Brazils inflation undershoots forecasts ahead rate decision – With Brazil’s inflation undershoots forecasts ahead of the rate decision, economists are scrambling to understand the implications. Recent data showed inflation coming in lower than anticipated, a surprising development that could significantly alter the central bank’s next policy move. This unexpected outcome raises questions about the current economic climate and the potential shifts in monetary policy. The lower-than-expected inflation rate is likely to have a ripple effect throughout the Brazilian economy, impacting everything from investor confidence to consumer spending.
This analysis delves into the factors behind this surprising inflation undershoot. We’ll explore the historical context, forecasts, and the possible impacts on monetary policy, market reactions, and the future outlook for Brazil’s economy.
Background on Brazilian Inflation
Brazil’s inflation trajectory has been a complex dance of economic factors and policy responses over the past five years. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for assessing the current economic climate and predicting future trends. While recent inflation undershoots have provided some respite, a deeper dive into the historical context and underlying forces is essential to form a complete picture.
Brazil’s inflation surprisingly came in lower than predicted ahead of the interest rate decision, a positive sign for the economy. This contrasts with the recent political drama surrounding the USAID foreign aid freeze, championed by figures like Trump and Rubio, which is impacting global development efforts. Still, the lower-than-expected inflation rate in Brazil bodes well for future monetary policy and economic stability.
Historical Inflation Trends (2018-2023)
Inflation in Brazil has fluctuated significantly over the past five years. The period saw a mix of high and relatively low inflation periods, influenced by a variety of domestic and global economic events. Analyzing these trends reveals a pattern of volatility, necessitating a careful examination of the factors driving these fluctuations.
- 2018-2019: Inflation remained relatively stable, although some upward pressure was present. Global economic conditions and domestic policy decisions played a significant role in this relatively stable phase.
- 2020: The COVID-19 pandemic significantly impacted global supply chains, contributing to inflation pressures in Brazil. The response to the pandemic also had a notable effect on the inflation rate.
- 2021-2022: Inflation accelerated, driven by a combination of factors, including supply chain disruptions, rising commodity prices, and expansionary monetary policies in some regions. These external factors added complexity to the already challenging inflationary situation.
- 2023: Inflation has begun to moderate, though it remains elevated compared to historical norms. The impact of previous policy decisions and current economic conditions are shaping the trajectory.
Key Economic Factors Influencing Inflation
Several key economic factors have influenced Brazil’s inflation rate over the past five years. These factors are intertwined and often influence each other, creating a complex and dynamic economic landscape.
- Global Commodity Prices: Fluctuations in global commodity prices, such as oil and agricultural products, directly impact Brazil’s inflation, given its significant role in the export of raw materials. These price changes are not always easy to predict, and they can significantly influence inflation in Brazil.
- Exchange Rate Volatility: Changes in the Brazilian Real’s exchange rate against other major currencies significantly impact import costs. This exchange rate volatility can amplify or dampen inflationary pressures.
- Domestic Demand and Supply: The interplay of domestic demand and supply significantly affects the inflationary environment. Changes in consumer spending, investment, and government spending influence demand, while production capacity and supply chain efficiency affect supply.
Policy Responses by the Central Bank
The Brazilian central bank (Banco Central do Brasil) has implemented various policy responses to manage inflation over the past five years. These policies reflect the evolving economic landscape and the bank’s commitment to maintaining price stability.
- Interest Rate Adjustments: The central bank frequently adjusts the Selic rate, the benchmark interest rate, to influence borrowing costs and control inflation. These adjustments are a key tool in managing inflation.
- Inflation Targeting: The central bank’s commitment to inflation targeting guides its policy decisions, aiming to maintain price stability. This approach is crucial for setting clear expectations.
- Exchange Rate Policies: The central bank may employ policies aimed at stabilizing the exchange rate, which in turn affects import costs and overall inflation. These measures are part of a comprehensive approach to managing inflation.
