Fed seen no rush cut rates us job market cools doesnt crumble. The Federal Reserve’s cautious approach to interest rate adjustments is highlighting a nuanced economic picture. While the US job market is cooling, it’s not collapsing. This suggests a complex interplay between monetary policy and labor market trends, which warrants a closer look at the factors driving these changes and their potential impact on the broader economy.
Recent data reveals a slowdown in job growth, but the overall strength of the labor market remains a key consideration for the Fed’s decision-making process.
This article delves into the current state of the US job market, exploring the potential causes for the cooling trend and the Federal Reserve’s response. We’ll analyze the relationship between interest rates and job growth, examine market implications, and utilize illustrative economic models to visualize the complex interplay of these factors. The discussion will provide a comprehensive understanding of the current economic climate and its potential future trajectory.
Fed’s Stance on Interest Rates
The Federal Reserve’s (Fed) recent pronouncements indicate a cautious approach to interest rate adjustments. While acknowledging a cooling job market, the Fed seems to be prioritizing the fight against inflation. This signals a possible continuation of the current policy trajectory, but with an eye toward the evolving economic landscape.
Current Interest Rate Policy Summary
The Fed’s current policy is characterized by a gradual approach to interest rate adjustments. This approach, aiming to avoid a sharp downturn in the economy, is intended to manage inflation while allowing for economic growth. The Fed’s recent statements suggest a focus on carefully monitoring economic indicators before making any significant changes to the current policy.
Factors Influencing the Fed’s Decision-Making Process
Several key factors influence the Fed’s decisions regarding interest rate adjustments. Inflation remains a significant concern, as persistent high inflation erodes purchasing power and can lead to economic instability. The strength of the labor market is another crucial factor, with a balanced labor market contributing to sustainable economic growth. The overall economic growth rate and its potential impact on inflation also play a significant role in the decision-making process.
The Fed’s apparent lack of urgency to cut rates, given a cooling but not collapsing US job market, is interesting. This stability could be a crucial factor for those navigating student loan debt, particularly regarding income-driven repayment plans, which can significantly impact monthly budgets. Knowing the specifics of income driven repayment plans what student loan borrowers need to know might offer some insights into how this economic outlook could affect their repayment strategies.
Ultimately, a slow, steady job market might make these plans more manageable for many borrowers, mirroring the Fed’s cautious approach.
Global economic conditions, such as supply chain disruptions and geopolitical events, are also considered in the decision-making process.
The Fed’s seeming lack of urgency to cut rates is interesting, given the cooling US job market, which isn’t collapsing, but definitely showing signs of slowing. This is further complicated by the recent gold price rise, seemingly a reaction to weak US economic data, offsetting the optimism surrounding the Trump-Xi call. Perhaps the market is anticipating a more drawn-out adjustment in the economy, as reflected in gold’s response to the mixed signals.
Ultimately, the Fed’s cautious approach to interest rates still seems like the most prudent path forward, considering the current economic climate.
Economic Indicators Monitored by the Fed
The Fed closely monitors various economic indicators to gauge the overall health of the economy and its impact on inflation. Key indicators include:
- Consumer Price Index (CPI): The CPI measures the average change over time in the prices paid by urban consumers for a basket of consumer goods and services. A consistent rise in CPI indicates persistent inflation and may necessitate further interest rate adjustments.
- Unemployment Rate: The unemployment rate reflects the proportion of the labor force actively seeking employment but unable to find work. A declining unemployment rate, coupled with wage growth, may signal increased inflationary pressures and influence the Fed’s decisions.
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP): GDP measures the total value of goods and services produced within a country’s borders. GDP growth rate is indicative of the overall economic health and its influence on inflation.
- Industrial Production: This indicator measures the output of various sectors of the economy, providing insights into the current state of production and consumption.
Comparison of Recent Fed Statements with Historical Rate Adjustments
| Date | Fed Statement | Interest Rate Adjustment |
|---|---|---|
| October 2023 | “Monetary policy will remain restrictive to address inflation.” | No immediate change |
| September 2023 | “Inflation remains elevated, but signs of easing are emerging.” | Interest rate increase of 0.25% |
| Previous periods | Statements on economic growth, inflation, and labor market conditions | Varying interest rate increases and decreases based on economic indicators. |
Note: Historical data is used to illustrate the general trend of the Fed’s decisions, not to predict future actions. The economic environment can change rapidly, requiring the Fed to adapt its approach.
