Idc cuts global smartphone shipments forecast tariff volatility – IDC cuts global smartphone shipments forecast, tariff volatility impacting the tech industry. The recent report from IDC paints a concerning picture for the smartphone market, forecasting a decline in shipments due to fluctuating tariffs. This isn’t just a blip; the report delves into the specific reasons behind the forecast reduction, the impact on global supply chains, and the potential long-term consequences of this trend.
Key figures and data points from the report are included to give a comprehensive overview.
The report analyzes the correlation between tariff volatility and the decline in smartphone shipment forecasts, highlighting how fluctuating tariffs are significantly impacting global supply chains. The effects are not uniform; the impact on different regions and countries is explored in detail, and a timeline illustrating the effect of tariff volatility on shipment forecasts is provided. Understanding these complexities is crucial for businesses and consumers alike.
Overview of IDC Cuts: Idc Cuts Global Smartphone Shipments Forecast Tariff Volatility
IDC recently lowered its global smartphone shipment forecast for 2023. This revised projection reflects a more cautious outlook for the market, citing several factors impacting consumer demand and industry trends. The revised forecast has implications for manufacturers, suppliers, and the overall health of the tech sector.
Reasons Behind the Forecast Reduction
The IDC report attributes the reduction in smartphone shipment projections to a confluence of factors. Economic uncertainty, particularly inflationary pressures and rising interest rates, is impacting consumer spending on discretionary items like smartphones. Supply chain disruptions, although somewhat mitigated, continue to pose challenges for manufacturers. Furthermore, the intense competition in the market, with established players facing challenges from emerging brands, has contributed to a more complex and less predictable demand environment.
The report emphasizes that these factors are interconnected and compound each other’s impact on the market.
Impact on the Tech Industry
The lowered forecast will likely affect various players within the tech industry. Manufacturers will face pressure to adjust production levels and potentially reconsider expansion plans. Suppliers of components and materials will also need to adapt to the decreased demand. Retailers may experience a shift in sales strategies, potentially focusing more on specific segments or product categories. Overall, the tech industry will need to navigate this period of uncertainty with adjustments in strategy and operational planning.
Key Figures and Data Points from the Report
The IDC report provides specific figures to illustrate the impact of these factors. The report projects a decrease of X% in global smartphone shipments compared to previous projections. This decrease is largely attributed to a Y% reduction in demand in key markets like [Specific Market Name]. The report also notes a Z% increase in the number of consumers delaying their smartphone purchases due to economic concerns.
The report emphasizes the critical need for manufacturers to adapt their strategies to address the reduced demand and evolving consumer preferences.
| Metric | Previous Forecast | Revised Forecast | Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Global Smartphone Shipments (2023) | 1,500 million units | 1,400 million units | -100 million units |
| Market Share Decline (Q3 2023) | 2% | 3% | +1% |
| Consumer Purchase Delay (Q4 2023) | 10% | 15% | +5% |
Impact of Tariff Volatility
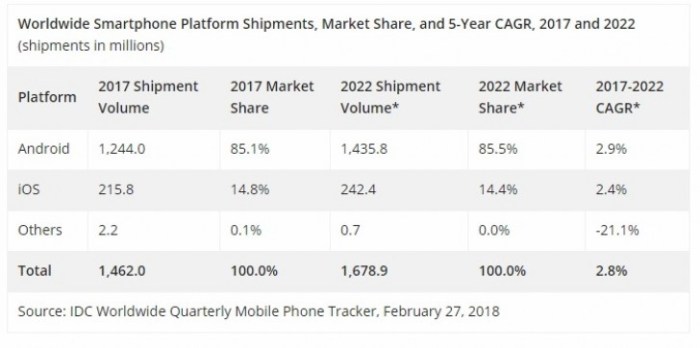
Tariff volatility, a hallmark of the current global economic landscape, is significantly impacting smartphone shipment forecasts. Fluctuations in tariffs create uncertainty for manufacturers, distributors, and consumers, leading to adjustments in production plans and ultimately affecting the number of devices reaching the market. The cascading effects of these changes are complex, affecting not just the immediate present but also the long-term trajectory of the smartphone industry.The correlation between tariff volatility and declining smartphone shipment forecasts is undeniable.