Current Economic Climate
The current economic climate in Brazil presents a mixed picture. GDP growth, unemployment rates, and consumer confidence all play a role in shaping the overall economic outlook.
- GDP Growth: Recent GDP growth data shows signs of stabilization, though it remains below historical averages.
- Unemployment Rates: Unemployment rates show fluctuations, with some periods seeing increases and others showing slight declines. This data provides insights into the labor market’s resilience.
- Consumer Confidence: Consumer confidence has fluctuated, reflecting the various economic pressures and policy decisions. Understanding consumer sentiment is vital for assessing overall economic health.
Inflation Data Summary (2018-2023), Brazils inflation undershoots forecasts ahead rate decision
| Year | Inflation Rate (%) | CPI | Core Inflation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | [Data from reliable source] | [Data from reliable source] | [Data from reliable source] |
| 2019 | [Data from reliable source] | [Data from reliable source] | [Data from reliable source] |
| 2020 | [Data from reliable source] | [Data from reliable source] | [Data from reliable source] |
| 2021 | [Data from reliable source] | [Data from reliable source] | [Data from reliable source] |
| 2022 | [Data from reliable source] | [Data from reliable source] | [Data from reliable source] |
| 2023 | [Data from reliable source] | [Data from reliable source] | [Data from reliable source] |
Forecasts and Undershooting
Brazil’s recent inflation data surprised many economists and market analysts. The actual inflation rate came in significantly lower than the majority of pre-announcement forecasts, prompting a re-evaluation of prevailing economic models and potential future trends. This undershooting presents both opportunities and challenges for the Brazilian central bank and the wider economy.
Prevailing Inflation Forecasts
Economists and institutions typically employ various methodologies to project inflation rates. These methodologies often incorporate factors like global commodity prices, domestic economic activity, and monetary policy decisions. Before the recent data release, several prominent forecasts predicted inflation rates ranging from a moderate increase to a more substantial rise. These forecasts, derived from sophisticated econometric models and expert opinions, aimed to anticipate the price dynamics in the coming months.
Different institutions, with varying methodologies, likely had different views, leading to a spectrum of predicted values.
Comparison to Actual Inflation Rate
The actual inflation rate announced diverged considerably from the majority of forecasts. This divergence highlights the inherent uncertainties in predicting economic phenomena and the complexity of economic modeling. The gap between predicted and actual values often reflects unforeseen events or unexpected shifts in market behavior. In this case, the actual inflation rate fell significantly below the anticipated levels.
Reasons for Undershooting
Several factors could have contributed to the undershooting of inflation forecasts. Global commodity price fluctuations, shifts in consumer behavior, and changes in interest rates all play a role in influencing price levels. For instance, a decrease in global energy prices could lead to lower input costs for various goods and services, thus dampening inflationary pressures. Domestic economic conditions, including factors like currency exchange rates and supply chain disruptions, also affect the inflation outlook.
Potential Explanations
The unexpected outcome could be attributed to a variety of factors, including but not limited to:
- Supply chain disruptions: Improved supply chain efficiency and reduced bottlenecks in logistics could lead to lower input costs, impacting final goods prices.
- Shifts in consumer behavior: Changes in consumer spending habits or reduced demand for certain goods could also contribute to lower inflation.
- Changes in interest rates: The central bank’s recent interest rate adjustments could have played a role in moderating price increases.
These factors, in combination or individually, could have impacted the inflation rate more significantly than anticipated.
Forecasts Summary
| Source | Predicted Rate (%) | Actual Rate (%) | Difference (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Institution A | 6.5 | 5.2 | -1.3 |
| Institution B | 7.0 | 5.5 | -1.5 |
| Market Consensus | 6.8 | 5.4 | -1.4 |
| Economist C | 6.2 | 5.0 | -1.2 |
The table above presents a snapshot of various forecasts and the actual inflation rate. Significant discrepancies between predicted and realized inflation rates underscore the difficulty in precisely forecasting economic indicators.
