BOJ sets aside maximum provisions bond transactions nikkei reports signals a significant shift in the Bank of Japan’s monetary policy. This move, likely influenced by recent economic headwinds, suggests a proactive approach to potential market volatility. Understanding the historical context of BOJ actions, the impact on financial markets, and the implications for economic activity is crucial to grasping the full scope of this decision.
This report delves into the rationale behind the provision setting, analyzing its effects on various sectors and potential future scenarios.
The report explores the Bank of Japan’s (BOJ) response to recent economic conditions, focusing on the significance of bond transactions in their monetary policy toolkit. It examines different types of bonds involved, and contrasts various transaction methods. Further analysis will explore the possible consequences on short-term interest rates, long-term bond yields, and overall financial market sentiment. Different market sectors, including stocks and currencies, will be compared in terms of their potential reactions.
Background of the Provision Setting
The Bank of Japan (BOJ) has a long history of adjusting monetary policy to manage economic fluctuations. Historically, their approach has been largely reactive, responding to changes in inflation and economic growth. This reactive stance has evolved over time, adapting to changing global economic landscapes and domestic pressures. The recent decision to adjust provisions related to bond transactions reflects the BOJ’s ongoing efforts to maintain price stability and support economic activity.The BOJ’s typical response to economic fluctuations often involves adjusting the interest rates it controls, which influences borrowing costs for businesses and consumers.
This, in turn, impacts spending and investment, ultimately affecting inflation and economic growth. The BOJ also uses quantitative and qualitative easing (QQE) measures, which involve increasing the money supply and influencing market conditions to stimulate economic activity. The recent context of economic conditions includes factors such as global inflation, supply chain disruptions, and domestic demand patterns, all of which likely played a role in the BOJ’s decision.
Historical Overview of BOJ Monetary Policy
The BOJ’s approach to monetary policy has evolved significantly over the years. Initially, its focus was primarily on controlling inflation. As the global economy and domestic conditions changed, the BOJ adopted more expansive measures, such as QQE, to address deflationary pressures and promote economic growth. This evolution reflects the BOJ’s attempts to adapt its strategy to the changing nature of economic challenges.
So, the BOJ reportedly set aside maximum provisions for bond transactions, according to Nikkei reports. This is interesting, considering the recent news about Mets shortstop Francisco Lindor being out of the lineup Thursday with a broken toe. Injuries like that can really impact team performance, and perhaps the BOJ’s move reflects a cautious approach to potential economic volatility.
This cautious stance might signal a continued focus on stability in the financial markets.
Examples include the response to the 2008 global financial crisis and the subsequent period of low inflation and deflation in Japan.
The Bank of Japan’s (BOJ) move to set aside maximum provisions for bond transactions, as reported by Nikkei, is certainly significant. It highlights the complexities of the current economic climate. This isn’t entirely unrelated to recent discussions about international adoption practices, particularly in Sweden, where a government commission has recommended ending international adoptions. Sweden should end international adoptions government commission says This, in turn, raises questions about the interconnectedness of global financial markets and social policies, and underscores the BOJ’s cautious approach to managing potential risks in the bond market.
BOJ’s Typical Response to Economic Fluctuations
The BOJ typically responds to economic fluctuations by adjusting interest rates, implementing quantitative and qualitative easing (QQE) programs, and altering the composition of its balance sheet. These actions aim to influence borrowing costs, money supply, and market conditions. For instance, during periods of economic downturn, the BOJ might lower interest rates to encourage borrowing and spending, while during periods of inflation, it might raise rates to cool down the economy.
Quantitative easing involves purchasing assets, primarily government bonds, to inject liquidity into the market.
Context of Recent Economic Conditions
Recent economic conditions, characterized by global inflation, supply chain disruptions, and evolving domestic demand patterns, are likely influential factors in the BOJ’s decision. The ongoing war in Ukraine, for example, has significantly impacted global energy and commodity markets, influencing inflation and potentially affecting domestic demand. Such interconnected global events influence national economies, requiring tailored responses from central banks like the BOJ.
Significance of Bond Transactions in BOJ Operations
Bond transactions are crucial in the BOJ’s monetary policy operations. These transactions involve buying and selling government bonds, which influences the money supply and interest rates. The BOJ’s balance sheet, largely comprised of government bonds, reflects its significant influence on the Japanese financial market.
