Rare earth china tariffs metals minerals are reshaping global supply chains. China’s dominance in rare earth mining and processing has long been a cornerstone of various industries, from electronics to renewable energy. However, recent tariffs and geopolitical shifts are forcing a re-evaluation of this dependence. This exploration delves into the historical context, the economic impact, alternative sources, environmental considerations, and the evolving geopolitical landscape surrounding these critical materials.
The global dependence on rare earth metals mined primarily in China has become a focal point of recent trade disputes and geopolitical maneuvering. Understanding the intricacies of this supply chain, from the extraction methods to the impact on consumer prices, is crucial to navigating the complexities of this market. The following sections will unpack the various dimensions of this global challenge.
Global Rare Earth Supply Chain
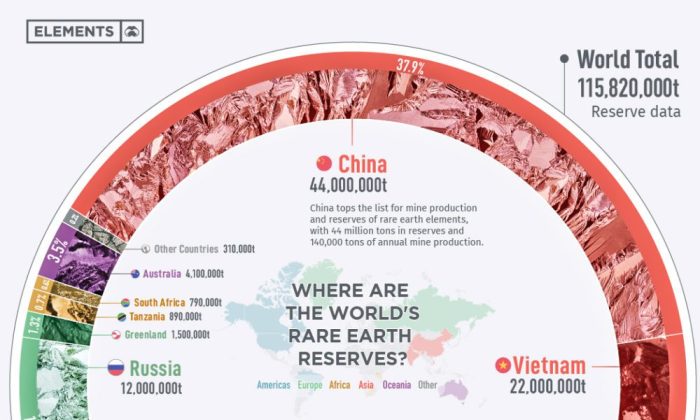
The global economy relies heavily on rare earth elements, critical components in numerous technologies, from smartphones to electric vehicles. Historically, China has dominated the production and processing of these essential minerals, raising concerns about supply chain vulnerabilities and geopolitical implications. This dominance stems from a combination of factors, including abundant resources, advanced extraction techniques, and a supportive industrial infrastructure.The intricate interplay between economic interests and geopolitical strategies significantly shapes the global rare earth supply chain.
Nations increasingly recognize the strategic importance of rare earth minerals, driving efforts to diversify sourcing and develop domestic production capabilities. This shift is fueled by concerns about China’s influence over the market and the potential disruption of supply chains.
Historical Dependence on Chinese Rare Earth
China’s dominance in rare earth production stems from decades of investment in mining, processing, and refining infrastructure. This has resulted in a significant dependence of many industries on Chinese-sourced rare earths. For instance, many manufacturers rely on China for critical rare earth components in their products. This dependence created a vulnerability in the supply chain, making industries susceptible to disruptions in Chinese production or export policies.
Geopolitical Factors Influencing the Global Supply Chain
Geopolitical tensions and trade disputes significantly impact the rare earth market. These factors often manifest as export restrictions or tariffs, impacting the availability and cost of rare earth materials. The political and economic climate in China can directly affect the production and pricing of these materials, thereby affecting global markets. For example, trade disputes can result in disruptions to the supply chain, leading to price fluctuations and delays in product development.
China’s dominance in rare earth metals and minerals has sparked international tariffs and trade disputes. Understanding the historical interplay between governments and universities, like exploring the topic in history government influence universities , reveals potential underlying motivations. Ultimately, the global market for these crucial materials is significantly impacted by this complex web of political and economic factors.
Timeline of Significant Events in the Rare Earth Market
- 2010: China imposed export restrictions on rare earth elements, impacting global supply and prices. This move highlighted China’s influence over the market and prompted other countries to seek alternative sources and methods of production.
- 2010-2020: Increased global demand for rare earth minerals, driven by technological advancements in sectors like renewable energy and electronics, intensified competition for these resources. This led to exploration of new mining areas and the development of new processing technologies.
- 2022: Further global supply chain disruptions, including geopolitical factors, significantly impacted the global market, prompting greater attention to the strategic importance of rare earth minerals.