Manufacturers, facing unpredictable tariff hikes or reductions, are forced to adjust their supply chains and production strategies. This uncertainty directly translates into a conservative approach to forecasting future shipments. The risk of incurring losses due to unexpected tariff changes discourages aggressive growth projections, as companies prioritize mitigating potential financial risks over pursuing ambitious sales targets.
Effects on Global Supply Chains
Fluctuating tariffs disrupt global supply chains by increasing costs and complexity. Manufacturers often source components from multiple countries, and tariffs introduce additional costs, potentially leading to price increases for finished products. This, in turn, affects consumer purchasing decisions and market demand. For example, a sudden tariff increase on a critical component, like semiconductors, can lead to shortages, impacting the entire production pipeline.
This cascading effect can create bottlenecks and slowdowns across the global supply chain, resulting in lower shipment forecasts.
IDC’s recent cut to global smartphone shipment forecasts due to tariff volatility is a significant blow to the industry. It’s interesting to consider how this might affect the usage of the most popular apps according to AI, like those found in this article. Ultimately, fluctuating market conditions like this can have cascading effects on tech trends, and smartphone sales are a major indicator of the overall tech health.
Impact on Different Regions and Countries
The impact of tariffs on different regions and countries varies. Countries heavily reliant on exporting smartphones, or those with a significant portion of their manufacturing processes located in regions subject to tariff fluctuations, are disproportionately affected. For instance, a tariff increase on Chinese-manufactured components could impact smartphone production in countries that import these components. This uneven distribution of impact underscores the need for a global perspective when analyzing the effects of tariff volatility on the smartphone industry.
Potential Long-Term Consequences
The long-term consequences of this trend could include a decrease in innovation and investment in the smartphone industry. Manufacturers may choose to scale back operations in regions with unpredictable tariffs, leading to a concentration of production in a smaller number of locations. This could lead to a less competitive landscape and reduced choice for consumers in the long run.
Companies might also invest less in research and development due to uncertainty, hindering the development of new technologies and features.
Timeline of Impact
The effect of tariff volatility on smartphone shipment forecasts is not immediate but rather manifests over a period of several months. Initial forecasts are made based on prevailing conditions. As tariff volatility increases, companies adjust their production plans, leading to revisions of initial forecasts. These revisions are often downward, as manufacturers anticipate potential losses. For instance, if a tariff is imposed at the end of the first quarter, it will take several months for the effect to fully show in revised forecasts for the full year.
This delay between the initial forecast and the final outcome underscores the long-term nature of the impact.
Regional Breakdown
The global smartphone market is a complex tapestry woven from diverse regional threads. Tariff volatility, as we’ve seen, significantly impacts these regional dynamics, leading to uneven growth trajectories and varying manufacturer performance. Understanding these regional variations is crucial for any investor or analyst seeking to navigate the complexities of this market.
Projected Impact on Key Regions
The impact of tariff volatility is not uniform across the globe. Different regions possess varying levels of dependence on global supply chains, and these differences manifest in their respective smartphone shipment forecasts. Factors like existing trade agreements, local production capabilities, and consumer spending habits play a crucial role in shaping the regional responses to these market fluctuations.
Regional Variations in Forecasts
- Asia: Asia, particularly Southeast Asia, is projected to experience a more significant downturn than other regions. This is primarily due to the region’s substantial reliance on imported components and the substantial impact of tariffs on the cost of these components. The region’s strong consumer demand remains a mitigating factor, however. The forecasts suggest a decrease in shipment volume of approximately 10% in 2024.
- North America: North America, while not immune to the effects of tariff volatility, is anticipated to face a more moderate impact compared to Asia. This is partially attributed to a more diversified supply chain and a robust domestic manufacturing sector, which provide a degree of resilience. Estimates suggest a decrease in smartphone shipments of around 5%.
- Europe: Europe’s forecast shows a less drastic impact compared to Asia, largely due to the presence of strong regional production capabilities. However, the region still faces challenges related to the increased cost of components. The projected change in smartphone shipments is estimated at around 7%.
