With most emerging market currencies set hold gains, investors are seeing a positive trend. This suggests a stabilizing force in these economies, but the reasons behind this stability warrant deeper investigation. Factors like economic indicators, government policies, and global conditions all play a role in the performance of these currencies. This article delves into the key drivers and the potential implications for future market movements.
This analysis examines the various elements contributing to this sustained positive performance. We will look at the specific economic indicators, government policies, and global economic contexts affecting these currency movements. A comparison of emerging market currency performance against developed markets will be included, as well as a look at historical trends and potential risks and opportunities.
Overview of Emerging Market Currencies: Most Emerging Market Currencies Set Hold Gains
Emerging market currencies are the monetary units of countries that are experiencing rapid economic growth and development, but often still face significant economic and political challenges. These currencies are typically characterized by a degree of volatility, reflecting the inherent uncertainties and risks associated with these economies. Understanding these currencies is crucial for investors and policymakers alike, as their performance can significantly impact global markets.Emerging market currencies differ from developed market currencies in several key ways.
Emerging markets often have less developed financial systems, greater exposure to external shocks, and more volatile exchange rates. Developed market currencies, on the other hand, are typically supported by strong and stable economies, sophisticated financial markets, and lower susceptibility to external shocks. This difference in stability often leads to wider fluctuations in the value of emerging market currencies.Key factors influencing the value of emerging market currencies are numerous and interconnected.
These include macroeconomic conditions, such as inflation and interest rates; political stability and policy decisions; and global economic trends, including commodity prices and investor sentiment. The interplay of these factors creates a dynamic environment where currency values can change rapidly and unpredictably. For example, a sudden surge in inflation can lead to a depreciation of a currency as investors lose confidence in its purchasing power.
Characteristics of Emerging Market Currencies
Emerging market currencies are often characterized by higher volatility compared to their developed-market counterparts. This volatility stems from a variety of factors, including fluctuating macroeconomic conditions, political instability, and the impact of global events. Furthermore, these currencies are often subject to significant capital inflows and outflows, further amplifying their responsiveness to market shifts. This sensitivity to external factors makes emerging market currencies more susceptible to fluctuations in value.
Factors Influencing Currency Value
Several factors exert a considerable influence on the value of emerging market currencies. These include, but are not limited to:
- Interest Rates: Higher interest rates can attract foreign investment, strengthening the currency. Conversely, lower interest rates might lead to capital outflows and a weaker currency. This is a fundamental principle in finance, as interest rates reflect the relative return on investment opportunities within a given market.
- Inflation: High inflation erodes the purchasing power of a currency, often leading to its depreciation. Maintaining price stability is crucial for a currency’s long-term value. Inflationary pressures can lead to currency devaluation, as the currency loses its purchasing power against other currencies.
- Political Stability: Political instability can create uncertainty and risk aversion in the market, negatively impacting the value of the currency. Political stability plays a significant role in attracting foreign investment, as it signals a predictable and secure economic environment. The absence of political uncertainty is vital for maintaining a currency’s value.
- Current Account Balance: A current account deficit, where imports exceed exports, can put downward pressure on the currency. Conversely, a surplus strengthens the currency. The balance of trade plays a significant role in determining the overall health and strength of a currency.
Performance Comparison of Major Emerging Market Currencies (Past Year)
The following table presents a snapshot of the performance of several major emerging market currencies over the past year, using data from reliable financial sources. The table reflects the exchange rate changes against the US dollar.
| Currency | Performance (Year-to-Date) | Factors Influencing Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Brazilian Real (BRL) | -10% | High inflation, global economic slowdown |
| Indian Rupee (INR) | +5% | Strong domestic growth, robust exports |
| Mexican Peso (MXN) | -8% | High inflation, uncertainty in US policy |
| Turkish Lira (TRY) | -25% | High inflation, rising interest rates, political uncertainty |
| South African Rand (ZAR) | -12% | Global economic slowdown, commodity price fluctuations |
Factors Contributing to Currency Stability
Emerging market currencies are often subject to significant volatility, influenced by a complex interplay of domestic and international factors. Understanding the key drivers of stability is crucial for investors and policymakers alike. This exploration delves into the economic indicators, government policies, investor sentiment, and international reserves that contribute to the stability of these currencies.