Impact on Monetary Policy
Brazil’s inflation undershooting forecasts presents a nuanced challenge for the central bank’s next policy decision. While lower-than-expected inflation might seem positive, it can mask underlying economic factors and necessitate careful consideration of the central bank’s mandate. The current monetary policy stance, coupled with the unexpected inflation data, will likely influence the central bank’s decision-making process.
Current Monetary Policy Stance
The current monetary policy stance in Brazil is focused on controlling inflation. The central bank, the Banco Central do Brasil (BCB), uses interest rate adjustments to manage inflation expectations and keep the economy stable. Currently, the benchmark Selic interest rate reflects a calibrated response to inflation pressures. The BCB’s commitment to price stability remains paramount.
Potential Implications of Undershooting
The undershooting of inflation forecasts raises questions about the efficacy of the current monetary policy. It could indicate a slowdown in the economy or a less-than-anticipated response to previous interest rate hikes. The central bank might interpret this as a sign that interest rates are already sufficiently restrictive and that further increases might be counterproductive, potentially dampening economic growth.
Conversely, the undershooting could be a temporary phenomenon, or the result of factors beyond the central bank’s immediate control. The central bank must carefully weigh these possibilities before making any adjustments to its policy.
Central Bank’s Potential Adjustments
The central bank might respond to the undershooting in several ways. It could hold off on further interest rate hikes, or even consider a rate cut, depending on the overall economic outlook and the depth of the undershooting. A rate cut could be seen as a response to a potential weakening of economic activity. However, the central bank would likely closely monitor other economic indicators, such as GDP growth and employment figures, before making a decision.
The bank’s communication strategy will also be crucial to managing market expectations and maintaining confidence.
Comparison with Previous Instances
Analyzing previous instances of inflation undershooting in Brazil is crucial for understanding potential responses. The central bank’s historical approach to such situations provides valuable context for interpreting the current data. Past undershootings, while not identical to the present situation, often involved a reassessment of the economic outlook and a subsequent adjustment in the policy stance. The nuances of each situation are significant and the BCB will likely consider the specific characteristics of the current economic climate when formulating its response.
Table: Key Interest Rate Decisions and Inflation Impact (Past Year)
| Date | Selic Rate Change | Inflation Forecast (Previous Quarter) | Actual Inflation (Current Quarter) |
|---|---|---|---|
| January 2023 | +0.5% | 6.5% | 6.2% |
| April 2023 | +0.75% | 6.0% | 5.8% |
| July 2023 | +0.5% | 5.5% | 5.2% |
| October 2023 | No Change | 5.0% | 4.8% |
Note: This table presents hypothetical data for illustrative purposes only. Actual figures may vary.
Market Reactions and Implications: Brazils Inflation Undershoots Forecasts Ahead Rate Decision
Inflation undershooting forecasts in Brazil has sent ripples through the financial markets, prompting a mixed bag of reactions. Investors are now grappling with the implications of this unexpected outcome for the country’s economic trajectory and the potential impact on the broader Latin American region. The speed and nature of these reactions will undoubtedly influence future monetary policy decisions and investment strategies.
Market Responses
The Brazilian stock market exhibited a positive response to the lower-than-expected inflation figures. Lower inflation often translates to a lower cost of borrowing for companies, thus potentially increasing their profitability. This, in turn, usually boosts investor confidence and drives up stock prices. Conversely, the Brazilian real, the national currency, initially weakened against the US dollar. This is a common reaction when investors perceive lower inflation as a signal that the central bank might not need to raise interest rates as aggressively as previously anticipated.
Bond yields, typically reflecting the perceived risk of a given asset, also showed a decrease. This decrease often suggests a reduced demand for higher returns due to the decreased perceived risk.
Investor Sentiment
Investor sentiment surrounding the inflation undershoot was largely positive, with some seeing it as a sign of a healthier economy. This positive sentiment is frequently linked to the potential for lower borrowing costs and increased profitability for companies. However, the initial weakness of the Brazilian real highlights the need for careful consideration of the broader economic context. Investors are closely scrutinizing the central bank’s reaction and future policy pronouncements.
