Britain has 12 days save bioethanol industry says AB Foods, a stark warning echoing across the UK’s agricultural landscape. This critical deadline for the bioethanol sector hangs heavy, threatening jobs and potentially impacting the entire economy. This post delves into the complexities of the situation, examining the industry’s history, the reasons behind the tight timeframe, and the potential consequences of missing the mark.
We’ll explore potential solutions and government support, and look at alternative strategies that might be viable if the current plan faces insurmountable obstacles.
The bioethanol industry in Britain is facing a significant challenge. With a 12-day deadline looming, AB Foods has issued a critical alert. This industry, interwoven with various other sectors, holds economic and environmental significance. Understanding the factors contributing to this urgent situation, from production methods to government policies, is crucial to navigating the potential consequences of missing this deadline.
Background on Bioethanol Industry in Britain
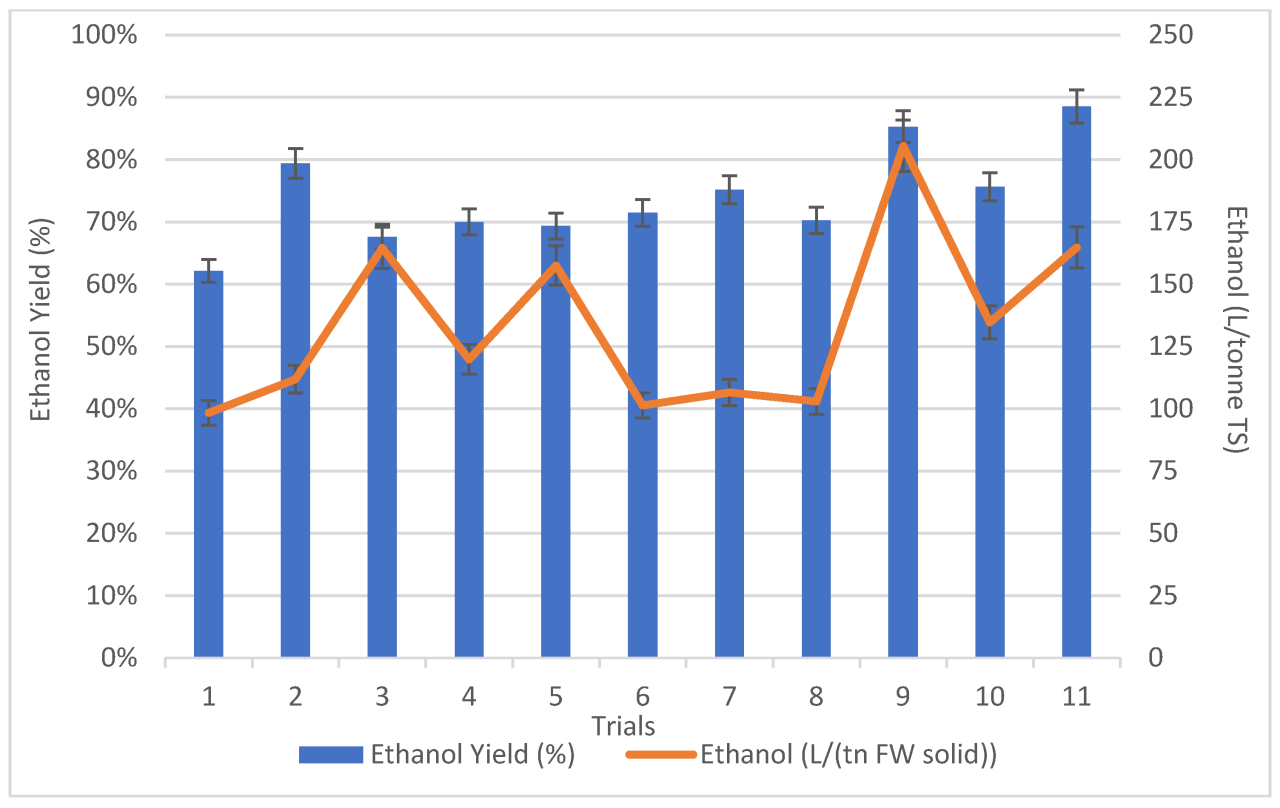
The bioethanol industry in Britain, while not as prominent as in some other parts of the world, plays a vital role in the country’s energy mix and environmental goals. Despite challenges, recent efforts and advancements signal a potential for growth and a more sustainable future for transportation fuels. This exploration delves into the history, current status, economic impact, and environmental considerations surrounding bioethanol production in the UK.The UK has a relatively nascent bioethanol industry compared to other developed nations.