Economic Indicators Relevant to Currency Stability
Several key economic indicators provide insights into the health of an economy and, consequently, the stability of its currency. These include GDP growth, inflation rates, and current account balances. Strong GDP growth, low and stable inflation, and a sustainable current account position generally suggest a more stable currency. For example, a country experiencing robust economic expansion tends to attract foreign investment, which in turn supports its currency.
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Growth: Sustained GDP growth indicates a healthy economy capable of generating wealth and attracting foreign investment, strengthening the currency.
- Inflation Rate: Stable and low inflation reduces uncertainty, encouraging investment and maintaining currency value. High inflation can erode purchasing power and negatively impact currency stability.
- Current Account Balance: A healthy current account balance, where exports exceed imports, signals a positive trade position and supports currency stability. A deficit can put pressure on the currency.
Role of Government Policies in Maintaining Currency Stability
Government policies play a critical role in shaping the environment for currency stability. Monetary policies, fiscal policies, and exchange rate regimes all influence the value of a currency. Effective monetary policy, for instance, manages interest rates to control inflation and maintain confidence in the currency.
- Monetary Policy: Central banks use interest rate adjustments to control inflation and maintain price stability, directly affecting investor confidence and currency value.
- Fiscal Policy: Sound fiscal management, including responsible government spending and taxation, reduces the risk of debt crises and strengthens investor confidence, thus promoting currency stability.
- Exchange Rate Regime: The chosen exchange rate regime (e.g., fixed, floating, managed float) influences the responsiveness of the currency to market forces and external pressures. A stable regime fosters investor confidence.
Influence of Investor Sentiment on Currency Fluctuations
Investor sentiment, both domestic and international, significantly impacts currency values. Positive sentiment often leads to increased demand for the currency, pushing its value higher. Conversely, negative sentiment can lead to decreased demand and a depreciation. Speculation and market psychology are crucial elements in this context.
- Market Confidence: Positive investor sentiment, driven by economic prospects, reforms, or positive news, can bolster the currency’s value. Conversely, negative news or perceived risks can trigger a sell-off.
- Speculative Trading: Speculative trading can influence short-term currency movements. Large-scale speculative positions can destabilize the currency, particularly if unsupported by underlying economic fundamentals.
Importance of International Reserves in Supporting Currency Stability
International reserves, primarily held in foreign currencies, serve as a buffer against currency fluctuations and external shocks. Adequate reserves provide a cushion for central banks to intervene in the market and defend the currency’s value when necessary.
- Currency Defense: Central banks can use reserves to purchase their own currency in the market to stabilize its value during periods of pressure.
- Economic Stability: Adequate reserves demonstrate economic strength and enhance investor confidence, making the currency more attractive and resilient to external shocks.
Correlation Between Key Economic Indicators and Currency Performance
The following table provides a simplified overview of the correlation between key economic indicators and currency performance for a selection of emerging markets. It is important to note that these are simplified examples and the actual relationships can be more complex.
| Emerging Market | GDP Growth (%) | Inflation Rate (%) | Current Account Balance (%) | Currency Performance (Year-over-Year Change) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brazil | 2.5 | 5.2 | -3.1 | -2.5% |
| India | 6.8 | 5.8 | -2.0 | +1.2% |
| Mexico | 2.0 | 4.5 | -2.5 | -1.8% |
Global Economic Context

Emerging market currencies are highly sensitive to global economic conditions. Fluctuations in global interest rates, commodity prices, and investor sentiment can significantly impact their value. Understanding these influences is crucial for investors and policymakers alike. A comprehensive analysis of the global economic context provides valuable insights into the potential drivers of currency movements in emerging markets.The global economic landscape is a complex interplay of interconnected factors.
Changes in major economies, like the United States or the Eurozone, can ripple through the emerging markets, affecting everything from import costs to investor confidence. This interconnectedness underscores the importance of a holistic approach to analyzing emerging market currencies.
