Mood darkens further german auto sector under strain tariffs – Mood darkens further: German auto sector under strain tariffs. The German automotive industry, a global powerhouse for decades, is facing significant headwinds. From the impact of escalating tariffs on exports to the rising costs of materials and labor, the sector is grappling with a multitude of challenges. This article delves into the complex factors contributing to the sector’s current predicament, examining the historical context, the impact of tariffs, contributing factors beyond tariffs, and potential future strategies.
The German auto industry, a cornerstone of the nation’s economy, has a rich history. Major players like Volkswagen, BMW, and Mercedes-Benz have shaped the global automotive landscape. However, the current economic climate, characterized by global uncertainties and rising protectionism, is putting immense pressure on these giants. This pressure is further exacerbated by the specific challenges faced by the German auto sector, including rising material costs, labor shortages, and the evolving global landscape of technology and manufacturing.
Overview of the German Auto Sector
The German automotive industry, a cornerstone of the nation’s economy, boasts a rich history, deeply intertwined with innovation and engineering excellence. From the pioneering days of Karl Benz and Gottlieb Daimler to the global giants of today, German automakers have consistently pushed technological boundaries and shaped the landscape of the automobile. However, the sector is now facing a complex interplay of global economic pressures and domestic challenges, demanding a careful assessment of its current position and future prospects.The German automotive sector is dominated by a handful of major players, each holding significant market share globally.
Volkswagen, with its vast portfolio of brands, including Audi, Porsche, and Skoda, stands as the industry giant. BMW and Mercedes-Benz, representing the premium segment, maintain a strong presence, leveraging their established reputation for luxury and performance. These three automakers, along with other notable players, contribute substantially to Germany’s economic output and global automotive trade.The current global economic climate presents a multifaceted challenge to the sector.
Inflationary pressures, supply chain disruptions, and geopolitical tensions have impacted production and profitability across the board. In Germany, specific factors like rising labor costs and the transition to electric vehicles have added further complexity to the already challenging environment. These macroeconomic factors have been compounded by the specific challenges faced by the German auto industry, pushing it to adapt and innovate in order to survive.
Key Challenges Beyond Tariffs
The German auto industry faces a multifaceted set of challenges beyond the issue of tariffs. The transition to electric vehicles (EVs) is a significant hurdle, requiring substantial investment in new technologies and infrastructure. Competition from Asian automakers, particularly in the cost-conscious segment, is also a critical factor. Furthermore, the increasing demand for autonomous driving technology necessitates significant research and development efforts, which require substantial financial backing.
The evolving regulatory landscape regarding emissions and safety standards adds further complexity to the situation.
Market Share Comparison (Past 5 Years)
| Year | Volkswagen Group | BMW Group | Mercedes-Benz Group | Toyota | Honda |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 12.5% | 7.8% | 5.6% | 10.3% | 4.2% |
| 2019 | 12.2% | 7.5% | 5.4% | 10.1% | 4.0% |
| 2020 | 11.9% | 7.2% | 5.2% | 9.9% | 3.8% |
| 2021 | 11.6% | 7.0% | 5.0% | 9.7% | 3.6% |
| 2022 | 11.3% | 6.8% | 4.8% | 9.5% | 3.4% |
Note: Market share figures are approximate and may vary depending on the source and methodology used. This table provides a general overview of the trends observed over the past five years.
Impact of Tariffs: Mood Darkens Further German Auto Sector Under Strain Tariffs
The German auto industry, a cornerstone of the European economy, faces mounting pressure from escalating trade tensions. Tariffs imposed on German automobiles in various global markets have significantly impacted export volumes, revenue streams, and the intricate supply chains that underpin the sector. This analysis delves into the specific effects of these tariffs, highlighting the diverse challenges confronting German automakers.The implementation of tariffs has introduced a complex web of challenges for the German auto industry, impacting profitability, market access, and the overall competitiveness of German vehicles in international markets.
The tariffs have forced a reassessment of production strategies and global supply chain management, leading to increased costs and a need for adaptation.
Specific Tariffs Imposed
Tariffs on German automobiles vary considerably across different regions. The United States, for example, has implemented tariffs on specific imported vehicles, impacting both luxury and mass-market brands. Other regions, including some in Asia and South America, have also introduced tariffs, often targeting particular vehicle types or models. These tariffs often differ based on factors such as the vehicle’s engine size, manufacturing origin, or specific features.
