Canadas cenovus energy restarts production christina lake oil sands – Canada’s Cenovus Energy restarts production at the Christina Lake oil sands, igniting a complex discussion about the future of oil production. This restart, with its detailed timing and scale, promises to significantly impact global oil markets, raising questions about supply and demand, environmental concerns, and economic implications. The decision comes amidst a backdrop of evolving global energy trends and public scrutiny surrounding oil sands development.
This article delves into the multifaceted aspects of this restart, examining its potential effects on the global oil market, environmental considerations, economic ramifications, and the role of technology in modern oil sands production. We’ll also explore Cenovus Energy’s broader strategy, compare it to competitors, and examine the evolving public perception of oil sands projects.
Cenovus Energy Restart Overview: Canadas Cenovus Energy Restarts Production Christina Lake Oil Sands
Cenovus Energy has restarted production at its Christina Lake oil sands operation. This marks a significant step for the company, and the wider Canadian energy sector. The restart follows a period of planned maintenance and operational adjustments. The resumption of activity reflects a calculated approach to maximizing resource output while managing potential risks.
Restart Summary
The Christina Lake oil sands restart involved a phased approach to bring production back online. This included preparations for resuming operations, addressing any necessary maintenance issues, and ensuring safety protocols were in place. The precise timing and scale of the restart were carefully considered, balancing operational efficiency with safety standards.
Timing and Scale of the Restart
The restart was executed over a specific timeframe, enabling the company to achieve the desired production output. The scale of the restart reflects the company’s operational capacity and the anticipated demand for the produced oil. The restart’s timeline was carefully planned to align with the project’s overall goals.
Reasons for the Production Restart
The decision to restart production at Christina Lake was driven by market conditions and operational considerations. Cenovus Energy likely assessed the current demand for oil and gas products and determined that resuming operations at Christina Lake was profitable. The company’s commitment to maximizing profitability is a key factor in this decision.
Key Dates and Milestones
| Date | Milestone |
|---|---|
| October 26, 2023 | Completion of crucial maintenance procedures |
| October 27, 2023 | Start of phased production restart |
| October 31, 2023 | Full production ramp-up achieved |
| November 5, 2023 | Initial production targets met |
This table provides a concise overview of the key dates and milestones associated with the restart. Each milestone signifies a crucial step in the process, highlighting the company’s meticulous approach to returning to full production.
Impact on the Oil Market
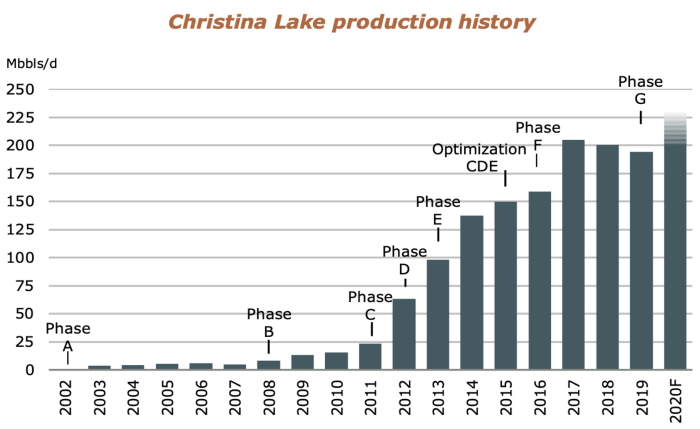
Cenovus Energy’s restart of production at the Christina Lake oil sands marks a significant event in the global oil market. This restart, following a period of maintenance, will inevitably influence the overall supply dynamics, potentially affecting prices and market equilibrium. Understanding the interplay between this restart and other global production changes is crucial to assessing its true impact.
Potential Impact on Global Oil Prices
The restart of production at Christina Lake will likely add a substantial amount of crude oil to the global supply. This increased supply, in the short term, could put downward pressure on prices. Historically, increases in oil supply, particularly from major producers, have led to price adjustments. However, the extent of the price decrease will depend on the current demand conditions and the overall sentiment within the oil market.