Comparison of Rare Earth Extraction Methods
Different extraction methods for rare earth minerals have varying environmental impacts and economic feasibility. For example, the conventional method of open-pit mining, while cost-effective, often involves significant land disturbance and environmental concerns. Hydrometallurgical processes, which use chemical leaching, offer a more environmentally friendly alternative but can have different economic tradeoffs. Furthermore, some methods are better suited for certain types of rare earth minerals than others.
Major Countries Involved in Rare Earth Mining and Processing
| Country | Mining Activity | Processing Activity |
|---|---|---|
| China | Extensive and historically dominant | Advanced and extensive |
| United States | Limited but increasing | Limited |
| Australia | Significant reserves | Limited |
| Brazil | Emerging production | Minimal |
| India | Increasing exploration | Developing |
Note: This table represents a snapshot of the situation and does not include all countries with potential rare earth resources.
Economic Impact of Tariffs
Rare earth metals and minerals are crucial for modern technology, powering everything from smartphones to electric vehicles. However, the global supply chain for these vital resources is complex and vulnerable to geopolitical tensions. Tariffs imposed on these materials have significant ripple effects throughout the global economy, impacting consumer prices, industrial production, and international trade.The imposition of tariffs on rare earth metals and minerals disrupts established trade patterns, leading to price fluctuations and supply chain disruptions.
This disruption can manifest in various ways, from increased manufacturing costs to reduced availability of specific materials, ultimately impacting the competitiveness of businesses relying on these materials. The consequences extend beyond the immediate producers and consumers to encompass a vast network of interconnected industries.
Consequences of Tariffs on Consumer Prices
Tariff implementation often leads to a rise in consumer prices. Increased costs for raw materials translate into higher production costs for manufacturers, which are frequently passed on to consumers. This can be observed in the electronics industry, where rare earth elements are essential components in many devices. For example, a tariff on neodymium, a crucial element in magnets used in hard drives and electric motors, could result in a noticeable price increase for computers and other electronic devices.
Similar effects can be seen in the automotive sector, where rare earth magnets are crucial for electric vehicle motors.
Impact on Industrial Production
Tariffs on rare earth metals and minerals directly impact industrial production by raising input costs. Manufacturers face challenges in sourcing materials at competitive prices, potentially hindering their ability to meet production targets and impacting their profitability. The automotive industry, heavily reliant on rare earth magnets for electric vehicles, could face significant production delays and cost increases due to tariffs.
China’s rare earth metals and minerals are a hot topic, especially with the tariffs. It’s a complex situation, and understanding the global supply chain is crucial. This all makes you wonder about your own health, and if you should be taking a fiber supplement. Considering the impact on everyday life, like the essential minerals we use, perhaps a balanced diet is key to your well-being.
This is important for everyone, and a good general health practice. Ultimately, the global supply chain issues, like those surrounding rare earth minerals and tariffs, will continue to affect our lives. should you take fiber supplement is a question many have, but the global market for these minerals continues to be an issue.
Effects on Global Trade Flows and Investment Decisions
Tariffs on rare earth metals and minerals can disrupt global trade flows by increasing the cost of imports and potentially reducing demand. This can lead to a shift in investment decisions, as companies may seek alternative sources of supply to mitigate the impact of tariffs. For instance, a tariff on Chinese rare earth exports could incentivize companies to explore alternative sources in other countries, potentially fostering the development of new mining and processing facilities.
China’s control over rare earth metals and minerals is a hot topic right now, with tariffs impacting the global supply chain. It’s a complex issue, but it’s a lot like setting boundaries with your own parents – you need to be assertive and clear about your needs and limits, without being overly aggressive. Learning how to set healthy boundaries with your family is a crucial skill that can be applied to navigating complex global trade issues, too.
Understanding these dynamics is key to navigating the future of these essential minerals, and finding fair trade practices, just like knowing how to set boundaries in personal relationships can help with family dynamics. how to set boundaries parents Ultimately, finding a sustainable solution for the global supply of these metals is crucial.