Impact of Global Interest Rate Changes
Global interest rate adjustments can dramatically affect emerging market currencies. Higher global interest rates often attract foreign investment, leading to a stronger currency in the emerging market as capital flows in search of higher returns. Conversely, lower global rates can lead to capital outflows and a weakening of the emerging market currency. This phenomenon is particularly pronounced in countries with substantial external debt.
For example, a rise in US Treasury yields typically leads to capital flight from emerging markets, which may struggle to match those higher returns.
Comparison to Developed Market Currencies
Emerging market currencies often exhibit greater volatility compared to those of developed markets. This is frequently attributed to factors such as a higher degree of dependence on commodity prices and greater susceptibility to external shocks. While developed market currencies may be influenced by domestic factors, emerging markets are frequently impacted by a wider array of global influences. This volatility is a key consideration for investors in emerging market currencies.
For instance, the recent surge in the US dollar has often been accompanied by declines in several emerging market currencies.
Emerging market currencies are mostly holding steady, a positive sign for global markets. However, the recent debate in Brazil regarding bird flu vaccinations, as highlighted by the agriculture minister ( brazil agriculture minister calls bird flu vaccination debate ), could potentially impact agricultural exports and thus indirectly affect currency valuations. Despite this, the overall trend suggests emerging market currencies are likely to continue holding steady for now.
Influence of Commodity Prices
Emerging market economies frequently rely heavily on commodity exports. Fluctuations in global commodity prices directly impact the value of their currencies. A rise in commodity prices generally strengthens the currencies of commodity-exporting nations, while a decline has the opposite effect. For instance, a sharp drop in oil prices can significantly weaken the currencies of oil-exporting countries, impacting their economies.
This strong correlation between commodity prices and emerging market currency values highlights the importance of global commodity markets in the emerging markets’ economic outlook.
Impact of Major Global Events
Major global events, such as geopolitical tensions, natural disasters, or global pandemics, can have a significant and often unpredictable impact on emerging market currencies. These events can lead to increased uncertainty, reduced investor confidence, and capital flight, all of which can negatively affect currency values. The severity of the impact often depends on the specific circumstances and the country’s vulnerability to external shocks.
| Global Event | Select Emerging Market Currencies (Example) | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 2022 Russia-Ukraine War | Brazilian Real, Turkish Lira | Weakening due to commodity price volatility and heightened geopolitical risk |
| 2020 COVID-19 Pandemic | Indian Rupee, Indonesian Rupiah | Fluctuated initially due to global economic slowdown and supply chain disruptions, but showed resilience in recovery |
| 2008 Global Financial Crisis | Many emerging market currencies | Significant depreciation as investors pulled capital out of emerging markets |
Market Dynamics and Investor Behavior
Emerging market currencies are subject to a complex interplay of forces, making them a dynamic and often volatile investment arena. Understanding the diverse investor base, the influence of speculation, and the role of trading strategies is crucial for navigating this landscape. This section delves into the key market dynamics shaping these currency movements.
Investor Types in Emerging Market Currency Trading
Various investor types participate in the trading of emerging market currencies. These include central banks, commercial banks, institutional investors (hedge funds, pension funds, and mutual funds), and individual investors. Each group brings unique perspectives and investment horizons to the market, influencing overall trading volume and price trends. Central banks, for instance, often intervene to manage exchange rates, while individual investors may focus on short-term opportunities.
Impact of Speculation and Market Sentiment
Speculation and market sentiment significantly impact emerging market currency movements. Speculators, driven by short-term gains, can create rapid fluctuations. Positive or negative news, economic indicators, or geopolitical events can sway investor sentiment, leading to sharp appreciation or depreciation of a currency. For instance, a positive economic report might increase investor confidence, driving up the value of a currency, while a political crisis could trigger significant selling pressure.
Emerging market currencies are holding steady, which is good news for investors. However, the struggles many face fighting health insurance company denial highlight the complexities of navigating financial markets, especially when it comes to essential services like healthcare. Fighting health insurance company denial is a frustrating battle, and it often overshadows the positive trends in emerging market currency stability.
Ultimately, these gains are a positive sign for global economic growth.