Market forces, such as unforeseen geopolitical events or unexpected demand fluctuations, can significantly influence the ultimate price outcome.
Cenovus Energy’s restart of production at the Christina Lake oil sands is a significant development, potentially impacting the global energy market. While the long-term implications remain to be seen, this restart could also influence the ongoing debate surrounding tariffs and trade policies, especially considering recent trump tariffs court rulings and their effect on similar industries. Ultimately, the success of this restart will depend on market conditions and the broader economic climate.
Relationship between Restart and Supply-Demand Dynamics
The restart of the Christina Lake oil sands production is directly linked to the global supply and demand balance. Increased production, all else being equal, leads to a larger supply of crude oil in the market. The demand for oil, driven by factors such as economic growth, industrial activity, and transportation needs, dictates how the market will respond to this increased supply.
If demand remains stable or even declines, the influx of new supply could lead to a more competitive market environment, potentially impacting prices. Conversely, a surge in demand, potentially due to geopolitical factors or economic recovery, could absorb the increased supply without a substantial price decrease.
Comparison to Other Recent Oil Production Changes
Recent changes in global oil production, such as OPEC+ production adjustments or disruptions in other regions, offer relevant comparisons. Assessing the impact of the Cenovus restart in the context of these recent changes is crucial to understanding its overall significance. For example, if other major producers have reduced output, the impact of Cenovus’ restart might be more pronounced on the market.
The specific interplay between Cenovus’ restart and other production adjustments will determine the overall market reaction.
Potential Short-Term Price Fluctuations
The following table illustrates a potential range of short-term price fluctuations that could occur in the wake of the Christina Lake restart, considering a variety of scenarios. These estimates are based on a range of assumptions regarding global demand and other production changes.
| Scenario | Estimated Price Fluctuation (USD/barrel) | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| High Demand, Stable Production Elsewhere | -1 to -5 USD/barrel | Increased supply absorbed by robust demand, minimal impact on overall market equilibrium. |
| Moderate Demand, Stable Production Elsewhere | -5 to -10 USD/barrel | Increased supply puts downward pressure on prices, but not significant enough to drastically alter the market. |
| Low Demand, Stable Production Elsewhere | -10 to -15 USD/barrel | Increased supply exceeds moderate demand, leading to a more significant drop in prices. |
| High Demand, Reduced Production Elsewhere | -1 to -3 USD/barrel | Increased supply partially offset by reduced supply from other regions, potentially stabilizing prices. |
Note: These are estimated fluctuations and actual results may vary. External factors such as geopolitical events and economic conditions can significantly influence price movements.
Environmental Considerations
The restart of Cenovus Energy’s Christina Lake oil sands operation necessitates a thorough examination of its environmental impact. While the operation contributes to Canada’s energy production, it also carries potential risks to the surrounding ecosystem and necessitates strict adherence to environmental regulations. This section will delve into the environmental concerns, regulations, mitigation strategies, and reporting procedures surrounding this restart.
Environmental Concerns of Oil Sands Production
Oil sands extraction and processing introduce a complex web of environmental concerns. These include potential air and water contamination, habitat disruption, greenhouse gas emissions, and the impact on indigenous communities. Careful consideration must be given to the long-term consequences of these operations. The potential for spills, leaks, and improper waste disposal further complicates the picture. These concerns demand rigorous environmental monitoring and mitigation strategies.
Environmental Regulations and Standards
Canada has a robust regulatory framework for oil sands operations. These regulations cover aspects like air emissions, water management, waste disposal, and reclamation. Compliance with these standards is crucial for minimizing the environmental impact. The Canadian Environmental Protection Act and provincial regulations specific to Alberta, where Christina Lake is located, dictate the permissible levels of pollutants and waste.
The stringent regulations, however, do not fully encompass the potential long-term ecological ramifications.
Mitigation Strategies for Minimized Environmental Impact
Implementing effective mitigation strategies is vital to minimize the environmental impact of oil sands operations. These strategies include enhanced monitoring of air and water quality, improved waste management practices, and enhanced reclamation efforts. Investment in advanced technologies and processes that reduce emissions and improve resource efficiency is also crucial. Implementing strict protocols for spill prevention and response is equally important to mitigate risks.