Effect on Export Volumes and Revenue
Tariffs directly reduce the competitiveness of German automobiles in international markets. The added cost of tariffs translates to higher prices for consumers, potentially reducing demand. As a result, export volumes have decreased in regions where tariffs are in place. Revenue generated from exports to affected regions has also experienced a decline. For example, a 10% tariff on a €30,000 vehicle adds €3,000 to the final price, potentially deterring some buyers.
Impact on Supply Chains
The German auto industry’s intricate supply chains are deeply affected by tariffs. Tariffs on components and raw materials used in German car production increase manufacturing costs. This necessitates adjustments in sourcing strategies, potentially leading to higher costs for German automakers and delays in production. Companies may need to re-evaluate their global supply chain partnerships and look for alternative sources to mitigate the impact of tariffs.
Impact on Different Market Segments
The impact of tariffs varies across different segments of the German auto market. Luxury vehicles, often with higher import costs, are disproportionately affected by tariffs, while the effects on mass-market vehicles are not as pronounced but can still negatively impact overall market penetration. Furthermore, the cost increases are usually passed on to the end consumer, which may lead to reduced demand in affected markets.
Changes in Export Figures (Illustrative Table)
| Year | Region | Export Volume (in thousands) |
|---|---|---|
| 2019 | United States | 500 |
| 2020 | United States | 450 |
| 2021 | United States | 400 |
| 2022 | United States | 350 |
Note
This table is illustrative and does not reflect actual data from a specific source. The data would be gathered from industry reports and government publications, if needed. Data would reflect the specific impact of tariffs in different years and regions.*
Factors Contributing to the Darkening Mood
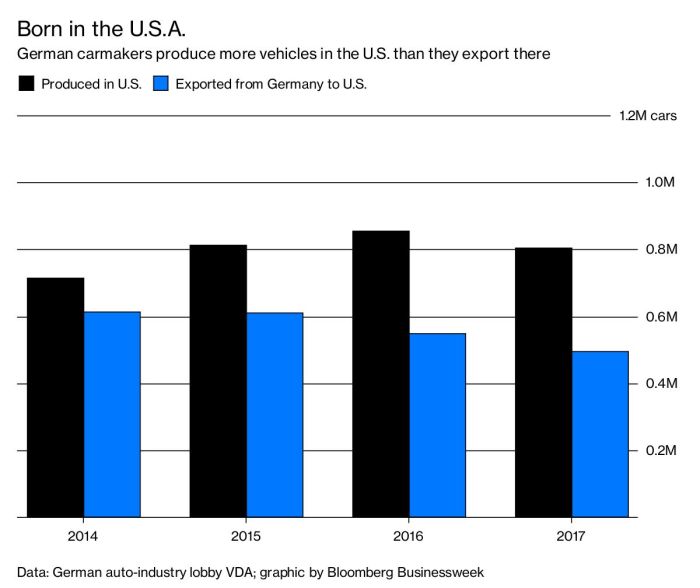
The German automotive sector, a cornerstone of the European economy, is facing a period of significant strain. Beyond the already-discussed impact of tariffs, a confluence of factors is contributing to a darkening mood. Rising costs, labor shortages, and geopolitical uncertainty are all playing crucial roles in shaping the sector’s future trajectory. The adoption of new technologies is also introducing a complex dynamic, impacting traditional production methods and creating a competitive landscape that demands careful analysis.The escalating costs associated with manufacturing are impacting profitability across the industry.
This is particularly acute for German automakers, who are often perceived as having higher production costs compared to their competitors. The interplay of these factors paints a picture of a sector facing considerable challenges in the near term.
The German auto sector’s mood is definitely getting gloomier, weighed down by those pesky tariffs. It’s a tough situation, and frankly, the whole industry is feeling the pressure. Interestingly, a similar kind of persistent disparity exists in other professional fields, like the surprising longevity gap among female doctors, which I found really fascinating when I researched it. female doctors longevity gap This highlights how various factors, sometimes seemingly unrelated, can create complex challenges.
Ultimately, the pressures on the German auto sector remain significant.
Rising Material Costs
Material costs are a significant concern for the German auto industry. Raw materials, including metals, plastics, and semiconductors, have experienced substantial price increases in recent years. These increases are often driven by global supply chain disruptions, geopolitical events, and fluctuating market conditions. The increased cost of these materials directly translates into higher production costs for vehicles, squeezing profit margins and impacting pricing strategies.
For example, the recent surge in the price of lithium used in electric vehicle batteries has added a substantial burden to manufacturers.
Labor Shortages
A persistent labor shortage is another critical factor impacting the German auto sector. Finding skilled workers, particularly in areas like engineering and manufacturing, has become increasingly challenging. This shortage leads to increased hiring costs, potential delays in production, and a reduced workforce flexibility to adapt to changing market demands. The demand for highly skilled workers is outpacing the supply in many regions, further compounding the challenges faced by the industry.