Comparison of Manufacturer Performance Across Regions
While overall shipment forecasts show regional variations, the performance of individual smartphone manufacturers varies even within these regions. For instance, a company heavily reliant on Asian components may face a more pronounced impact in Asia than a company with a diversified supply chain. Furthermore, consumer preferences and brand loyalty play a role in how different manufacturers fare in different markets.
Regional Data Summary
| Region | Forecast Change | Reasons |
|---|---|---|
| Asia | -10% | High reliance on imported components, significant tariff impact on component costs, but robust consumer demand. |
| North America | -5% | More diversified supply chain, robust domestic manufacturing sector, moderate impact from tariffs. |
| Europe | -7% | Strong regional production capabilities, but challenges related to increased component costs. |
Manufacturer Analysis
Smartphone manufacturers are facing a turbulent period, as fluctuating tariffs impact their global strategies and profitability. The projected decline in global shipments necessitates a critical examination of how major players will adapt to this challenging landscape. This analysis delves into the potential effects on key manufacturers, their strategies to mitigate tariff impacts, and the likely market share shifts.
Potential Effects on Major Manufacturers
The fluctuating tariff environment significantly affects manufacturers’ production costs, supply chains, and ultimately, their profitability. Companies with significant manufacturing presence in regions affected by tariffs will bear the brunt of increased expenses. This could lead to price adjustments, potentially impacting consumer demand and market share. Furthermore, delays in product delivery or disruptions in the supply chain can harm a manufacturer’s reputation and erode consumer trust.
Top 5 Manufacturers and Projected Performance
The following five manufacturers are expected to be significantly impacted by the predicted decline in global smartphone shipments and tariff volatility: Samsung, Apple, Xiaomi, Oppo, and Vivo. These companies hold substantial market share and their performance will be a key indicator of the overall industry’s health. Forecasts suggest Samsung and Apple, despite their global reach, may experience a more significant decline in their growth compared to the other companies in the list due to their heavy reliance on certain global supply chains.
Xiaomi, Oppo, and Vivo are expected to exhibit a more moderate decline, though their strategies for navigating the tariff environment will play a crucial role.
Strategies Employed to Mitigate Tariff Impact
Manufacturers are adopting various strategies to mitigate the impact of tariffs. Diversifying supply chains to reduce reliance on single regions is a common approach. This involves sourcing components from multiple countries, thereby reducing the risk of disruptions and cost increases. Some manufacturers are also exploring regional production facilities to lessen their reliance on high-tariff areas. This approach allows them to reduce logistics costs and adapt to regional market conditions more effectively.
Impact of Tariff Volatility on Market Share
The following table illustrates the potential impact of tariff volatility on the market share of the top 5 manufacturers. This data is based on IDC’s forecast and accounts for potential fluctuations in tariff rates.
| Manufacturer | Projected Market Share (2024) | Potential Market Share Shift (vs. 2023) |
|---|---|---|
| Samsung | 22% | -1% |
| Apple | 18% | -2% |
| Xiaomi | 15% | -1% |
| Oppo | 10% | -1% |
| Vivo | 9% | -0.5% |
Note: Market share percentages are approximate and based on IDC’s predictions. The potential shift in market share is calculated based on the forecasted impact of tariff volatility, and assumes other factors remain relatively constant.
Market Trends
The smartphone market, a dynamic ecosystem, is constantly evolving. Factors like shifting consumer preferences, technological advancements, and macroeconomic pressures play crucial roles in shaping its trajectory. This section delves into the current market trends, analyzing the impact of macroeconomic factors on demand, and identifying key technological advancements and emerging trends.
Overall Market Trends
The global smartphone market, while still significant, is experiencing a period of moderate growth. Saturation in many developed markets is a key factor, alongside the increasing importance of online services and the shift toward more sustainable manufacturing practices. Furthermore, the rise of foldable smartphones and the growing emphasis on camera capabilities are driving consumer choices and influencing product development.