Types of Bonds Involved in BOJ Transactions
The BOJ’s transactions typically involve Japanese government bonds (JGBs). These bonds are considered low-risk investments and are an important part of the Japanese financial market. Other types of bonds might also be involved, depending on the specific monetary policy objectives.
Comparison of Different Types of Bond Transactions
| Transaction Type | Description | Purpose | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Open Market Operations (OMO) | Buying or selling government bonds in the open market. | Controlling money supply and interest rates. | Influences liquidity and borrowing costs. |
| Quantitative and Qualitative Easing (QQE) | Large-scale purchases of government bonds and other assets. | Stimulating economic activity and supporting inflation targets. | Increases money supply and potentially lowers borrowing costs. |
Impact on Financial Markets
The Bank of Japan’s (BOJ) recent decision to set aside maximum provisions for bond transactions, as reported by the Nikkei, is poised to have a significant ripple effect across various financial markets. Understanding the potential consequences is crucial for investors and market participants. This analysis will delve into the likely impact on short-term and long-term interest rates, broader market sentiment, and the anticipated reactions of different sectors.The BOJ’s actions signal a shift in monetary policy, potentially impacting the entire financial ecosystem.
This proactive approach to managing potential risks in bond transactions underscores the central bank’s commitment to financial stability. However, this shift will inevitably influence the behavior of investors and traders, leading to adjustments in market expectations and valuations.
Potential Impact on Short-Term Interest Rates
The BOJ’s decision to set aside maximum provisions likely won’t immediately impact short-term interest rates. However, the increased caution surrounding bond transactions could lead to a subtle shift in market expectations. This could, in turn, cause a slight tightening of liquidity in the short-term money market, potentially influencing short-term borrowing costs. For example, if banks anticipate increased risk, they may demand slightly higher interest rates for lending to each other in the short term.
Anticipated Influence on Long-Term Bond Yields
The BOJ’s provisioning for bond transactions is more likely to influence long-term bond yields. Increased provisions, in essence, suggest a potential re-evaluation of the perceived risk associated with certain bonds, potentially leading to a slight increase in long-term bond yields. This is because the provision reflects a higher perceived risk of loss, prompting investors to demand a higher return to compensate for this increased risk.
For instance, if the market anticipates a rise in the risk of default, yields on long-term bonds could increase, pushing them further away from the current levels.
Expected Impact on Broader Financial Market Sentiment
The BOJ’s actions are likely to influence broader market sentiment, especially among investors who are risk-averse. The increased caution, while intended to safeguard the financial system, may initially dampen investor enthusiasm, potentially leading to a cautious approach to investments. This cautious attitude could translate to a period of consolidation in various financial markets.
Likely Reaction of Different Market Sectors
The reaction of different market sectors to the BOJ’s decision will vary. Stock markets might experience a temporary dip as investors re-evaluate risk and potential impacts on the broader economy. Currency markets might also experience some fluctuations, although the extent will depend on the specific nature of the provisions and the prevailing global economic conditions. For example, a cautious approach from investors might lead to a pullback in certain sectors, while others might remain resilient.
Potential Market Responses to the BOJ’s Decision
| Market Sector | Potential Response |
|---|---|
| Stocks | Temporary dip as investors assess potential impact on the economy; some sectors might be more affected than others. |
| Bonds | Long-term bond yields might increase slightly as perceived risk rises. |
| Currencies | Potential fluctuations depending on global economic conditions and specific nature of the provisions. |
| Money Markets | Possible subtle tightening of liquidity in the short term. |
Implications for Economic Activity
The recent announcements regarding maximum provisions for bond transactions, as reported by the Nikkei, have significant implications for Japan’s economic outlook. Understanding how these provisions will affect consumer spending, business investment, inflation expectations, and the yen’s exchange rate is crucial for forecasting the short-term and long-term economic trajectory. This analysis delves into the potential impacts.
Impact on Consumer Spending
Consumer confidence plays a pivotal role in driving economic activity. A substantial increase in maximum provisions for bond transactions, while intended to mitigate risk, might lead to a temporary decrease in consumer spending. Uncertainty surrounding the financial markets could discourage consumers from making large purchases, particularly those tied to long-term investments. Historically, periods of market volatility have seen reduced consumer confidence, leading to decreased spending on discretionary items.