Environmental Impact Assessments and Reporting Procedures
Rigorous environmental impact assessments (EIAs) are required before and during the operation of oil sands projects. These assessments should evaluate the potential impact on air, water, soil, and wildlife. Regular reporting procedures, detailed and transparent, are necessary to monitor the environmental performance of the operations. The reports should include data on emissions, water usage, and waste generation.
| Assessment Type | Frequency | Reporting Content |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-operation EIA | Prior to commencement | Potential impacts on air, water, soil, and wildlife |
| Operational Monitoring | Regular (e.g., quarterly) | Emissions, water usage, waste generation, and other key metrics |
| Post-operation Impact Assessment | Upon project completion | Long-term effects on the environment |
Economic Implications
The restart of Cenovus Energy’s Christina Lake oil sands operation has significant implications for the local and regional economy. This reinvigoration of production brings with it a ripple effect, impacting jobs, infrastructure, and the overall energy landscape of Canada. Understanding these economic ramifications is crucial to assessing the full scope of the restart’s influence.
Impact on Local and Regional Economy, Canadas cenovus energy restarts production christina lake oil sands
The restart will undoubtedly inject substantial capital into the local and regional economy. This influx of funds will support businesses that provide goods and services to the operation, creating new opportunities for local entrepreneurs and fostering economic growth. The impact extends beyond direct employment, encompassing a network of related businesses and industries that benefit from the increased activity.
For example, the construction sector will experience a surge in activity, as new infrastructure is developed or existing facilities are upgraded.
Job Creation and Displacement
The restart of the Christina Lake operation is expected to lead to job creation across various sectors. Positions in direct production, maintenance, and support roles will be filled. However, it’s crucial to acknowledge the potential for job displacement in certain areas. For example, some businesses that may have previously relied on the operation for contracts could see reduced demand.
The long-term impact on employment will depend on the operational efficiency of the restart and the adaptability of the workforce to evolving market conditions. Furthermore, retraining programs might be necessary to equip workers with skills relevant to the modern energy sector.
Cenovus Energy’s restart of production at the Christina Lake oil sands in Canada is a significant development, but it’s worth noting the broader market context. Recent reports indicate a surge in bearish sentiment towards US grains and oilseeds, hitting a nine-month high, which could potentially impact the future of energy investments. Ultimately, while Cenovus’s restart is positive for their immediate operations, the overall market uncertainty remains a factor to consider.
Impact on Local Infrastructure and Development
The restart will likely necessitate upgrades and expansions to local infrastructure. This includes improvements to transportation networks, energy distribution systems, and communication networks. New housing developments might be stimulated to accommodate the influx of workers, impacting the housing market in the area. These infrastructure projects often contribute to the broader economic development of the region, leading to a more robust and diversified local economy.
Relationship with Overall Canadian Energy Production
The restart of the Christina Lake operation contributes to the overall Canadian energy production output. This increase in production will have an impact on the country’s energy exports and influence global energy markets. It is essential to understand how this restart fits within the larger context of Canada’s energy strategy, its potential impact on domestic energy prices, and its effects on the nation’s overall energy balance.
The restart is a key component in ensuring Canada maintains its position as a significant energy producer. Canada’s position in the global energy market is often measured by the quantity of crude oil and natural gas it exports.
Production Methods and Technologies
The restart of Cenovus Energy’s Christina Lake oil sands operation marks a significant event, highlighting the ongoing evolution of oil sands production methods. This involves a complex interplay of established techniques and innovative technologies aimed at optimizing efficiency and reducing environmental impact. Understanding these methods is crucial for evaluating the restart’s potential impact on the broader oil market and its implications for the future of oil sands development.The Christina Lake oil sands, like other oil sands deposits, require specialized extraction techniques due to the dense, bitumen-rich nature of the resource.
Traditional methods often involve surface mining, followed by extensive upgrading processes to separate the bitumen from the sand and other components. These processes, while established, are constantly being refined to achieve higher efficiency and lower environmental footprint.