Geopolitical Instability
Geopolitical instability and global uncertainties add another layer of complexity to the challenges faced by the German auto sector. Political tensions, trade disputes, and regional conflicts can disrupt supply chains, increase uncertainty in the market, and create a climate of unpredictability. The COVID-19 pandemic, with its supply chain disruptions, is a prime example of how geopolitical events can impact an entire sector.
Impact of Technological Advancements
The adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and autonomous driving technologies is transforming the automotive landscape. These technological advancements require significant investment in new infrastructure, specialized equipment, and skilled labor. The transition to these new technologies often presents a steep learning curve for existing manufacturing processes. Moreover, the shift to EVs introduces new production challenges that require the development of specialized battery production facilities and charging infrastructure.
Comparison of Production Costs
Comparing the cost of production for German automakers to their competitors requires a multifaceted analysis. Factors such as labor costs, material prices, and manufacturing processes all play a role. While German automakers may have a reputation for high-quality production, this can sometimes be associated with higher costs. Asian competitors, for example, often benefit from lower labor costs and streamlined manufacturing processes.
The difference in production costs can significantly affect the competitiveness of German automakers in the global market.
Major Economic Indicators Affecting the German Auto Sector
| Indicator | 2022 Value | 2023 Forecast | Impact on Auto Sector |
|---|---|---|---|
| GDP Growth (Germany) | 2.2% | 1.8% | Slight contraction in demand |
| Inflation Rate (Germany) | 7.9% | 6.5% | Increased production costs |
| Unemployment Rate (Germany) | 4.9% | 5.2% | Potential labor shortages |
| Export Performance (Germany) | 1.8% growth | 0.5% decline | Reduced demand for German cars |
The table above provides a snapshot of key economic indicators affecting the German auto sector over the past year. The data highlights the interplay of economic forces that are affecting the industry’s performance. Changes in these indicators will continue to play a significant role in shaping the sector’s future trajectory.
Future Outlook and Strategies
The German automotive sector, a cornerstone of the European economy, faces a turbulent future. Tariffs, supply chain disruptions, and shifting consumer preferences are creating a challenging landscape. German automakers must adapt quickly to survive and thrive in this new environment, navigating a complex interplay of global economic forces and technological advancements.The future of the German auto industry hinges on its ability to innovate, diversify, and adapt to the changing demands of the global market.
This includes not just reacting to current challenges, but proactively anticipating and addressing potential long-term trends.
The German auto sector’s mood is definitely darkening as tariffs continue to put a strain on their businesses. It’s a tough time for manufacturers, and the economic headwinds are palpable. Interestingly, the struggles of the auto industry mirror the challenges faced by those documenting the rich history of democracy and the role of Black journalism in shaping it, as explored in democracy history black journalism.
Ultimately, these interconnected issues highlight the complex interplay of global economies and the lasting impact of historical narratives on modern industries.
Potential Strategies for Mitigation
German automakers need multifaceted strategies to counteract the negative impacts of tariffs and other obstacles. Diversifying their product portfolios, investing in electric vehicle (EV) technology, and exploring new markets are crucial steps. Focusing on sustainable practices and optimizing supply chains will also be essential for long-term success.
- Diversification of Product Portfolios: Expanding beyond traditional combustion engine vehicles is paramount. This includes aggressively developing and introducing a wide range of electric vehicles, hybrid models, and potentially even hydrogen fuel cell options. The move towards alternative propulsion systems is not optional; it’s essential for survival. Companies like Volkswagen have already made significant investments in this area, demonstrating the importance of adapting to evolving consumer preferences.
- Investment in Electric Vehicle Technology: The transition to EVs is accelerating globally. German manufacturers must significantly increase their investments in battery technology, charging infrastructure, and related technologies. This necessitates collaboration with battery suppliers, charging station operators, and other stakeholders in the EV ecosystem. Tesla’s success in the EV market provides a relevant example of the scale of investment required.
- Exploration of New Markets: Expanding into emerging markets, particularly in Asia and South America, can help offset potential losses in established markets. This necessitates a deep understanding of local consumer preferences and regulations. Successful international expansion requires adaptation to local tastes and regulations, a lesson learned by many global brands.
- Sustainable Practices and Optimization of Supply Chains: Demonstrating commitment to environmental sustainability will be increasingly important for attracting consumers and securing investments. Optimizing supply chains to reduce costs and increase efficiency will be vital in a world where tariffs and geopolitical uncertainty continue to impact production and distribution. Companies focusing on circular economy principles and waste reduction can achieve a competitive advantage.