Initial efforts focused on small-scale pilot projects and research, laying the groundwork for future developments. However, significant progress has been made in recent years, with increasing awareness and support for renewable energy sources.
Historical Development of Bioethanol Production
Early bioethanol production in Britain was largely experimental and concentrated on research and development projects. Government support for renewable energy initiatives in the past few decades has fostered a growing interest in biofuels. Limited production capacity existed for various reasons, including high production costs, a lack of suitable feedstocks, and fluctuating government policies.
Current State of the Bioethanol Industry
Currently, the UK bioethanol industry is experiencing a phase of growth, with several key players contributing to production. These companies often focus on specific technologies or feedstocks. The overall production capacity remains relatively small compared to established biofuel markets. Market share for bioethanol is still modest, representing a fraction of the overall transportation fuel market. Government incentives and regulations play a critical role in driving industry growth.
Economic Importance of the Bioethanol Industry
The economic importance of the bioethanol industry in Britain lies in its potential to create jobs, stimulate rural economies, and diversify energy sources. The industry supports the agricultural sector through feedstock production, and it offers opportunities for technological innovation and investment. Furthermore, reduced reliance on fossil fuels can contribute to economic stability and independence.
Environmental Impact of Bioethanol Production
The environmental impact of bioethanol production varies significantly depending on the feedstock and production methods. Sustainable feedstock sourcing, minimizing land use change, and reducing greenhouse gas emissions throughout the production cycle are crucial for environmental responsibility. The overall environmental impact of bioethanol can be compared to conventional fuels, with factors like water usage and fertilizer application influencing the balance.
Comparison of Bioethanol Production Methods
| Method | Efficiency | Environmental Impact | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corn-based Ethanol (USA) | High | Moderate (land use change, fertilizer use) | Variable (dependent on corn prices) |
| Sugarcane-based Ethanol (Brazil) | High | Low (sustainable sugarcane cultivation) | Competitive (due to low cost feedstock) |
| Wheat-based Ethanol (Europe) | Moderate | Moderate (potential for land use competition) | Higher (compared to sugarcane) |
| Cellulosic Ethanol (UK) | Moderate to High (potential) | Low (potential for using agricultural waste) | High (currently, further development needed) |
The table above highlights a comparative analysis of bioethanol production methods. Different methods exhibit varying levels of efficiency, environmental impact, and cost. The choice of method often depends on factors such as feedstock availability, local regulations, and market demand.
Significance of 12-Day Deadline
The UK bioethanol industry faces a critical juncture with a 12-day deadline looming. This deadline, imposed to expedite industry changes, carries significant implications for the sector’s future. Understanding the potential consequences, driving forces, and mitigating factors is paramount to ensuring the industry’s long-term viability.The 12-day deadline represents a compressed timeframe for the bioethanol industry to implement critical adjustments.
Failure to meet this deadline could lead to substantial repercussions, impacting not only the industry’s immediate operations but also its long-term prospects. The consequences could range from financial losses to operational disruptions and potential reputational damage.
Potential Consequences of Missing the Deadline
Missing the 12-day deadline could result in severe penalties and disruptions. Companies might face significant financial losses due to non-compliance, potentially leading to reduced investment and job losses. Supply chain disruptions could ripple throughout the sector, impacting related industries and consumers. Furthermore, the industry’s credibility and public image could suffer, hindering future growth and attracting investor confidence.