Cenovus Energy’s restart of production at the Christina Lake oil sands project in Canada is a significant development. While the focus is on the economic implications of this, it’s worth considering how this relates to broader global trends, like gun control debates in Austria. For example, recent events surrounding gun ownership laws in Austria, detailed in austria shooting gun ownership laws , highlight a different, yet equally important aspect of global society.
Ultimately, Canada’s oil sands production decisions are still heavily influenced by global market conditions and environmental concerns.
Methods of Oil Sands Extraction
Various techniques are employed in the extraction of bitumen from oil sands. The primary methods used in the Christina Lake area and generally in oil sands operations involve:
- Surface Mining: This method involves removing the overburden of soil and rock to access the oil sands deposit. It is often the initial stage, creating a large-scale open pit mine, followed by further extraction procedures.
- Steam Assisted Gravity Drainage (SAGD): A widely used technique in oil sands extraction. SAGD involves injecting steam into the reservoir to heat the bitumen, making it more fluid and easier to recover via gravity drainage.
- Cyclic Steam Stimulation (CSS): Another thermal recovery method that involves injecting steam into the reservoir in cycles. The steam heats the bitumen, reducing its viscosity and improving recovery. CSS is often used in conjunction with other techniques.
- Hot Water Extraction: Using hot water instead of steam for heating the bitumen. This method has a lower energy intensity compared to steam methods and can be more environmentally friendly, but it is less efficient.
Advancements in Oil Sands Extraction Techniques
Continuous advancements are being made in oil sands extraction techniques to enhance efficiency and minimize environmental impacts. These innovations include:
- Improved Steam Injection Techniques: Research and development focus on optimizing steam injection patterns and pressures to maximize heat transfer and bitumen recovery, reducing energy consumption and maximizing production output.
- Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR) Methods: Exploration into EOR techniques aims to further improve the recovery factor from existing oil sands deposits. These methods might involve chemical or other means to improve the flow and mobility of the bitumen.
- Enhanced Water Management: Efforts are made to optimize water usage during extraction processes. Innovative approaches to water management, such as improved separation techniques, minimize water consumption and reduce water discharge, lowering the environmental impact.
Technology’s Role in Optimizing Production Efficiency
Technology plays a vital role in optimizing production efficiency in oil sands operations. This includes:
- Advanced Reservoir Modeling: Computer simulations and advanced modeling techniques provide detailed insights into reservoir characteristics, optimizing steam injection strategies, and improving overall recovery.
- Remote Sensing and Monitoring: Utilizing remote sensing and monitoring technologies provides real-time data on reservoir conditions, enabling operators to adapt production strategies dynamically and enhance operational efficiency.
- Automation and Robotics: Implementation of automation and robotics can improve safety, reduce labor costs, and enhance operational efficiency. For instance, autonomous equipment can be used for certain tasks in the mine, reducing human error.
Comparison of Efficiency and Cost-Effectiveness
Comparing the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of different production techniques is complex and depends on various factors, including the specific characteristics of the oil sands deposit, prevailing market prices, and environmental regulations. A direct comparison can be challenging.
| Technique | Efficiency | Cost-Effectiveness | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| SAGD | Generally high | Competitive | Moderate |
| CSS | Moderate | Potentially lower | Moderate |
| Hot Water Extraction | Lower | Potentially lower | Lower |
Note: Efficiency and cost-effectiveness are relative and depend on the specific conditions.
Industry Analysis
The restart of Cenovus Energy’s Christina Lake oil sands operation marks a significant event in the Canadian oil sands industry. This restart, following a period of reduced activity, reflects current market dynamics and Cenovus’s overall strategy for navigating the complex landscape. Understanding the broader industry context is crucial to evaluating the impact of this decision.Cenovus’s decision to resume production at Christina Lake is intricately linked to its broader strategic objectives.
The company’s aim is likely to maximize returns in a market where oil prices remain a key variable. This restart could be part of a larger plan to regain market share and bolster profitability. Analyzing the competitors’ responses and the overall industry outlook for the near future provides a comprehensive understanding of the context surrounding this restart.