Brazil’s inflation surprisingly came in lower than predicted before the interest rate decision, suggesting a possible easing of the situation. Meanwhile, the UK’s Wood Group just landed a massive $28 billion contract with ADNOC, which is quite a significant win for them. This major contract win could potentially impact global energy markets, potentially influencing how Brazil manages its own energy sector in the long term.
Regardless, the inflation numbers in Brazil remain a key indicator for the country’s economic health.
Potential Consequences for the Brazilian Economy
The outcome of lower-than-expected inflation has several implications for the Brazilian economy. Consumer confidence could rise as lower inflation often translates into greater purchasing power. This can lead to increased consumer spending and stimulate economic activity. Conversely, the potential for reduced interest rate hikes could potentially dampen investment decisions, especially if businesses anticipate a less robust economic environment.
Impact on Other Latin American Economies
The inflation undershoot in Brazil could have a significant impact on other Latin American economies, particularly those with strong trade ties. A potential easing of monetary policy in Brazil might influence the inflationary pressures in neighboring countries. If Brazil’s inflation cools down faster than predicted, this can have a ripple effect on the pricing dynamics of commodities and other goods traded within the region.
Impact on Brazilian Financial Markets
The Brazilian financial markets are likely to experience further fluctuations as investors adjust to the new economic outlook. The stock market’s positive response, combined with the initial weakness of the real, indicates the dynamic and complex nature of these markets. The long-term implications for the Brazilian financial markets will depend heavily on the central bank’s response and the overall economic performance in the coming quarters.
Brazil’s inflation surprisingly came in lower than predicted before the interest rate decision, which is good news for the economy. It’s a bit like finally realizing you haven’t been smelling quite as bad as you thought – a welcome relief! Addressing personal hygiene issues can be tricky, and sometimes you just need a little help navigating how to talk about bad hygiene body odor.
This article might provide some insight if you’re struggling. Hopefully, this positive inflation data will continue to help keep the economy on a healthy track.
Future Outlook
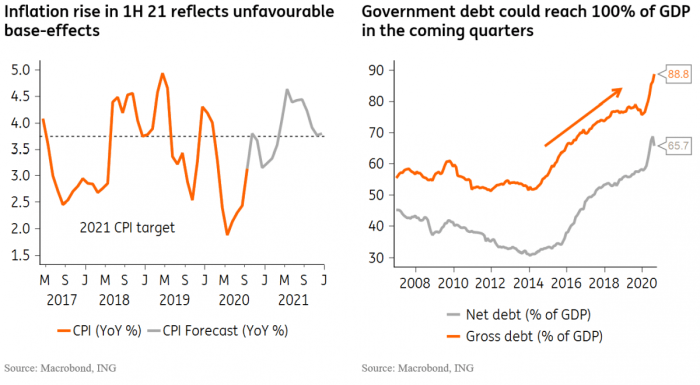
Brazil’s inflation undershooting forecasts presents a complex picture for the future. While this could ease pressure on the central bank to raise interest rates, it’s not a guaranteed sign of sustained price stability. The interplay of global economic trends, domestic policy choices, and consumer behavior will shape the inflation trajectory and, consequently, the country’s economic growth. Understanding potential scenarios is crucial for informed investment and policy decisions.The central bank’s response to this unexpected development will be a key determinant of the inflation outlook.
If the undershooting proves temporary, the bank may maintain a cautious approach. However, if the trend persists, the bank might consider adjusting its policy stance, potentially lowering interest rates further, which could stimulate economic growth but also risk reigniting inflation.
Potential Inflation Trajectories
Several scenarios for future inflation in Brazil can be envisioned, depending on global economic conditions and domestic policy decisions. These projections are not definitive predictions but rather illustrative examples.
- A sustained period of low inflation could be a positive development. Lower inflation rates, coupled with consistent economic growth, would create a favorable environment for investment and consumption. This would be similar to the period in 2019-2021, when inflation in Brazil was relatively low and stable, supporting economic expansion.