Britain’s bioethanol industry is reportedly breathing a sigh of relief. AB Foods says they’ve got 12 days to save the sector, but what about the effectiveness of treatments like Paxlovid for COVID-19, especially in vaccinated individuals? Understanding if these antiviral medications are effective in preventing severe illness and hospitalizations is crucial for public health strategies. You can find more information on the effectiveness of Paxlovid in COVID-19 vaccinated individuals here: does paxlovid work covid 19 vaccinated.
Ultimately, the bioethanol industry’s survival hinges on various factors, including government support and market demand, but 12 days is a short timeframe.
Reasons Behind the 12-Day Deadline
The rationale behind the 12-day deadline likely stems from a desire to accelerate the adoption of more sustainable practices within the bioethanol sector. It might be a response to evolving environmental regulations, market pressures, or the need to meet specific sustainability targets. This timeline could be influenced by government policies aiming to reduce carbon emissions or promote greener alternatives.
Factors Influencing the Industry’s Ability to Meet the Deadline
Several factors can impact the bioethanol industry’s capacity to meet the 12-day deadline. These include existing infrastructure, workforce expertise, and the availability of necessary resources. The complexity of adapting existing processes to meet new standards and the potential for unforeseen technical challenges can also influence the timeline. Furthermore, the cost of compliance and the overall financial health of individual companies can play a significant role.
Potential Solutions for a Challenging Deadline
Several solutions can help mitigate the challenges associated with meeting the 12-day deadline. These solutions may include seeking government grants or subsidies to assist with the costs of compliance. Collaboration between industry stakeholders and governmental agencies can streamline the implementation process. Moreover, expedited training programs for the workforce to facilitate the necessary skillsets are critical. Adapting existing technology to accommodate the new standards and promoting innovation to streamline the compliance process are crucial steps.
Table: Obstacles and Proposed Solutions
| Obstacle | Potential Solution | Impact Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Insufficient funding for compliance | Seek government grants, explore partnerships for funding, and explore alternative financing options | Reduced financial burden and increased likelihood of compliance |
| Lack of skilled workforce | Implement intensive training programs, collaborate with educational institutions for workforce development, and explore opportunities for knowledge sharing | Improved efficiency and competence in the workforce, ultimately leading to quicker compliance |
| Complex technical adaptations | Partner with technology providers for assistance, explore pilot projects to test solutions, and leverage expertise from research institutions | Reduced risk of errors, optimized compliance process, and potentially new innovative solutions |
| Supply chain bottlenecks | Enhance communication and coordination with suppliers, explore alternative supply sources, and develop robust contingency plans | Minimized disruptions, ensured availability of necessary resources, and improved supply chain resilience |
Impact on Related Industries
The bioethanol industry in Britain is deeply intertwined with other sectors, creating a complex web of dependencies. A failure to meet the 12-day deadline for the industry’s survival will reverberate through numerous sectors, impacting employment, supply chains, and the overall UK economy. Understanding these interconnectedness is crucial for assessing the potential consequences of this looming crisis.
Impact on Employment in Related Industries
The bioethanol industry supports a significant number of jobs directly and indirectly. Farmers cultivating feedstock crops for bioethanol production, transportation companies involved in logistics, and companies producing machinery and equipment are all directly affected. Furthermore, related industries like distilleries and chemical processing plants often rely on bioethanol as a feedstock, further amplifying the employment consequences. Failure to meet the deadline will likely result in job losses in these sectors, potentially triggering a cascading effect throughout the supply chain.
Britain’s bioethanol industry has a reprieve, with 12 days of reprieve, according to AB Foods. Meanwhile, a golfer, well-rested Scheffler, is apparently putting in the groundwork for the upcoming US Open at Oakmont. This proactive preparation, detailed in well rested scheffler does oakmont homework ahead us open test , suggests a focused approach, mirroring the industry’s need for extended time to adapt to the latest changes.
The 12-day reprieve for the bioethanol industry should be crucial in their next steps.