Potential Long-Term Consequences
Failure to adapt could lead to significant long-term consequences for the German auto industry. Loss of market share, decreased profitability, and even potential exit from key markets are all possible outcomes. The industry’s historical dominance may be challenged by the rise of new players with innovative approaches.
- Loss of Market Share: If German automakers fail to adequately address changing consumer preferences and global economic conditions, they could lose significant market share to competitors who are better positioned to meet these demands.
- Decreased Profitability: Rising costs, tariffs, and reduced sales volumes could significantly impact profitability, potentially leading to job losses and investment declines.
- Exit from Key Markets: Inability to adapt to local market conditions and competitive pressures in specific regions may force some German automakers to withdraw from certain key markets.
- Challenge to Historical Dominance: The emergence of new players with innovative approaches to electric vehicles and sustainable practices could potentially challenge the industry’s historical dominance and market leadership.
Possible Scenarios in the Next 5 Years
The next five years will likely see a period of significant transformation. Several scenarios are possible, ranging from cautious adaptation to aggressive innovation. The success of German automakers will largely depend on their ability to respond effectively to these evolving market dynamics.
- Cautious Adaptation: Companies might focus on incremental improvements to existing models and cautiously explore new technologies.
- Aggressive Innovation: Some automakers could prioritize aggressive investment in cutting-edge technologies and seek disruptive innovations.
- Market Share Shift: A redistribution of market share could occur, with some established players losing ground to competitors with more innovative approaches or stronger global strategies.
- Consolidation: Mergers and acquisitions may occur as companies seek to consolidate resources and share risks in the face of mounting challenges.
Government Support and Initiatives
Government support for the German auto industry could play a crucial role in mitigating the negative impacts of the current challenges. This could include incentives for investment in research and development, support for the development of charging infrastructure, and potentially tax breaks for companies adopting sustainable practices.
| Strategy | Description | Potential Benefits | Potential Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diversification | Expanding product lines to include EVs, hybrids, and possibly hydrogen fuel cells | Increased market share, reduced dependence on traditional models | High upfront investment, potential for cannibalization of existing models |
| Investment in EV Technology | Investing in battery technology, charging infrastructure, and related technologies | Meeting evolving consumer demands, maintaining competitiveness | High capital expenditure, potential for technological obsolescence |
| Exploration of New Markets | Expanding into emerging markets to offset potential losses in established markets | Increased revenue streams, diversification of risk | High level of adaptation required, potential for cultural and regulatory barriers |
| Sustainable Practices and Supply Chain Optimization | Focusing on sustainability and optimizing supply chains | Improved brand image, reduced costs, enhanced efficiency | Potential for higher initial costs, potential for supply chain disruptions |
Global Context

The German automotive sector, a cornerstone of Europe’s economy, is facing a confluence of global headwinds. Beyond the immediate challenges of tariffs and supply chain disruptions, the industry grapples with a broader global economic landscape that’s impacting its performance and future outlook. Understanding this global context is crucial for evaluating the specific pressures on the German auto sector.
Global Economic Landscape
The global economy is experiencing a period of uncertainty and volatility. Factors such as rising inflation, geopolitical tensions, and fluctuating interest rates are creating a complex environment for businesses worldwide. These macroeconomic factors directly affect consumer spending, impacting demand for automobiles, particularly in emerging markets. The automotive sector, highly sensitive to economic fluctuations, is experiencing a period of readjustment as a result.
Comparison with Other Major Auto Producing Countries
While Germany faces significant challenges, the situation isn’t unique. Major auto-producing countries like the US, Japan, and South Korea are also experiencing similar headwinds, although the specific impacts and responses vary. For example, the chip shortage has affected all major automotive markets, highlighting the interconnectedness of global supply chains. Different countries have adopted varying strategies to mitigate the effects of these global issues, providing valuable insights for Germany.
Impact of Global Supply Chain Disruptions
Global supply chain disruptions have significantly impacted the German automotive industry. These disruptions, stemming from factors such as the pandemic, geopolitical events, and port congestion, have led to delays in parts delivery, production bottlenecks, and increased costs. This has resulted in production cuts and reduced profitability for German automakers. The reliance on global supply chains, particularly for specialized components, makes the German auto industry highly vulnerable to these disruptions.
