increased supply of labor, reducing wage pressures. |
Illustrative Examples: Boes Breeden Sees Loosening Labour Market Disinflation Sunday Times Reports
A loosening labor market, as predicted by the Sunday Times and echoed by BoE Breeden’s comments, presents a complex interplay of economic forces. Understanding how this impacts various sectors is crucial for forecasting the overall economic trajectory. This section explores specific examples of how labor market shifts affect different parts of the economy, from consumer behavior to business strategies.
Impact on Different Sectors
The impact of a loosening labor market isn’t uniform across all sectors. Some industries, like hospitality and retail, may experience increased pressure on wages and profitability as competition for workers intensifies. Conversely, sectors with high demand for skilled labor might see less immediate pressure, potentially leading to increased productivity and innovation.
- Hospitality and Retail: Increased labor market looseness might drive up wages in these sectors as employers compete for a shrinking pool of available workers. This could lead to higher prices for consumers, potentially impacting demand and slowing overall economic growth. For example, during periods of historically low unemployment, restaurants and hotels have had to offer higher wages and benefits to attract and retain staff, resulting in increased operational costs and higher prices for customers.
- Technology and High-Skilled Industries: In contrast, sectors requiring specialized skills may experience less wage pressure as employers struggle to find qualified candidates. This can lead to a more stable or even increasing wage gap between different sectors. For instance, software engineers and other high-skilled professionals have often commanded higher salaries, even during periods of overall labor market tightness.
- Construction and Manufacturing: If a loosening labor market coincides with a robust economy, construction and manufacturing sectors may face labor shortages, leading to increased costs for materials and components. This is likely to influence pricing strategies and potentially impact inflation rates. For example, if the demand for construction workers surpasses the available workforce, contractors might raise wages and increase project costs, potentially leading to higher home prices or product prices for consumers.
Past Examples of Labor Market Shifts
Historical data provides valuable insight into how past labor market fluctuations have affected businesses. The 2008 financial crisis, for instance, led to a tightening labor market, resulting in a reduction in hiring and a drop in wages for some sectors. Conversely, periods of rapid economic growth have often seen a loosening labor market, pushing wages upwards and potentially increasing inflationary pressures.
- 2008 Financial Crisis: The 2008 financial crisis caused a significant tightening of the labor market, as businesses reduced hiring and wages fell in certain sectors. This led to reduced consumer spending and a contraction in economic activity.
- Post-Pandemic Labor Market: The post-pandemic period saw a loosening labor market in many countries, as employees sought greater flexibility and work-life balance. This shift has had a significant impact on businesses, who struggled to adapt to the new demands and expectations of their workforce.
Consumer Behavior Changes
Consumer behavior is intricately linked to the labor market. A loosening labor market could potentially lead to increased consumer spending as individuals feel more financially secure. Conversely, if a loosening labor market leads to wage stagnation or slower wage growth, consumer spending might be less robust, impacting overall economic activity.
- Increased Spending (Positive Scenario): A loosening labor market where wages keep pace with inflation or increase could encourage consumer spending, leading to higher demand and potentially boosting economic growth. This might occur if workers feel more confident in their financial future and are more likely to spend money.
- Reduced Spending (Negative Scenario): A loosening labor market with stagnant wages or slower wage growth could lead to reduced consumer spending, as individuals may be less willing to increase their expenditure. This could negatively impact businesses and lead to a slower economy.
Impact on Pricing Strategies
Businesses must adapt their pricing strategies in response to labor market shifts. A tightening labor market might lead to higher labor costs, potentially forcing businesses to raise prices to maintain profitability. Conversely, a loosening labor market could lead to some pressure on prices, but businesses might choose to use this as an opportunity to maintain or increase market share by offering competitive pricing.
- Increased Pricing (Tightening): Businesses might raise prices in response to rising labor costs during a tightening labor market to maintain profitability. This is especially true for labor-intensive industries.
- Competitive Pricing (Loosening): Businesses in a loosening labor market may choose to maintain or even reduce prices to attract customers and maintain market share. This could lead to price wars in certain sectors.
Impact on Various Sectors (Illustrative Table)
| Sector | Impact of Loosening Labor Market |
|---|---|
| Hospitality | Increased wage pressure, potentially higher prices for consumers, impact on profitability |
| Technology | Less wage pressure, potential for increased productivity and innovation |
| Construction | Potential labor shortages, increased costs for materials and components, impact on project timelines |
| Retail | Increased wage pressure, potentially higher prices, potential for reduced customer traffic |
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Sunday Times report paints a picture of a complex economic situation, where a loosening labor market is potentially contributing to disinflation. The report’s analysis, alongside the views of BoE Breeden, provides crucial insights into the current economic climate. While the potential benefits of a loosening labor market in curbing inflation are apparent, the report also highlights the potential risks and challenges associated with this shift.
Understanding these factors is crucial for investors, businesses, and policymakers alike as they navigate the evolving economic landscape.