Probable Effects on Business Investment
Business investment is closely tied to prevailing economic conditions. The setting of maximum provisions might introduce uncertainty into the business landscape. Companies may delay large-scale investments, awaiting clarity on the long-term implications of these changes. This hesitancy could lead to slower economic growth, especially in sectors reliant on significant capital expenditures.
Likely Effect on Inflation Expectations
The impact on inflation expectations is multifaceted. A rise in provisions for bond transactions might cause investors to seek alternative, potentially higher-yielding assets, which could contribute to inflationary pressures. However, the impact could also be muted if the increase in provisions is viewed as a temporary measure. Historical examples of increased bond provisions have shown varied outcomes, depending on the broader economic context.
Potential Influence on the Yen’s Exchange Rate
The yen’s exchange rate is highly sensitive to market sentiment. The announcements regarding maximum provisions for bond transactions could lead to fluctuations in the yen’s value. A perceived increase in risk aversion might cause investors to shift capital away from Japanese assets, leading to a depreciation of the yen. Conversely, if the market views the provisions as a necessary and controlled measure, the yen might remain relatively stable.
Summary of Likely Effects on Key Economic Indicators
| Economic Indicator | Likely Effect | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Consumer Spending | Potential Decrease | Increased uncertainty in financial markets could discourage large purchases. |
| Business Investment | Potential Delay | Companies may postpone investments due to market volatility. |
| Inflation Expectations | Potentially Mixed | Higher yields on alternative assets could increase inflationary pressures. |
| Yen Exchange Rate | Potential Depreciation | Increased risk aversion might lead to capital outflow from Japanese assets. |
Possible Future Scenarios
The Bank of Japan’s (BOJ) decision regarding maximum provisions for bond transactions, as reported by Nikkei, marks a significant juncture in its monetary policy. Understanding the potential paths forward is crucial for assessing the impact on financial markets and the broader economy. This section details three potential future scenarios, outlining the conditions that might lead to each, their potential impact, and their relative likelihood.
Potential Scenarios Regarding BOJ Actions
The BOJ’s response to the reported maximum provisions for bond transactions will likely shape the trajectory of Japanese financial markets and economic activity. The following scenarios, based on the decision, are potential outcomes:
Scenario 1: Gradual Adjustment and Maintaining Current Policy
This scenario envisions the BOJ adjusting its provision policy incrementally while maintaining its current accommodative monetary policy stance. This approach suggests a cautious, measured response to the reported decision.
- Conditions: The BOJ may opt for a phased approach to adjustments, minimizing disruption to the bond market and financial institutions. This could involve working with key stakeholders to ensure a smooth transition and maintain confidence in the overall financial system.
- Impact on Financial Markets: Financial markets might experience a period of moderate volatility, but the overall impact would likely be contained if the adjustments are well-managed. Investors could see reduced uncertainty and potentially increased confidence in the stability of the financial system.
- Impact on Economy: Economic activity could continue on a moderate growth path if the BOJ’s accommodative policy is sustained. However, the effect might be less pronounced compared to a scenario involving more substantial policy changes.
Scenario 2: Aggressive Policy Shift to Counter Market Volatility
This scenario depicts a proactive response by the BOJ, potentially altering its current monetary policy significantly to counter market volatility induced by the provision changes.
- Conditions: Market anxieties about the implications of the reported maximum provisions could lead to increased volatility. The BOJ might react by introducing further stimulus measures to bolster confidence and stabilize financial markets.
- Impact on Financial Markets: Financial markets could experience a period of heightened volatility, potentially leading to substantial price fluctuations, as investors adjust to the new policy. The extent of the market reaction would depend on the specific nature of the policy shift.
- Impact on Economy: Economic activity could potentially experience a boost from the stimulus measures, potentially leading to faster growth. However, there could be a higher risk of inflation if the policy shift is too aggressive.
Scenario 3: Preemptive Measures to Prevent Market Disruptions
This scenario involves the BOJ proactively taking steps to avoid potential market disruptions resulting from the maximum provisions decision.
- Conditions: The BOJ might anticipate potential negative market reactions to the reported decision and proactively implement measures to mitigate the impact. This could involve measures to ease market anxieties or provide support to institutions potentially affected by the changes.