Current State of the Canadian Oil Sands Industry
The Canadian oil sands industry is currently characterized by a complex interplay of factors. Declining production from some operations, along with varying levels of investment, create a dynamic landscape. Government policies and regulations, environmental concerns, and fluctuating global oil prices are major influences on the sector’s trajectory. The overall production capacity in the oil sands is being carefully managed.
Industry stakeholders are monitoring the market carefully.
Comparison to Cenovus Energy’s Broader Strategy
Cenovus Energy’s restart of the Christina Lake facility aligns with its overall strategic goals. The company likely assessed the current market conditions, including demand projections, production costs, and anticipated returns. This strategic decision suggests a commitment to sustained production, while carefully weighing the risks and potential rewards of the current market.
Key Competitors and Their Responses
Several major players in the Canadian oil sands sector exist, including Suncor Energy, Imperial Oil, and others. Their responses to Cenovus’s restart will likely vary, influenced by their individual strategies and financial positions. Some competitors may choose to increase their own production if market conditions are favorable, while others might remain cautious. The reactions of competitors will provide a more comprehensive view of the oil sands market dynamics.
A careful assessment of competitor strategies will help to predict future actions. For example, if Suncor observes that Cenovus’s restart is successful in boosting market share, they might consider similar actions in the near future.
Industry Outlook for the Near Future
The near-term outlook for the Canadian oil sands industry hinges on several factors, including the global demand for oil, fluctuating energy prices, and the effectiveness of government policies. Government support for the oil sands sector will play a significant role. Industry projections suggest a potential increase in production, but this will depend on global demand, market fluctuations, and regulatory compliance.
For instance, if global energy demand surges, the Canadian oil sands industry might see significant expansion, and vice-versa. Economic and political conditions can significantly influence the outlook.
Public Perception and Stakeholder Relations
The restart of Cenovus Energy’s Christina Lake oil sands production presents a complex challenge in managing public perception and stakeholder relations. Public opinion on oil sands projects is often highly polarized, with strong concerns about environmental impacts and economic consequences. Effective communication and engagement with various stakeholders are crucial for navigating these sensitivities and building trust.Successfully navigating this restart requires a proactive and transparent approach.
Cenovus must demonstrate a commitment to responsible development and environmental protection to build trust and mitigate potential opposition. This includes demonstrating a clear understanding of community concerns and incorporating those concerns into the restart plan.
Public Perception of Oil Sands Production
Public perception of oil sands production is generally negative, with many associating it with significant environmental damage, such as greenhouse gas emissions and water contamination. Concerns often stem from the perceived lack of sustainable practices and the potential for irreversible harm to ecosystems. Public trust is often eroded by perceived lack of transparency and accountability in the industry’s environmental management practices.
This negative perception significantly influences public support for oil sands development, and companies must address these concerns directly and constructively.
Stakeholder Engagement in the Restart Process
Effective stakeholder engagement is critical to the success of the restart. This encompasses not only environmental groups but also Indigenous communities, local governments, and residents. Cenovus must actively solicit feedback, address concerns, and proactively communicate updates throughout the process. Genuine dialogue and active listening are essential to building trust and demonstrating a commitment to community well-being. This includes not just informing stakeholders but also actively incorporating their perspectives into decision-making processes.
Examples of successful stakeholder engagement include regular meetings, town halls, and the establishment of dedicated communication channels.
Strategies for Managing Public Relations During the Restart
A robust public relations strategy is vital to manage public perception during the restart. This involves proactive communication, transparency about environmental mitigation measures, and demonstrable commitment to environmental protection. Cenovus should highlight its investments in technology and practices aimed at reducing environmental impact. For example, showcasing advancements in carbon capture and storage or water management techniques can positively influence public perception.
Clear, consistent, and accessible communication channels are essential for disseminating information to the public, fostering trust and managing expectations. Transparency in the decision-making process is equally important, including proactively addressing potential concerns and demonstrating a willingness to engage with stakeholders.