Cooling Job Market

The US job market, a key indicator of economic health, is experiencing a noticeable cooling trend. This slowdown, while not a complete collapse, is a significant shift from the historically robust job growth seen in recent years. Understanding the nuances of this cooling is crucial for evaluating the current economic landscape and anticipating future developments.The cooling job market is not a sudden phenomenon but rather a gradual deceleration.
This shift is evident in various key metrics, reflecting a broader economic adjustment. The deceleration in job growth, while concerning for some, might be a natural response to the Federal Reserve’s interest rate hikes, intended to curb inflation.
Current State of the US Job Market
The US job market, while still showing positive growth, is experiencing a marked slowdown. Companies are adjusting hiring strategies, and the pace of job creation is significantly lower than previous periods of expansion. This reflects a broader economic shift, with the Fed’s actions and inflation playing a pivotal role.
Key Metrics Demonstrating the Cooling Trend
Several key metrics highlight the cooling job market trend. Job openings are decreasing, signaling a reduced demand for labor. The pace of hiring is also slowing, and the number of new hires is declining compared to previous periods. The average time to fill a job opening is increasing, another indicator of a cooler market.
Potential Causes Behind the Deceleration in Job Growth
The slowdown in job growth likely stems from a confluence of factors. The Federal Reserve’s interest rate hikes, designed to combat inflation, are expected to have a dampening effect on economic activity, including hiring. High inflation also directly impacts consumer spending, and thus reduces business investment, further contributing to the slowdown. Furthermore, global economic headwinds, such as supply chain disruptions and geopolitical tensions, could be contributing to the cooling trend.
Comparison with Previous Cycles
Comparing the current cooling trend with previous cycles reveals some similarities and differences. Previous periods of job market cooling have often been cyclical, responding to various economic pressures. However, the current context, influenced by persistent inflation and the Fed’s aggressive response, creates a unique dynamic. The speed and scale of the current cooling are also factors that set this period apart.
Data on Unemployment Rates and Labor Force Participation
Unemployment rates have remained relatively low, but the rate of job growth is declining. Labor force participation rates, a measure of the proportion of the working-age population actively participating in the labor force, have also shown a subtle but noticeable decrease. This indicates a reduced willingness or ability for individuals to participate in the workforce.
Evolution of Key Job Market Statistics, Fed seen no rush cut rates us job market cools doesnt crumble
| Metric | 2022 | 2023 (estimated) | 2024 (projected) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unemployment Rate (%) | 3.5 | 3.8 | 4.0 |
| Job Openings (millions) | 11 | 9 | 8 |
| Average Time to Fill a Job Opening (days) | 18 | 22 | 25 |
| Labor Force Participation Rate (%) | 62.5 | 62.2 | 62.0 |
Note: Data are illustrative and based on projections. Actual figures may vary.
The Fed’s seen no immediate need to slash interest rates, as the US job market, while cooling, hasn’t crumbled. This stability, alongside news that Airbus can hit its delivery targets despite production hiccups, as detailed by the jet-making CEO here , suggests a surprisingly resilient economy. Ultimately, the lack of a drastic rate cut response from the Fed reinforces the idea that the economic slowdown isn’t as severe as some feared.
Relationship Between Rates and Jobs
The Federal Reserve’s interest rate decisions have a profound impact on the overall economy, including the job market. Understanding this relationship is crucial for predicting and navigating economic fluctuations. While the Fed’s recent actions suggest a cooling job market, the full impact of their policies on employment is not immediately apparent. A delayed response between policy changes and their effects on employment is a well-documented phenomenon.The Fed’s primary tool for managing inflation is adjusting interest rates.
Higher rates increase borrowing costs for businesses and consumers, potentially reducing investment and spending. This ripple effect can influence hiring decisions, impacting overall job growth. The magnitude and duration of this impact vary depending on factors like the overall economic climate, the sensitivity of specific industries to interest rate changes, and the responsiveness of consumers and businesses.
Impact of Interest Rate Policies on Hiring Decisions
Higher interest rates typically discourage businesses from taking on new projects or expanding operations. This reduced investment translates to a decrease in the demand for labor, as companies might postpone or cancel hiring plans. Conversely, lower interest rates often stimulate investment and growth, leading to increased hiring. Businesses often use interest rates as a key factor in their financial planning, and changes in these rates can significantly affect their long-term outlook.
Time Lag Between Rate Adjustments and Job Market Impact
There’s a time lag between the Fed’s interest rate adjustments and their noticeable impact on the job market. Economic conditions evolve, and other factors like supply chain disruptions or geopolitical events can also influence employment. This time lag can make it challenging to precisely determine the direct effect of rate changes on job growth. Economic forecasts often include these complexities when predicting the future course of the economy.