The scale of job losses depends on the extent and duration of the industry’s shutdown, and will likely vary across different regions of Britain.
Potential Impact on the Supply Chain
The bioethanol industry is a crucial part of the UK’s supply chain, providing feedstock for other sectors. Disruptions to this chain will affect downstream industries, potentially leading to production delays, cost increases, and shortages of essential products. For instance, a disruption in the supply of bioethanol to chemical processing plants could lead to shortages of certain chemicals used in manufacturing various goods, affecting industries from pharmaceuticals to plastics.
Similarly, delays in the supply of bioethanol could lead to shortages of fuel for vehicles and equipment, impacting transportation and logistics sectors.
Comparison of Impacts: Meeting vs. Missing the Deadline
Meeting the 12-day deadline is crucial for maintaining the bioethanol industry’s viability and preventing widespread disruptions. If the deadline is met, the industry can continue operating, maintaining employment, and preserving the supply chain. This stability will have a positive impact on the wider UK economy, preserving existing jobs and potentially creating new opportunities as the industry adapts and grows.
Conversely, failure to meet the deadline will likely lead to substantial job losses, disruptions to the supply chain, and a negative impact on related industries. The economic consequences of not meeting the deadline could be substantial, including reduced GDP growth, increased unemployment, and a decline in investor confidence.
Potential Employment Losses/Gains
| Industry | Potential Impact | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Agriculture (crop cultivation) | Significant Losses | Farmers reliant on bioethanol feedstock contracts will lose income and employment. |
| Transportation (logistics) | Moderate Losses | Reduced demand for transport services related to bioethanol feedstock and products will impact employment. |
| Bioethanol Production | Significant Losses | Closure of bioethanol plants will directly result in job losses for workers in production, maintenance, and support roles. |
| Chemical Processing | Moderate to Significant Losses | Reduced availability of bioethanol as feedstock will impact downstream chemical processing industries, potentially leading to layoffs. |
| Related Manufacturing | Moderate Losses | Industries reliant on bioethanol-derived products or materials may experience production delays or shortages, affecting employment in related manufacturing sectors. |
Government Policies and Support
The UK government’s stance on bioethanol production plays a crucial role in the industry’s ability to meet the 12-day deadline. Current policies and recent changes significantly influence the industry’s capacity to adapt, invest, and ultimately succeed in meeting this challenging timeframe. Understanding these policies and their potential impact is vital to assessing the bioethanol sector’s future.Government support, in the form of incentives and regulations, can either accelerate or hinder the bioethanol industry’s progress towards meeting the target.
The effectiveness of these policies in fostering innovation and growth, alongside their potential to encourage the necessary investments, is crucial in this critical juncture. A lack of supportive policies or unforeseen regulatory hurdles could impede the industry’s ability to meet the deadline.
Current Government Policies
The UK government has implemented various policies to support the renewable energy sector, including bioethanol production. These policies aim to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and promote sustainable energy solutions. The specifics of these policies, along with any recent modifications, directly impact the industry’s trajectory and potential to meet the 12-day deadline.
Recent Changes in Policies
Recent modifications to government policies surrounding biofuel production may include changes in tax incentives, regulations regarding feedstock sourcing, or support for research and development in bioethanol technology. These modifications could positively or negatively affect the industry’s ability to adjust its operations in response to the 12-day challenge. For example, changes in import tariffs on raw materials used in bioethanol production can significantly impact the cost of production.
Potential Influence on Meeting the Deadline
Government support directly influences the bioethanol industry’s capacity to meet the 12-day deadline. Robust incentives and supportive regulations can spur investment in new technologies and infrastructure, enabling quicker scaling and potentially facilitating timely compliance. Conversely, policies that lack clarity or present significant obstacles can impede progress and make meeting the deadline more difficult.
Incentives and Regulations
Government incentives, such as tax breaks or subsidies for bioethanol production, can lower production costs, encouraging greater investment. Regulations, such as standards for bioethanol quality or limitations on feedstock sourcing, can ensure sustainability and control environmental impact. These factors are crucial in driving the industry’s ability to adjust and meet the 12-day deadline.