Impact on Different Sectors
| Sector | Effect of Tariffs |
|---|---|
| Electronics | Increased prices for consumer electronics, reduced availability of specific components, potential for sourcing shifts. |
| Automobiles | Higher production costs for electric vehicles, potential for delays in EV production, impact on overall automotive industry profitability. |
| Renewable Energy | Increased costs for wind turbines and other renewable energy technologies, potential for reduced deployment of renewable energy projects. |
Potential for Diversification of Rare Earth Supply Sources
Tariffs on rare earth metals and minerals can create opportunities for the diversification of supply sources. Countries with existing rare earth reserves or mining capabilities may see increased investment and production, while other countries might seek to develop their own rare earth extraction industries. For instance, the United States’ efforts to bolster its rare earth supply chain demonstrate the potential for diversification and reduce reliance on specific regions.
This diversification could potentially mitigate the economic impact of tariffs and strengthen global supply chains.
Alternative Sources and Technologies
The reliance on China for rare earth minerals has created a vulnerability in global supply chains. Diversifying sources and developing alternative technologies are crucial for mitigating this risk and ensuring future supply. This exploration examines the potential of alternative sources, current research efforts, and promising technologies to reduce reliance on Chinese rare earths.The shift towards alternative rare earth sources and substitute materials is not just about geopolitical security; it also presents an opportunity for innovation in various sectors.
The development of these alternative approaches can lead to more sustainable and resilient supply chains, potentially impacting environmental footprints and economic structures.
Potential of Alternative Rare Earth Sources
Alternative sources of rare earth minerals exist across the globe. These include countries like Australia, Brazil, and the United States, although extraction and processing infrastructure may not be as developed as in China. Developing these alternative sources requires substantial investment in infrastructure, mining, and processing facilities. The potential of these alternative sources depends heavily on the specific rare earth element, geological formations, and existing infrastructure.
Current Research and Development Efforts
Extensive research is underway to identify and develop rare earth substitutes. Researchers are exploring materials like iron-based compounds, magnesium-based compounds, and other elements to achieve similar functionalities. This research aims to reduce the dependence on rare earth elements in high-tech applications. The progress of these research and development efforts varies depending on the specific element and its application.
Promising Technologies for Reducing Rare Earth Demand
Several technologies aim to reduce the demand for rare earth metals by improving existing technologies or finding alternative solutions. For example, advancements in permanent magnet materials and other magnetic technologies are leading to new designs with reduced rare earth content. Specific examples include the development of high-efficiency motors and generators with less reliance on neodymium-iron-boron magnets.
- Optimized Design and Manufacturing Processes: Implementing efficient design and manufacturing techniques can reduce the overall need for rare earth elements in certain applications. Examples include modifying manufacturing processes for wind turbines to lessen their reliance on neodymium-based magnets.
- Improved Recycling Technologies: Developing more efficient and cost-effective recycling processes for rare earth elements can significantly reduce the demand for newly mined resources. This approach can lessen the environmental impact and create a closed-loop system.
- Material Science Innovations: Innovative material science research is continuously pushing the boundaries of alternative materials for applications that traditionally relied on rare earth elements. The development of new materials that can perform similar functions with reduced rare earth content is an active area of research.
Comparison of Rare Earth Extraction Methods
| Extraction Method | Cost-Effectiveness | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|
| China’s Current Methods | Generally lower cost due to economies of scale and established infrastructure. | High environmental impact, often involving significant water usage and potential pollution. |
| Alternative Extraction Methods (e.g., hydrometallurgy) | Potentially higher initial costs, but can be more sustainable in the long run. | Potentially lower environmental impact through reduced water consumption and waste generation. |
| Secondary Recovery (Recycling) | Lowest cost, as it leverages already extracted material. | Lowest environmental impact due to reduced demand for primary extraction. |
Developing and Implementing New Technologies
Developing and implementing new rare earth extraction technologies and applications involves several steps. Firstly, research and development is needed to identify promising solutions. Secondly, pilot projects and demonstrations are critical to assess the feasibility and efficiency of the new technologies. Thirdly, scaling up these technologies requires significant investment in infrastructure and workforce training. This process typically involves a multi-stage approach, from initial laboratory experiments to large-scale production and deployment.
Government support and private sector investment play a crucial role in accelerating the development and adoption of these technologies.