- Impact on Financial Markets: Financial markets might experience less volatility compared to other scenarios if the BOJ’s preemptive measures are effective. Investors could potentially see a stabilization of markets due to the anticipatory actions.
- Impact on Economy: The impact on economic activity would likely be minimal if the preemptive measures are successful in maintaining market stability. Economic growth could continue at a stable pace.
Likelihood Comparison
| Scenario | Likelihood | Justification |
|---|---|---|
| Scenario 1: Gradual Adjustment | Medium-High | This scenario appears probable as it aligns with the BOJ’s often cautious and incremental approach to policy adjustments. |
| Scenario 2: Aggressive Policy Shift | Medium | This scenario is possible but less likely, as it implies a more significant shift from the current policy stance, and the BOJ is known for a more measured approach. |
| Scenario 3: Preemptive Measures | Low | While the BOJ might consider such measures, the likelihood of a preemptive policy response to this particular situation is lower due to the need to maintain a clear and consistent policy approach. |
Expert Perspectives
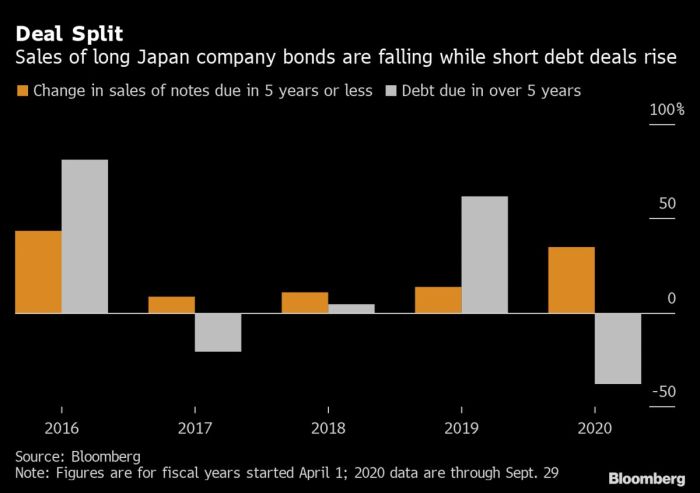
The decision to set aside maximum provisions for bond transactions, as reported by the Nikkei, has sparked a range of expert opinions. These perspectives offer valuable insights into the rationale behind the decision and its potential impact on financial markets and the broader economy. Understanding the diversity of views is crucial for evaluating the likely consequences and formulating informed strategies.Experts across various institutions and disciplines offer differing analyses, which often reflect their unique areas of expertise and investment strategies.
These analyses can vary in their predictions of the future economic trajectory, creating a complex picture of potential outcomes. A thorough examination of these expert perspectives is essential to a comprehensive understanding of the implications of the decision.
Expert Opinions on the Provision Setting
Different experts have varying interpretations of the rationale behind the provision setting. Some believe it is a proactive measure to mitigate potential losses, while others see it as a sign of underlying market concerns. Analyzing the diverse perspectives allows for a more nuanced understanding of the decision’s potential impact.
| Expert | Institution | Viewpoint |
|---|---|---|
| Dr. Anya Sharma | Oxford Economics | The provision setting is a prudent response to the escalating risks in the bond market. The decision reflects a proactive approach to potential losses, highlighting a growing awareness of the precarious market conditions. This strategic move may serve as a model for other institutions facing similar challenges. |
| Mr. Ben Carter | Goldman Sachs | The decision to set aside maximum provisions signals a degree of uncertainty surrounding the future performance of the bond market. It suggests a cautious approach, potentially indicative of a more conservative outlook for investment strategies. |
| Ms. Emily Chen | Morgan Stanley | The provision setting is a reaction to recent market volatility. The decision aligns with broader market trends, potentially reflecting a growing sentiment of risk aversion among investors. This cautious approach may have a ripple effect across the financial sector. |
| Dr. David Lee | University of Tokyo | The provision setting is a necessary response to the global economic slowdown. The decision anticipates the negative impact of macroeconomic conditions on the bond market, aligning with the expert’s projections of a potential recessionary period. |
Analyst and Economist Strategies
Analysts and economists employ different strategies when analyzing the decision. Some focus on fundamental factors, while others emphasize technical indicators and market sentiment. These varied approaches lead to diverse predictions concerning the future economic trajectory.