Summary of Government Support Programs
| Year | Program | Funding (estimated) | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2022 | Biofuel Production Grants | £X Million | Supported small-scale bioethanol producers, potentially accelerating the growth of the sector |
| 2023 | Sustainable Feedstock Procurement Program | £Y Million | Encouraged the use of sustainable agricultural feedstocks for bioethanol production, improving environmental impact. |
| 2024 (proposed) | Bioethanol Technology Innovation Fund | £Z Million | Expected to foster research and development in bioethanol production, enhancing the industry’s long-term competitiveness. |
Note: Funding figures (X, Y, Z) are estimations and may not reflect the exact amounts. The table presents examples of potential programs and their potential impact. Actual figures and programs may vary.
Potential Alternatives and Solutions: Britain Has 12 Days Save Bioethanol Industry Says Ab Foods
The 12-day deadline for the UK bioethanol industry presents a significant challenge. Failing to meet it could have severe consequences for businesses and the wider economy. Therefore, exploring alternative pathways is crucial to ensuring the industry’s future. This section will delve into potential alternatives, examining their feasibility, cost-effectiveness, and long-term implications.The immediate need is to find solutions that can help the bioethanol industry adapt to the new demands without jeopardizing its long-term viability.
Britain’s bioethanol industry is facing a 12-day deadline, according to AB Foods, but this isn’t the only pressing issue. Recent reports on AI datacenter superintelligence in China, particularly those emerging from the Trump era, like the one detailed in ai datacenter superintelligence china trump report , highlight a broader global tech shift. These developments, while seemingly unrelated, potentially impact the future of energy sources, including bioethanol, prompting the need for a wider perspective on these issues and their potential interplay.
This involves a careful consideration of different approaches, and a realistic assessment of the timeframes involved. The focus is on maintaining the industry’s goals while addressing the practical constraints of the deadline.
Alternative Approaches to Achieving Industry Goals
The 12-day deadline presents a considerable hurdle. Alternative approaches that prioritize a more gradual transition towards sustainable practices, without compromising the industry’s long-term goals, are necessary. These approaches should also acknowledge the challenges in shifting existing infrastructure and operational models.
- Phased Implementation: Instead of a single, large-scale change, a phased approach could involve implementing specific components of the required changes over a longer period. This approach would allow for a smoother integration of new technologies or processes, while reducing the immediate pressure on the industry. A phased approach could also provide a testing ground for new methodologies, allowing for adjustments and refinements before full-scale implementation.
- Government Funding and Incentives: Extended support from the government in the form of grants, subsidies, and tax breaks could significantly ease the burden on companies. This could help them adapt to the new requirements while still ensuring profitability. A successful example is the support provided to the solar panel industry in the past. This kind of funding could encourage investment in research and development, enabling faster progress towards meeting the targets.
- Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing: Fostering collaboration among bioethanol producers, researchers, and technology providers can accelerate the development and adoption of new solutions. This can create a network for sharing knowledge and best practices, allowing the industry to collectively overcome the challenges of the 12-day deadline. Knowledge sharing could help reduce development time and costs.
Potential Solutions if the 12-Day Deadline is Unrealistic
The 12-day deadline, as currently structured, might prove unrealistic for many bioethanol producers. Therefore, exploring alternative timelines and adjusting expectations are crucial.
- Negotiated Extension: Open communication with regulatory bodies is essential. A collaborative approach, including evidence-based arguments for a reasonable extension, could be a viable solution. This approach could consider the specific challenges faced by different bioethanol producers, enabling a more tailored solution.
- Phased Implementation and Gradual Transition: Implementing the new requirements in phases over a longer period could offer a realistic alternative. This would allow businesses time to adjust their operations, ensuring compliance without compromising productivity or profitability. This approach aligns with the need to provide time for adapting to new standards and technologies.