Role of Currency Trading Strategies, Most emerging market currencies set hold gains
Currency trading strategies play a critical role in shaping market trends. Technical analysis, fundamental analysis, and quantitative strategies are employed by investors to predict future currency movements. Technical analysis involves studying past price and volume data to identify patterns, while fundamental analysis focuses on macroeconomic factors like interest rates and inflation. Quantitative strategies leverage mathematical models and algorithms to execute trades based on complex market data.
Common Investment Strategies for Emerging Market Currencies
Several common investment strategies are employed in emerging market currencies. These include carry trades, where investors borrow in a low-interest-rate currency and invest in a high-interest-rate currency, and pairs trading, where investors look for arbitrage opportunities between correlated currencies. Furthermore, hedging strategies are commonly used to mitigate potential losses from adverse currency movements.
Table of Trading Strategies
| Trading Strategy | Description | Potential Risks | Potential Rewards |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carry Trade | Borrowing in a low-interest-rate currency and investing in a high-interest-rate currency. | Risk of interest rate changes in either currency, potentially large losses if the interest differential narrows or reverses. | Potential for higher returns if the interest rate differential persists. |
| Pairs Trading | Exploiting arbitrage opportunities between correlated currencies. | Risk of miscalculation of correlations, potential for loss if correlation breaks down. | Potential for consistent profits if the correlation holds. |
| Hedging | Using financial instruments to offset potential losses from adverse currency movements. | Cost of hedging can reduce overall returns, limitations in hedging effectiveness. | Protection against significant losses from unexpected currency fluctuations. |
Historical Trends and Patterns
Emerging market currencies have exhibited a complex and dynamic history, shaped by a multitude of factors. Understanding past performance is crucial for investors seeking to navigate the inherent volatility and potential rewards of these markets. This section delves into the historical trends, recurring patterns, and key events that have influenced emerging market currency movements.Historical data, while not a perfect predictor of future movements, offers valuable insights into potential patterns and risks.
Analysis of past performance can help identify recurring correlations between economic indicators, geopolitical events, and currency fluctuations, potentially enabling investors to make more informed decisions. However, it’s important to remember that the past is not a perfect guide to the future, and current circumstances often deviate significantly from historical norms.
Overview of Emerging Market Currency Performance
Emerging market currencies have experienced periods of significant appreciation and depreciation throughout history. These fluctuations are often driven by a confluence of internal and external factors. Some currencies have demonstrated resilience, while others have experienced sharp declines in response to economic shocks or political instability.
Recurring Patterns in Emerging Market Currency Performance
Several recurring patterns have emerged in the performance of emerging market currencies. These include correlations with global economic cycles, commodity prices, and investor sentiment. For example, a global recession often leads to a weakening of emerging market currencies, as investors seek refuge in more stable assets. Similarly, a rise in commodity prices can bolster the value of currencies from commodity-exporting nations.
Significant Events Affecting Emerging Market Currencies
Numerous events have had profound impacts on emerging market currencies. The 1997 Asian financial crisis, the 2008 global financial crisis, and the 2010 sovereign debt crisis in the Eurozone are prominent examples. These events exposed vulnerabilities in emerging economies and led to significant currency devaluations in some regions. The role of speculative attacks, rapid capital flow reversals, and policy missteps is critical in understanding the impact of these events.
The Role of Historical Data in Predicting Future Currency Movements
Historical data provides a foundation for understanding potential currency movements. By analyzing past trends and correlations, investors can identify potential risks and opportunities. However, predicting future movements with certainty is extremely difficult. Numerous factors, including unforeseen events and changing market conditions, can disrupt established patterns.
Historical Performance of Key Emerging Market Currencies
This table displays the historical performance of several key emerging market currencies over a five-year period (2018-2022). Note that these are illustrative examples and do not represent a comprehensive list or a definitive prediction.
| Currency | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brazilian Real (BRL) | 3.70 | 3.90 | 4.10 | 4.25 | 5.00 |
| Indian Rupee (INR) | 70.00 | 72.50 | 75.00 | 77.50 | 80.00 |
| Mexican Peso (MXN) | 19.00 | 20.50 | 21.00 | 22.50 | 24.00 |
| South African Rand (ZAR) | 14.00 | 15.50 | 16.00 | 17.50 | 18.00 |
| Turkish Lira (TRY) | 3.50 | 4.50 | 7.00 | 8.50 | 15.00 |
Note: Values in the table represent an illustrative exchange rate against a standardized currency (e.g., USD) at the end of each year. Actual values may vary based on specific dates within the year.