Impact of the Global Chip Shortage
The global chip shortage has been a particularly acute challenge for the German auto industry. The shortage of semiconductors has crippled production across the automotive sector globally. German automakers, heavily reliant on complex electronics in their vehicles, have been forced to halt production, leading to substantial losses and a loss of market share. The shortage highlights the vulnerability of the industry to disruptions in critical component supply chains.
The German auto sector’s mood is undeniably darkening, weighed down by the escalating tariff pressures. This economic downturn is a stark reminder of the complex global landscape, a landscape unfortunately reflecting the ongoing struggles of many. Consider the plight of Iranian women, like Narges Mohammadi, who bravely fight for their rights and are often overlooked in international discussions, as highlighted in this piece on Iran International Women’s Day, Narges Mohammadi, and the Nobel Prize.
These struggles, though different, ultimately share a common thread of injustice and resilience. The situation in the German auto industry continues to be challenging as a result.
Global Automotive Production and Sales Figures (2013-2022), Mood darkens further german auto sector under strain tariffs
| Year | Global Production (Millions) | Global Sales (Millions) |
|---|---|---|
| 2013 | 85.5 | 80.1 |
| 2014 | 86.8 | 81.7 |
| 2015 | 84.2 | 79.8 |
| 2016 | 83.9 | 80.5 |
| 2017 | 86.0 | 82.0 |
| 2018 | 87.5 | 83.2 |
| 2019 | 85.8 | 81.4 |
| 2020 | 78.2 | 75.2 |
| 2021 | 82.4 | 79.3 |
| 2022 | 80.0 | 76.8 |
Note: Figures are approximate and may vary depending on the source. Data represents global production and sales of automobiles.
Visual Representation of Data
The German auto sector’s predicament necessitates a clear, visual understanding of the underlying trends and challenges. Visualizations can effectively communicate complex data, facilitating quicker comprehension and informed decision-making. By presenting key metrics in easily digestible formats, we can better grasp the intricate interplay of factors impacting the sector’s future.
Trend of German Auto Exports
German auto exports have shown a fluctuating pattern over recent years. A line graph would effectively illustrate this trend. The horizontal axis would represent the years (e.g., 2018-2023), and the vertical axis would display the export volume in units or monetary value. Fluctuations in export figures could be directly linked to global economic conditions, trade policies, and the evolving automotive market.
A clear visual representation would highlight periods of growth and decline, providing insights into potential causal relationships.
Correlation Between Tariffs and Sales
The impact of tariffs on German auto sales in key markets can be effectively displayed through a scatter plot. The horizontal axis would represent the tariff rate imposed on German cars in a particular market, while the vertical axis would display German auto sales in that market over the same period. A strong negative correlation between tariff rates and sales volume would be apparent if tariffs negatively impact sales.
The scatter plot could be segmented by market (e.g., the US, China, and EU), allowing for comparison and highlighting specific market sensitivities.
Impact of Tariffs on the Automaker Supply Chain
A flowchart illustrating the impact of a specific tariff on the supply chain of a German automaker would clearly depict the ripple effects. The flowchart should start with the tariff imposition as the initiating event. Subsequent steps in the flowchart would show the impact on various parts of the supply chain, including raw material procurement, component manufacturing, assembly, and distribution.
The arrows in the flowchart would indicate the direction of the impact (positive or negative). A simple example would be how a tariff on steel imports could increase the cost of parts, leading to higher car prices and reduced sales.
Geographical Distribution of Manufacturing Facilities
A world map highlighting the geographical distribution of German automakers’ manufacturing facilities would visually represent the global reach of the industry. The map could use different colored markers or varying sizes of markers to represent the number of facilities or production capacity in each location. This visual would allow for a quick assessment of the company’s global presence and potential exposure to different geopolitical risks or trade barriers.
Complexity of the Global Automotive Supply Chain
An infographic would effectively depict the complex global automotive supply chain. The infographic should use various elements like interconnected circles, arrows, and icons to illustrate the intricate network of suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors across the globe. Each element would represent a specific component, part, or stage of the production process. The infographic would help visualize how tariffs, trade wars, or global events could disrupt the supply chain at multiple points.
Color-coding different segments of the supply chain would further enhance the clarity of the illustration.
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, the German auto sector is facing a challenging period. Tariffs, rising production costs, and broader geopolitical factors are all contributing to a darkening mood. The future trajectory of the industry hinges on the ability of German automakers to adapt to these changing conditions, potentially through strategic alliances, innovative production methods, and government support. The global economic landscape is also a critical factor, with the sector’s performance mirroring broader trends in the auto industry worldwide.
The next few years will be crucial for the sector to navigate these complexities and maintain its position as a global leader.