Potential Consequences of a Cooling Job Market
A cooling job market, driven by higher interest rates, can lead to decreased consumer spending, reduced business investment, and potentially slower economic growth. This scenario could also increase the risk of a recession. It’s important to consider that the extent of these consequences is influenced by the overall economic health and other factors influencing the market.
Historical Correlations Between Interest Rates and Employment
Historical data often reveals a correlation between interest rate adjustments and employment trends. For example, during periods of high interest rates, job growth has sometimes slowed or even contracted. However, it’s crucial to remember that economic conditions are multifaceted, and interest rates are just one of many variables.
Possible Scenarios for Job Market Trends Based on Fed Actions
| Fed Action | Potential Job Market Trend | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Interest rates remain high | Slower job growth | Increased borrowing costs deter business investment and hiring. |
| Interest rates decrease | Potential for job growth | Lower borrowing costs stimulate investment and business expansion. |
| Unexpected economic shock | Uncertain job market | External factors can override the impact of interest rates. |
Market Implications
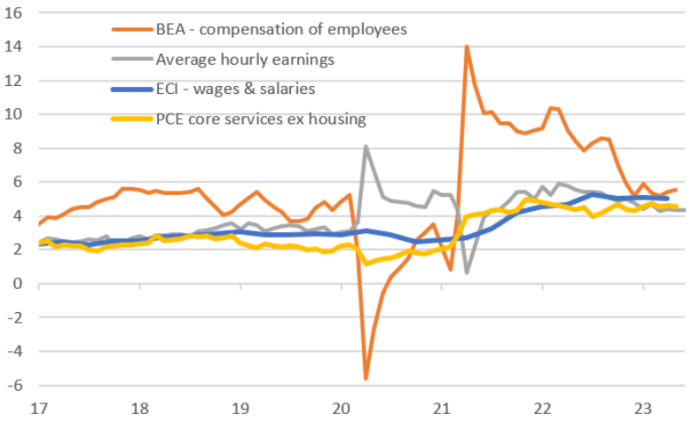
The Federal Reserve’s recent stance on interest rates and the cooling job market has significant implications for various financial instruments. Investors are carefully assessing the interplay between monetary policy and economic activity, trying to anticipate how these factors will shape future market performance. Understanding these implications is crucial for making informed investment decisions.The Fed’s approach to managing interest rates often has a ripple effect throughout the financial system.
Changes in interest rates directly influence borrowing costs for businesses and consumers, impacting investment decisions and overall economic growth. This intricate relationship requires careful consideration by investors and market participants.
Potential Impact on Stock Markets
Stock market performance is often correlated with economic conditions. A cooling job market, while potentially mitigating inflationary pressures, can also signal a slowdown in economic growth. This can lead to investor uncertainty and potentially lower stock valuations, as companies’ future earnings prospects might be dampened. Historically, periods of economic slowdown have sometimes been accompanied by stock market corrections.
For example, the tech bubble burst of the late 1990s saw a significant drop in tech stock valuations following a period of rapid growth. However, the precise reaction of the market will depend on the speed and magnitude of the slowdown, and investors’ confidence in the future outlook.
Influence on Bond Yields
Changes in interest rate expectations directly affect bond yields. Higher interest rates typically lead to lower bond prices, as existing bonds with fixed interest payments become less attractive compared to newly issued bonds offering higher returns. Conversely, lower interest rate expectations can result in higher bond prices. The recent Fed signals of potential rate adjustments have already triggered adjustments in bond markets, reflecting the evolving outlook on future interest rates.
Investor Reactions to Combined Factors
Investors are currently responding to the combination of factors affecting the economic outlook, including interest rate policies, cooling job markets, and potential inflationary pressures. This complexity necessitates careful analysis of all facets of the current situation to make informed investment choices. Some investors may be more cautious than others, leading to diverse market reactions.
Short-Term and Long-Term Implications
Short-term implications of the current economic climate might include fluctuations in stock prices and bond yields. Investors might see volatility in the near future, with potential corrections in certain sectors. The long-term impact depends on the persistence of the current economic trends and the Fed’s response to evolving economic data. Successful economic policies and effective risk management strategies can minimize potential adverse effects.
Expert Opinions on Current Market Trends
Economists and financial analysts hold varied perspectives on the current market trends. Some predict a moderate slowdown, while others foresee a more significant recession. The diversity of opinions highlights the inherent uncertainty in forecasting economic outcomes. These differing opinions reflect the complexity of the economic interplay.