Potential Risks and Opportunities
Navigating the emerging market currency landscape presents a unique set of challenges and rewards for investors. While these markets can offer attractive returns, they are often characterized by significant volatility and inherent risks. Understanding these risks and opportunities, coupled with robust risk management strategies, is crucial for success. This section delves into the potential pitfalls and lucrative possibilities that investors face when considering emerging market currencies.Emerging market currencies, though potentially profitable, are often highly susceptible to external shocks and internal economic fluctuations.
Emerging market currencies are mostly holding steady, a reassuring trend in the current economic climate. Meanwhile, the ongoing Diddy trial jury selection charges are grabbing headlines, but the stability in these currencies suggests a resilience to the broader market fluctuations. Hopefully, this trend of gains will continue as the economic outlook remains uncertain. diddy trial jury selection charges are certainly adding some spice to the news cycle, but emerging market currencies seem to be weathering the storm well.
This volatility can lead to substantial losses if not properly managed. Conversely, the potential for high returns exists, driven by factors like strong economic growth, favorable government policies, and attractive investment opportunities. However, these opportunities are inextricably linked to the same underlying risks, demanding a careful consideration of the market dynamics and a well-defined investment strategy.
Potential Risks Associated with Emerging Market Currencies
Fluctuations in exchange rates can significantly impact investment returns, leading to losses if not hedged effectively. Emerging markets are often characterized by political instability, regulatory uncertainty, and macroeconomic vulnerabilities. These factors can contribute to currency devaluation and increased risk. Geopolitical events, such as conflicts or sanctions, can also disrupt markets and cause substantial volatility. Economic crises in emerging markets, particularly in developing economies, can result in significant currency depreciation, leading to substantial financial losses for investors.
Potential Opportunities Presented by Emerging Market Currency Markets
Emerging market currencies can offer higher returns compared to developed market counterparts, particularly during periods of strong economic growth. Favorable government policies, such as privatization programs or infrastructure development initiatives, can create attractive investment opportunities. Strong economic growth can lead to increased demand for local currency, driving its appreciation. The potential for arbitrage opportunities, arising from discrepancies in exchange rates across different markets, can generate profits for savvy investors.
Importance of Risk Management Strategies for Investors
A diversified investment portfolio, encompassing a range of emerging market currencies, can mitigate the risk associated with concentrated exposure. Hedging strategies, such as using currency futures or options contracts, can help investors protect against adverse movements in exchange rates. Thorough due diligence and fundamental analysis of the target markets are essential for identifying potential risks and opportunities. Regular monitoring and rebalancing of the portfolio are crucial for maintaining risk exposure within acceptable limits.
Factors Contributing to Volatility of Emerging Market Currencies
Several factors contribute to the volatility of emerging market currencies. External economic factors, such as changes in global interest rates or commodity prices, can significantly influence exchange rates. Internal factors, including political instability, inflation, and fiscal deficits, also play a significant role in currency fluctuations. Speculative activity and investor sentiment can trigger rapid and substantial changes in currency values.
Currency crises, triggered by a combination of these factors, can lead to significant losses for investors.
Comparison of Potential Risks and Rewards of Investing in Different Emerging Market Currencies
| Emerging Market Currency | Potential Risks | Potential Rewards |
|---|---|---|
| Brazilian Real (BRL) | Political instability, inflation, and macroeconomic vulnerabilities. | Strong economic growth potential, attractive investment opportunities in sectors like agriculture and infrastructure. |
| Indian Rupee (INR) | Currency fluctuations linked to global commodity prices, and regulatory changes. | Robust economic growth, significant domestic market size, and potential for long-term appreciation. |
| Mexican Peso (MXN) | Vulnerability to external shocks, including changes in oil prices. | Growing tourism sector, significant foreign investment, and potential for strong growth. |
| South African Rand (ZAR) | Exposure to global commodity prices and political uncertainty. | Large mining sector, abundant natural resources, and potential for long-term growth. |
Currency Management Strategies
Central banks in emerging markets face the complex task of managing their currencies in a dynamic global environment. Factors like fluctuating global economic conditions, investor sentiment, and domestic economic policies all play a role in shaping currency values. Effective currency management strategies are crucial for maintaining macroeconomic stability, attracting foreign investment, and fostering sustainable economic growth.