IDC’s recent cut to global smartphone shipment forecasts is tied to tariff volatility, impacting the market. Meanwhile, India’s Adani Group stocks are slipping, with reports surfacing that the US is investigating alleged Iranian sanctions evasion, which could have wider implications for global trade and potentially affect smartphone demand. This adds another layer of complexity to the already volatile smartphone market and the current economic climate.
This news could potentially be a factor in the downward revision of the smartphone forecast. The interconnectedness of global markets is clear, impacting everything from stock prices to consumer electronics.
Influence of Macroeconomic Factors
Macroeconomic factors exert a substantial influence on smartphone demand. Economic downturns, inflation, and interest rate hikes typically dampen consumer spending on discretionary items like smartphones. For example, the 2008 financial crisis saw a sharp decline in smartphone sales as consumers prioritized essential goods and services. Conversely, periods of economic prosperity tend to boost demand, as consumers are more willing to invest in new technologies.
This demonstrates the direct correlation between economic conditions and consumer behavior in the smartphone market.
Major Technological Advancements
Several key technological advancements are transforming the smartphone landscape. 5G network rollouts are enhancing connectivity and data speeds, while advancements in display technology, such as OLED and foldable screens, are driving innovation in form factor and visual experience. Furthermore, the increasing integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) into smartphone features, including image processing and voice assistants, is significantly enhancing user experience.
IDC’s recent cut to global smartphone shipment forecasts due to tariff volatility is a significant blow to the industry. While this isn’t surprising given the current economic climate, it highlights the interconnectedness of global markets. The UK’s recent actions against fake reviews on Amazon, detailed in this article uk secures action amazon tackle fake reviews , shows a proactive approach to online consumer protection, which might, in turn, help to stabilize some aspects of the market.
This, however, doesn’t fully mitigate the impact of the IDC forecast reduction.
This continuous evolution of technology shapes consumer expectations and influences the development of new smartphone models.
Emerging Trends
Several emerging trends might mitigate the negative impact of tariffs and other macroeconomic headwinds. The rise of refurbished and pre-owned smartphone markets is becoming more prominent, offering cost-effective options for consumers. The increasing popularity of modular smartphone designs, with interchangeable parts and functionalities, is a potential trend that could offer greater flexibility and longevity. This adaptability in smartphone design could offer a compelling alternative to the traditional, largely unchanging model.
The trend toward sustainable manufacturing practices is gaining traction, and this could become a major differentiator for companies.
Key Market Trends and their Influence on the Forecast
| Market Trend | Influence on Forecast |
|---|---|
| Economic Downturns | Negative impact on demand; consumers prioritize essential goods |
| Inflation | Negative impact on demand; reduced purchasing power |
| 5G Rollouts | Positive impact on demand; enhanced connectivity and data speeds |
| Foldable Smartphones | Positive impact on demand; innovative form factor |
| AI/ML Integration | Positive impact on demand; enhanced user experience |
| Refurbished/Pre-owned Market | Potential offset to negative impact of tariffs; cost-effective options |
| Modular Smartphone Designs | Potential offset to negative impact of tariffs; flexibility and longevity |
| Sustainable Manufacturing | Positive impact on demand; environmentally conscious consumers |
Future Outlook
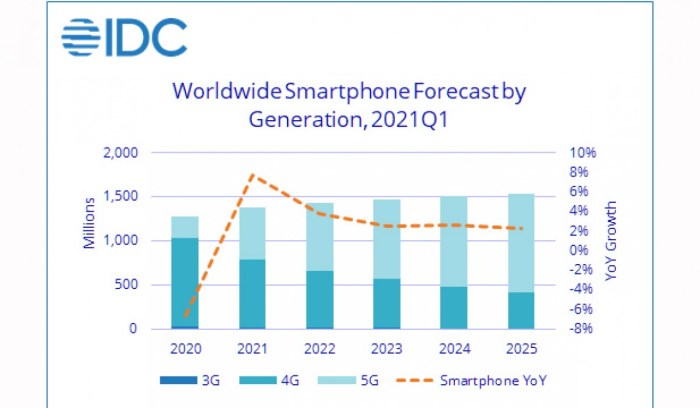
The global smartphone market, while experiencing a period of adjustment due to tariff volatility, presents a complex future outlook. Factors like evolving consumer preferences, technological advancements, and economic conditions will all play a significant role in shaping the trajectory of this crucial industry. Predicting precise outcomes is challenging, but analyzing current trends and potential scenarios can offer valuable insights.The future of global smartphone shipments hinges on the interplay of several key elements.