Environmental Groups’ Concerns and Perspectives
Environmental groups frequently express significant concerns about the environmental impacts of oil sands production. These concerns include air and water pollution, greenhouse gas emissions, and habitat destruction. They often advocate for stricter regulations, increased environmental safeguards, and a transition towards cleaner energy sources. These groups often play a critical role in shaping public opinion and advocating for environmental protection.
Strategies to address these concerns include actively engaging with environmental groups, demonstrating a commitment to environmental sustainability, and providing comprehensive data on environmental performance. For example, independent audits of environmental impact and transparent reporting on emission reductions can help address these concerns.
Illustrative Case Study
Restarting an oil sands project is a complex undertaking, requiring meticulous planning and execution. A critical aspect of this process is learning from past experiences, specifically in similar projects. Examining previous restarts provides valuable insights into potential challenges and successful strategies. This case study will explore a comparable oil sands restart to illuminate the lessons applicable to the Cenovus Energy Christina Lake restart.A comparable case study will examine the restart of the Syncrude Mildred Lake oil sands project.
This project, like the Christina Lake restart, faced challenges related to equipment maintenance, workforce availability, and environmental compliance. Understanding the approaches taken and outcomes of the Syncrude Mildred Lake restart will offer a benchmark for the Christina Lake operation.
Syncrude Mildred Lake Restart: A Comparative Analysis
The Syncrude Mildred Lake restart, following a period of reduced production, presented a unique set of circumstances mirroring the Christina Lake scenario. Both involved significant infrastructure upgrades, workforce re-training, and careful consideration of environmental impacts.
Similarities and Differences
Both restarts involved significant capital expenditures to refurbish and upgrade facilities, but the specific upgrades varied. The Mildred Lake restart, for instance, may have focused on specific technologies to enhance efficiency, while Christina Lake might prioritize different technological solutions. Critical similarities include the need for skilled labour, environmental compliance measures, and careful market analysis. Differences lie in the specific technological advancements, economic conditions at the time of restart, and the particular regulatory environment.
| Characteristic | Syncrude Mildred Lake Restart | Cenovus Energy Christina Lake Restart |
|---|---|---|
| Production Capacity (bbl/day) | Approximately X bbl/day (estimated) | Approximately Y bbl/day (estimated) |
| Timeframe for Restart | X months (estimated) | Y months (estimated) |
| Key Technological Upgrades | Implementation of advanced extraction techniques, such as improved solvent injection. | Focus on optimizing existing technology and reducing operational costs. |
| Market Conditions at Restart | Global oil prices at Z level (example). | Global oil prices at A level (example). |
| Environmental Compliance Measures | Adherence to specific environmental regulations (e.g., emissions standards). | Adherence to current environmental regulations (e.g., emissions standards). |
Lessons Learned and Application to Christina Lake
The Syncrude Mildred Lake restart demonstrated the importance of meticulous planning and stakeholder engagement. Critical lessons include the need for a comprehensive risk assessment, proactive communication with regulatory bodies, and a clear understanding of the evolving market conditions. These factors, if applied to the Christina Lake restart, could minimize potential setbacks. Furthermore, the Syncrude experience highlighted the significance of maintaining a skilled workforce and addressing potential workforce shortages through retraining and recruitment.
These elements could be crucial for the Christina Lake restart’s success.
Conclusion
The Syncrude Mildred Lake restart provides a valuable case study for the Cenovus Energy Christina Lake restart. Understanding the similarities and differences, along with the lessons learned, allows for a more informed approach to this complex undertaking. Careful planning, stakeholder engagement, and a thorough understanding of the project’s specific context will be vital for success.
Closing Summary

In conclusion, Canada’s Cenovus Energy restart at Christina Lake represents a significant event with far-reaching consequences. From the intricacies of oil market dynamics to the crucial environmental considerations, the restart sparks a complex debate about the future of energy production. This detailed analysis explores the various facets of this restart, from its economic implications to the public perception, and highlights the ongoing challenges and opportunities surrounding the Canadian oil sands industry.