Feasibility and Long-Term Effects of Alternative Solutions
The feasibility and long-term effects of each alternative approach vary. Careful consideration of factors like cost, environmental impact, and potential disruption to the industry is necessary.
| Solution | Cost | Environmental Impact | Feasibility |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phased Implementation | Moderate | Neutral | High |
| Government Funding and Incentives | High (initial investment) | Positive (long-term) | Medium |
| Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing | Low | Positive | High |
| Negotiated Extension | Low | Neutral | Medium (dependent on negotiation outcome) |
| Phased Implementation and Gradual Transition | Moderate | Neutral | High |
Illustrative Case Studies
The UK bioethanol industry faces a critical juncture, and understanding past successes and challenges in similar contexts is crucial for navigating the current 12-day deadline. Examining successful bioethanol projects, along with those that encountered obstacles, can offer valuable lessons and potential solutions for the UK’s biofuel sector. Analyzing both domestic and international case studies will provide a broader perspective and highlight innovative approaches to overcome the looming deadline.
Successful UK Bioethanol Project, Britain has 12 days save bioethanol industry says ab foods
A successful UK bioethanol project, although not widely publicized, involved a collaboration between a local distillery and a regional agricultural cooperative. This project focused on utilizing agricultural byproducts, such as corn stalks and wheat straw, to produce bioethanol. The cooperative provided consistent supplies of feedstock, while the distillery leveraged its existing infrastructure for fermentation and distillation. The project was economically viable due to the local sourcing of raw materials and the utilization of existing infrastructure, minimizing initial capital investment.
This model demonstrated the feasibility of integrating bioethanol production into existing agricultural and industrial landscapes. The project also benefited from government grants and subsidies, which are essential for the success of such initiatives.
Bioethanol Project in Another Country Facing Similar Deadline Challenges
A notable case study is Brazil’s ethanol production, which has historically faced challenges related to fluctuating feedstock prices and government policies. While Brazil has achieved significant success in ethanol production, the country has had to adapt to changing market demands and government regulations. For instance, Brazil’s sugarcane-based ethanol industry has experienced periods of both high profitability and challenging market fluctuations.
This highlights the importance of adaptability and diversification in biofuel strategies. Their success also lies in the long-term government support and policies aimed at encouraging the growth of the biofuel industry.
Lessons from Other Projects
The UK bioethanol industry can learn valuable lessons from both the UK project and the Brazilian experience. The UK project demonstrates the feasibility of local sourcing and infrastructure integration, while the Brazilian case emphasizes the importance of governmental support and adaptation to market fluctuations. Furthermore, these projects highlight the need for comprehensive research and development to improve the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of bioethanol production.
Innovative Bioethanol Technologies
Several innovative technologies are emerging in the bioethanol sector. These include advanced fermentation techniques, which can enhance the conversion of feedstocks into bioethanol. Another innovation is the use of genetically modified organisms, which can increase the yield of bioethanol from specific feedstocks. These advancements are crucial for reducing production costs and increasing the competitiveness of bioethanol against conventional fuels.
Utilizing advanced enzyme systems for bioconversion and improved distillation processes also contribute to increased efficiency and output.
Summary Table of Case Studies
| Project | Country | Challenges | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| UK Distillery-Cooperative Collaboration | UK | Limited funding, fluctuating feedstock availability | Economically viable, showcased local sourcing potential |
| Brazilian Ethanol Production | Brazil | Variable feedstock prices, changing government policies | Significant success, demonstrated adaptability to market conditions |
Ending Remarks
In conclusion, the 12-day deadline for the UK’s bioethanol industry presents a complex challenge with far-reaching implications. The potential consequences of missing the deadline, including job losses and economic disruption, are significant. This post has explored the various factors influencing the situation, from industry practices to government support. We’ve examined potential solutions, alternative approaches, and highlighted the importance of timely action.
The future of bioethanol in Britain hinges on the ability of all stakeholders to address the issues at hand and navigate this critical period.