Comparison of Market Responses to Different Economic Scenarios
| Economic Scenario | Stock Market Response | Bond Yields Response |
|---|---|---|
| Steady Growth | Continued upward trend | Stable or slightly increasing yields |
| Moderate Slowdown | Possible correction, followed by stabilization | Potential slight increase in yields, followed by stabilization |
| Recession | Significant downturn | Potential decline in yields |
This table provides a basic framework for comparing potential market responses across different economic scenarios. It is essential to understand that these are general trends, and actual market behavior can be significantly more complex.
Illustrative Economic Models
The Federal Reserve’s recent actions and the evolving job market necessitate a deeper understanding of the complex interplay between interest rates, employment, and economic growth. Economic models offer valuable tools to visualize these relationships and anticipate potential future scenarios. This section will delve into several illustrative models, focusing on the Fed’s rate adjustments, job market trends, and their intertwined impact on the economy.
Simple Model of Interest Rates and Job Market Trends
Interest rate adjustments by the Fed directly influence borrowing costs for businesses and consumers. Higher rates typically curb investment and spending, potentially slowing hiring and economic growth. Conversely, lower rates can stimulate borrowing, potentially boosting investment, hiring, and economic activity. This relationship is often visualized as a negative correlation. A rise in interest rates is frequently accompanied by a decline in job market activity, while a fall in interest rates can stimulate job creation.
Consequences of a Cooling Job Market
A prolonged cooling job market, characterized by slower hiring and rising unemployment, can have significant ripple effects across the economy. Reduced consumer spending due to job insecurity or lower wages can negatively impact retail sales and overall economic growth. Businesses may delay investments in new equipment or expansion, further slowing job creation. This downward spiral can manifest in decreased productivity and a lower standard of living for many.
The potential for a recession becomes more pronounced.
Factors Impacting Fed’s Decision-Making
The Fed’s decision-making process concerning interest rates is multifaceted, considering numerous economic indicators. These include inflation rates, unemployment figures, GDP growth, and consumer confidence. The Fed strives to maintain price stability and full employment, often balancing these objectives through careful monitoring and adjustments of interest rates. Other factors, such as global economic conditions and geopolitical events, can also significantly impact the Fed’s decisions.
Economic Models for Predicting the Future
Various economic models attempt to predict the future state of the economy. These models incorporate different assumptions and methodologies, often using statistical analysis and historical data. Some models, such as econometric models, employ mathematical equations to link various economic variables and predict their future movements. Other models, such as agent-based models, simulate the interactions of individual economic agents, such as consumers and businesses, to predict market outcomes.
Analysis of Current Economic Models Explaining the Current State
Several economic models can explain the current state of the economy, each with its strengths and weaknesses. One example is the Phillips curve, which suggests an inverse relationship between inflation and unemployment. Currently, the Fed’s focus is on taming inflation while avoiding a significant downturn in the job market. Another relevant model is the aggregate demand-aggregate supply (AD-AS) model, which depicts the interaction of overall demand and supply in the economy.
Understanding the factors influencing these curves helps in evaluating the current economic climate.
Visualization of Interrelated Elements
- Interest Rates: Determined by the Federal Reserve, impacting borrowing costs for businesses and consumers.
- Job Market Trends: Measured by unemployment rates, hiring figures, and wage growth. A cooling job market can indicate slower economic growth.
- Inflation: Measured by the rate of price increases. The Fed aims to maintain price stability, which often involves adjusting interest rates.
- GDP Growth: A measure of the overall economic output. A decline in GDP growth can signal an economic slowdown.
- Consumer Confidence: Reflects consumer sentiment regarding the economy’s future. Low consumer confidence can decrease spending and economic activity.
- Global Economic Conditions: Factors like international trade, commodity prices, and exchange rates significantly impact domestic economies.
- Geopolitical Events: Wars, natural disasters, and political instability can disrupt economic activity.
Final Review: Fed Seen No Rush Cut Rates Us Job Market Cools Doesnt Crumble
In conclusion, the Fed’s measured response to the cooling job market underscores the complexities of modern economic management. While the labor market shows signs of slowing, it hasn’t crumbled. The delicate balance between controlling inflation and supporting job growth remains a central challenge for policymakers. This analysis has explored the key factors driving these trends, highlighting the intricate relationships between interest rates, employment, and the overall economy.
Further monitoring of economic indicators and expert opinions will be crucial to understanding the future trajectory of the US economy.