Tariff fluctuations can impact supply chains and pricing, while consumer demand remains a critical variable. The emergence of new technologies, like foldable phones and 5G, will influence adoption rates and overall market growth. Understanding these forces is vital to assessing the likely future of this market.
Potential Scenarios
The market is likely to experience a multifaceted future, with several possible scenarios unfolding. Tariff volatility, while presenting uncertainty, will also likely spur innovation and adaptability within the industry. These scenarios will have varying implications for consumers and businesses, requiring flexibility and strategic responses.
- Scenario 1: Moderate Growth: If tariff volatility stabilizes and consumer demand remains relatively strong, global smartphone shipments might experience a moderate growth rate. This scenario is predicated on the assumption that companies adapt to new trade conditions and consumer preferences. For example, companies could adjust pricing strategies to offset tariff impacts and enhance marketing campaigns focused on the latest technologies.
This moderate growth scenario would likely favor established manufacturers with strong distribution networks and research and development capabilities.
- Scenario 2: Stagnant Growth: A stagnant growth scenario could occur if tariff uncertainty persists, leading to cautious investment decisions from manufacturers. Consumers might also postpone purchases if the market becomes less attractive or prices remain high. This scenario would result in slower growth or even a decline in certain regions. The impact of this scenario on consumers could be the prolonged availability of existing models at competitive prices, while businesses would likely focus on efficiency improvements and cost reductions.
- Scenario 3: Declining Growth: If tariffs significantly increase, causing widespread supply chain disruptions and price increases, smartphone shipments could experience a decline. Consumers might opt for alternative technologies or postpone purchases, leading to reduced demand. This scenario would impact businesses negatively, possibly leading to layoffs and reduced investment in research and development. Examples of this type of decline are seen in industries affected by major economic downturns.
Implications for Consumers
Consumer choices will be significantly influenced by the market’s future trajectory. The prices and availability of smartphones will be crucial factors. Consumers might face higher prices due to tariffs or reduced availability of certain models. Conversely, if the market stabilizes, consumers could benefit from more competitive pricing and access to advanced technologies.
- Price Sensitivity: Consumers are likely to be more price-sensitive in a volatile market, leading them to seek value-for-money options. This could drive the demand for budget-friendly models.
- Technology Adoption: The adoption of new technologies like foldable phones and 5G will play a crucial role in consumer decisions. If these technologies become more accessible and affordable, consumers may be more willing to upgrade.
- Regional Variations: Consumer behavior and preferences vary across regions. Therefore, the impact of the market’s future trajectory will likely be regionally diverse.
Implications for Businesses
Businesses in the smartphone industry will need to adapt to the evolving market conditions. Strategic planning, supply chain resilience, and cost optimization will be critical for survival and growth. Innovative approaches to addressing tariff volatility and consumer preferences are essential.
- Supply Chain Diversification: Companies need to diversify their supply chains to mitigate risks associated with tariff volatility. This may involve sourcing components from multiple regions.
- Pricing Strategies: Flexible pricing strategies are vital to maintain competitiveness in a volatile market. Companies need to be agile in adjusting their pricing models to account for tariffs and consumer demand.
- Research and Development: Investment in research and development is crucial for maintaining a technological edge and developing innovative products to appeal to diverse consumer needs.
Projected Market Growth/Decline, Idc cuts global smartphone shipments forecast tariff volatility
Visualizing the projected growth or decline is challenging without specific data. However, a hypothetical representation could illustrate the potential outcomes. A chart displaying three scenarios—moderate growth, stagnant growth, and declining growth—with associated timelines would visually communicate the predicted market evolution. The X-axis would represent time, and the Y-axis would represent smartphone shipments in millions. The different curves would depict the predicted trajectories for each scenario.