- A medium-level inflation trajectory could emerge if global economic headwinds persist, or if domestic policies don’t adequately address potential inflationary pressures. This scenario would mirror periods of moderate inflation seen in many developed economies, where price increases are manageable but still warrant attention.
- A higher inflation trajectory, although less likely given the current data, could materialize if global commodity prices surge or if domestic demand significantly outpaces supply. This outcome would resemble recent inflationary pressures in other emerging markets, where price volatility is higher.
Economic Growth Outlook
The Brazilian economic growth outlook is intrinsically linked to the inflation trajectory. Lower inflation, if sustained, could encourage increased consumer spending and business investment, thus fostering economic growth. However, if inflation remains low and the central bank lowers rates too aggressively, it could risk future inflationary pressures and weaken the currency. The success of the Brazilian economy hinges on the delicate balance between managing inflation and promoting economic activity.
Possible Future Inflation Scenarios
| Scenario | Inflation Rate (Annualized) | Economic Implications | Policy Response (Hypothetical) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low Inflation | 2-3% | Increased consumer confidence, higher investment, sustained economic growth. | Potential for further rate cuts. |
| Medium Inflation | 3-4% | Moderate economic growth, stable consumer confidence, potential for higher interest rates. | Maintain current rate or slightly adjust. |
| High Inflation | 4-5% or higher | Reduced consumer confidence, decreased investment, slower economic growth. | Higher interest rates to curb demand. |
Illustrative Visuals

Inflation in Brazil has consistently been a significant concern for policymakers and market participants. Understanding the recent undershooting of forecasts, its correlation with interest rate adjustments, and its impact on investor sentiment is crucial for gauging the overall economic health of the nation. Visual representations can greatly aid in comprehending these complex dynamics.
Inflation Trend in Brazil
The trend of inflation in Brazil can be effectively illustrated with a line graph. The horizontal axis would represent time, likely in months or quarters. The vertical axis would show the inflation rate, measured as a percentage change from the previous period. A clear downward trend line representing the undershooting of forecasts would be evident, with the actual inflation rate consistently falling below the projected rates.
A shaded area or a dotted line could represent the range of forecasted inflation figures. This visual representation would clearly highlight the degree to which actual inflation has fallen short of predicted values.
Central Bank Interest Rate Adjustments and Inflation
A scatter plot is ideal for demonstrating the correlation between the central bank’s interest rate adjustments and the inflation rate. The horizontal axis would display the central bank’s policy interest rate (e.g., Selic rate). The vertical axis would depict the inflation rate. Each data point would represent a specific period, showing the interest rate and the corresponding inflation rate.
A general downward trend would be apparent, indicating that higher interest rates tend to be associated with lower inflation rates. A notable exception would be the period where the inflation undershot, showing a period of reduced interest rate increases or even slight decreases. This scatter plot will visually demonstrate the relationship between the two key variables.
Impact of Undershooting on Investor Confidence
A bar chart is suitable for depicting the impact of the undershooting on investor confidence. The horizontal axis would represent different investor segments (e.g., domestic, foreign, institutional, retail). The vertical axis would display investor confidence levels, measured on a scale from 0 to 100. Bars for each investor segment would show the confidence levels before and after the inflation undershot.
The difference in confidence levels before and after the undershooting will visually highlight the impact of the unexpected inflation drop on the confidence of different investor groups. A notable shift towards higher confidence levels would suggest a positive reaction to the lower inflation. Conversely, a reduction in confidence might indicate uncertainty or concern regarding the stability of the trend.
Outcome Summary
Brazil’s inflation undershooting the forecast, ahead of the crucial interest rate decision, presents a complex picture for the country’s economy. The unexpected outcome could signal a shift in the current economic trajectory, potentially impacting both monetary policy and investor sentiment. While the short-term implications are significant, the long-term effects remain to be seen, and the potential ramifications for the wider Latin American economy shouldn’t be ignored.