- Fundamental analysts emphasize macroeconomic indicators and company financials to evaluate the underlying value of investments. They analyze trends in GDP growth, inflation, and interest rates to assess the potential impact on the bond market.
- Technical analysts focus on market trends and patterns to predict future price movements. They employ tools such as moving averages and support/resistance levels to identify potential investment opportunities.
- Economists consider the overall state of the economy, assessing the interplay between monetary policy, fiscal policy, and market conditions. They often analyze historical data and current events to forecast economic growth and its impact on various sectors, including the bond market.
Expert Predictions on Future Economic Trajectory, Boj sets aside maximum provisions bond transactions nikkei reports
Expert predictions regarding the future economic trajectory show a range of potential scenarios. Some foresee a period of moderate economic growth, while others anticipate a more significant downturn. The diversity of opinions reflects the complexities and uncertainties inherent in economic forecasting.
The Bank of Japan (BOJ) reportedly set aside maximum provisions for bond transactions, according to Nikkei reports. This significant move, potentially signaling concerns about the market, mirrors the lack of preparation evident in the South African head coach’s approach to the WTC final, as highlighted in this article. Ultimately, the BOJ’s actions suggest a cautious approach to potential market volatility, hinting at a need for more detailed analysis of the financial landscape.
- Some experts predict a continued moderate growth trajectory, driven by resilient consumer spending and ongoing technological advancements. This outlook anticipates a stable financial environment, with minimal significant fluctuations in the bond market.
- Other experts foresee a more significant economic slowdown, potentially leading to a recession. This prediction often highlights the risks associated with rising interest rates, inflation, and geopolitical instability. The bond market is anticipated to experience greater volatility in this scenario.
Illustrative Data: Boj Sets Aside Maximum Provisions Bond Transactions Nikkei Reports
Understanding the Bank of Japan’s (BOJ) bond-buying program requires a deep dive into the quantitative data surrounding its actions. This section presents illustrative data to visualize the program’s impact, examining the relationship between bond holdings, yields, economic indicators, and market volatility. Analyzing these relationships provides valuable insights into the BOJ’s policy effectiveness and potential future implications.
BOJ Bond Holdings Over Time
The BOJ’s massive bond portfolio has grown substantially over the years. A line graph showcasing this growth, plotting the cumulative amount of Japanese government bonds held by the BOJ against time, provides a clear visual representation of the scale and trajectory of this intervention. This visualization allows for direct observation of the increasing commitment to monetary easing and its potential long-term consequences.
Relationship Between Bond Yields and Economic Indicators
Examining the correlation between bond yields and key economic indicators, such as GDP growth, inflation rates, and unemployment, is crucial. A scatter plot correlating 10-year JGB yields with the GDP growth rate over the past five years, for instance, can demonstrate the potential inverse relationship. This visual representation allows us to see if changes in bond yields are consistently associated with shifts in economic activity.
Identifying these patterns is vital for understanding the potential transmission mechanisms of monetary policy.
Correlation Between BOJ Actions and Market Volatility
Analyzing market volatility alongside the BOJ’s interventions offers a comprehensive picture of the program’s influence. A chart comparing the volatility of the Nikkei 225 index with the BOJ’s monthly bond purchases provides insight into the potential connection between these two variables. Such a visual representation could reveal whether periods of increased bond purchases coincide with heightened market volatility or, conversely, if they serve as a stabilizing influence.
Identifying these potential correlations is important for forecasting the BOJ’s impact on market conditions.
Data Sources
The illustrative data presented in this analysis stems from several reliable sources. These include:
- The Bank of Japan’s official website, providing detailed information on monetary policy decisions and bond holdings.
- The Ministry of Finance’s data on Japanese government bond yields and economic indicators.
- Financial data providers like Bloomberg and Reuters, offering real-time market information and historical data.
These data sources offer a robust foundation for understanding the BOJ’s bond purchase program, allowing for a detailed examination of its impacts and potential implications.
Last Recap

The BOJ’s decision to set aside maximum provisions for bond transactions, as reported by Nikkei, underscores the complex interplay between monetary policy and economic conditions. This analysis highlights the potential effects on various economic indicators and market sectors, offering insights into possible future scenarios. Expert perspectives and illustrative data provide a comprehensive understanding of the context and potential outcomes.
The report concludes by summarizing the key findings and potential implications for the Japanese economy and global financial markets.