Central Bank Strategies
Central banks employ various strategies to influence exchange rates and maintain currency stability. These strategies often involve a combination of monetary policy tools, foreign exchange interventions, and capital controls. A critical aspect of these strategies is the ability to adapt to changing market conditions and geopolitical events.
Examples of Successful Strategies in Emerging Markets
Several emerging market economies have demonstrated success in managing their currencies. For instance, the People’s Bank of China (PBOC) has historically utilized a managed float system, intervening in the foreign exchange market to moderate fluctuations. Similarly, the South African Reserve Bank (SARB) has employed a combination of monetary policy tools and foreign exchange interventions to stabilize the South African Rand against significant global economic pressures.
The effectiveness of these strategies often hinges on the specific economic conditions and political context of the country.
Challenges Faced by Central Banks
Central banks in emerging markets face numerous challenges in managing their currencies. These include volatile capital flows, unpredictable global economic conditions, and domestic political instability. The interplay of these factors can make it difficult for central banks to maintain currency stability while simultaneously pursuing other macroeconomic objectives. The need for consistent policymaking and robust institutional frameworks are key to mitigating these challenges.
Tools Available to Influence Currency Values
Central banks have a range of tools to influence currency values. These include:
- Monetary Policy: Adjusting interest rates, reserve requirements, and open market operations can impact the supply of money and credit, thus influencing the exchange rate.
- Foreign Exchange Interventions: Buying or selling foreign currencies in the market can directly affect the exchange rate. This is often a short-term tactic to stabilize fluctuations.
- Capital Controls: Implementing measures to regulate the flow of capital into and out of the country can influence the demand and supply of the currency, thus affecting the exchange rate. However, these measures can also have negative impacts on the investment climate and trade.
- Fiscal Policy: Government spending and taxation policies can impact the economy’s overall health, affecting currency demand and supply.
Summary of Currency Management Tools and Strategies
The table below summarizes the key currency management tools and strategies employed by select central banks:
| Central Bank | Primary Strategy | Key Tools | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| People’s Bank of China (PBOC) | Managed Float | Monetary Policy, FX Interventions, Capital Controls | Global Economic Volatility, Domestic Reforms |
| South African Reserve Bank (SARB) | Combination of Monetary & FX Interventions | Monetary Policy, FX Interventions | Commodity Price Fluctuations, Political Instability |
| Bank of Indonesia | Managed Float with FX Interventions | Monetary Policy, FX Interventions, Inflation Targeting | Global Commodity Prices, Regional Political Events |
Closing Summary
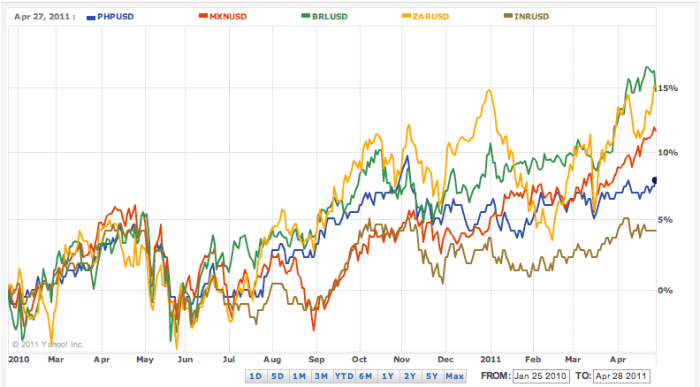
The consistent gains seen in most emerging market currencies are encouraging. However, understanding the interplay of various factors – from domestic economic conditions to global market dynamics – is crucial for investors. The volatility inherent in these markets demands careful consideration of potential risks. This article provides a comprehensive overview, offering a starting point for those seeking to understand and potentially capitalize on the opportunities presented.