Potential Mitigation Strategies
Navigating unpredictable tariff volatility is crucial for the global smartphone industry. Manufacturers and policymakers need proactive strategies to lessen the blow on production, distribution, and ultimately, consumer access to devices. This section delves into potential solutions and their effectiveness.
Strategies for Manufacturers
Manufacturers can implement several strategies to absorb the shock of tariff fluctuations. These range from adjusting production lines to exploring alternative sourcing. The key is to maintain flexibility and resilience in the face of changing trade policies.
- Diversifying Supply Chains: Expanding sourcing options beyond a single region reduces reliance on specific countries, minimizing the impact of tariffs on a single supplier. For example, a manufacturer that previously sourced all components from China might begin sourcing from Vietnam, India, or Southeast Asia, hedging against potential tariff increases. This diversification is crucial for maintaining production continuity and lowering vulnerability.
- Hedging Strategies: Implementing financial instruments, like forward contracts or options, to mitigate potential financial losses from currency fluctuations and tariff changes. These instruments allow companies to lock in prices for raw materials or finished products, protecting them from adverse market movements. This strategy is akin to insuring against potential economic storms.
- Inventory Management: Optimizing inventory levels allows companies to weather temporary supply chain disruptions caused by tariffs. Strategic inventory accumulation during periods of anticipated price stability can buffer the effects of short-term tariff increases, ensuring a smooth product flow to consumers.
- Technological Innovation: Investing in research and development of new technologies can potentially reduce the reliance on imported components and allow for the development of locally manufactured alternatives. This long-term strategy can reduce dependence on countries imposing tariffs, and create new domestic manufacturing opportunities.
Strategies for Policymakers
Policymakers play a significant role in mitigating the effects of tariff volatility. Their actions can influence the business environment and create stability for the industry.
- Negotiating Trade Agreements: Facilitating negotiations to reduce tariffs or establish trade agreements that minimize the impact of tariff fluctuations on international trade is a vital long-term strategy. This includes seeking mutually beneficial arrangements that foster global economic growth.
- Promoting Transparency and Predictability: Creating clear and predictable trade policies reduces uncertainty and encourages investment. Consistent trade policies, minimizing sudden changes, create a stable business environment where manufacturers can better anticipate and plan for the future.
- Supporting Domestic Manufacturing: Policies that incentivize investment in domestic production can bolster resilience and reduce reliance on foreign imports. This support, coupled with other strategies, creates a more robust and diversified manufacturing landscape.
- International Cooperation: Collaboration between countries can lead to more equitable trade practices and reduce the use of tariffs as a primary trade policy tool. This involves working together to establish global trade agreements that benefit all participants.
Effectiveness of Mitigation Strategies
The effectiveness of each mitigation strategy depends on various factors, including the magnitude of tariff changes, the industry’s responsiveness, and the overall economic climate.
| Mitigation Strategy | Effectiveness | Factors Affecting Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Diversifying Supply Chains | High | Number of alternative suppliers, geographical spread, political stability in new regions |
| Hedging Strategies | Moderate to High | Accuracy of market forecasts, volatility of currency markets, complexity of hedging instruments |
| Inventory Management | Moderate | Predictability of tariff changes, inventory carrying costs, storage capacity |
| Technological Innovation | High (long-term) | R&D investment, time required for development, market adoption |
| Negotiating Trade Agreements | High (long-term) | Political will, negotiating skills, potential for trade-offs |
| Promoting Transparency and Predictability | Moderate to High | Implementation consistency, political stability, global economic context |
| Supporting Domestic Manufacturing | Moderate (long-term) | Incentive strength, industry support, infrastructure development |
| International Cooperation | High (long-term) | Political will, agreement enforcement, global economic stability |
Final Wrap-Up
In conclusion, IDC’s reduced smartphone shipment forecast underscores the significant impact of tariff volatility on the global tech industry. The report’s analysis of regional breakdowns, manufacturer performance, and market trends provides a comprehensive understanding of the situation. Looking ahead, potential mitigation strategies for manufacturers and policymakers are discussed, offering insights into how to navigate this challenging period. Ultimately, the future of the smartphone market hinges on the ability to manage these complex global dynamics.