Environmental Considerations
The extraction and processing of rare earth elements (REEs) pose significant environmental challenges. These vital minerals, crucial for modern technologies, are often found in complex geological formations, requiring extensive mining and processing activities. The environmental impact of these activities ranges from habitat destruction to water pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. Understanding and mitigating these impacts are critical for ensuring the responsible and sustainable development of the REE industry.
Environmental Impact of Rare Earth Mining and Processing
Rare earth mining frequently involves large-scale excavation, altering natural landscapes and impacting biodiversity. Processing methods, including chemical leaching and separation, often generate substantial amounts of hazardous waste. These wastes can contaminate soil and water sources, posing risks to human health and ecosystems. Furthermore, air pollution from mining operations and processing plants can have adverse effects on local communities.
Role of Sustainable Practices in Rare Earth Mining and Extraction
Implementing sustainable practices is crucial to minimize the environmental footprint of REE extraction. This includes employing techniques that reduce habitat disruption, minimize water usage, and control waste generation. Using environmentally friendly extraction methods and technologies is essential. Careful site selection, reclamation efforts, and stringent waste management protocols are vital components of sustainable REE mining operations.
Environmental Regulations Impacting Rare Earth Production
Environmental regulations regarding REE production vary significantly across countries. Some jurisdictions have stringent regulations aimed at protecting natural resources and ecosystems. These regulations often mandate environmental impact assessments, waste management plans, and pollution control measures. Other countries may have less stringent regulations, leading to potential environmental risks.
Comparison of Environmental Footprints of Different Rare Earth Extraction Methods
Different REE extraction methods have varying environmental impacts. For instance, the traditional “wet chemistry” process often involves significant water consumption and the generation of hazardous chemical waste. More advanced technologies, like magnetic separation or hydrometallurgical methods, may offer lower environmental footprints by reducing water usage and waste production. Comparative studies assessing the environmental impacts of these methods are crucial for guiding sustainable development.
Examples of Environmentally Friendly Technologies for Rare Earth Processing
Several environmentally friendly technologies are being developed for REE processing. These include bioleaching methods, which use microorganisms to extract REEs, reducing the need for harsh chemicals. Advanced separation techniques, such as solvent extraction, can improve the efficiency and reduce the environmental impact of REE processing. Plasma technologies are emerging as promising methods for REE recovery, potentially minimizing waste generation and water usage.
Examples of Successful Sustainable Practices
Companies and governments are increasingly adopting sustainable practices in REE extraction. Examples include the implementation of water recycling systems in mining operations, the development of closed-loop recycling processes, and the use of renewable energy sources in processing plants. These initiatives demonstrate a growing commitment to responsible mining and extraction, contributing to the sustainability of the REE supply chain.
Industry Response to Tariffs: Rare Earth China Tariffs Metals Minerals
The imposition of tariffs on rare earth metals and minerals has significantly impacted global supply chains, forcing industries reliant on these critical materials to adapt and innovate. Companies are reassessing their sourcing strategies, exploring alternative materials, and investing in research and development to mitigate the effects of these trade restrictions. This shift presents both challenges and opportunities for long-term resilience and sustainability in the global economy.
Diversification of Supply Chains
Companies are actively diversifying their supply chains to reduce reliance on specific regions and countries for rare earth elements. This involves identifying alternative sources, including those in countries with less stringent environmental regulations or more favorable trade policies. A significant focus is on establishing more robust and resilient relationships with suppliers in different geographical locations. This diversification strategy is crucial for maintaining production continuity and reducing vulnerability to future geopolitical uncertainties.
Sourcing Alternative Materials
The search for alternative materials to rare earth elements is intensifying. Companies are evaluating substitute materials with comparable properties and exploring technological advancements to improve the performance of these alternatives. This often involves research and development into new manufacturing processes and material science to achieve similar outcomes without relying on rare earth elements. Examples include using different types of magnets in electric motors or exploring advanced ceramic materials in certain applications.
Technological Advancements
Technological innovation is playing a crucial role in addressing the challenges posed by rare earth tariffs. Research and development efforts are focused on creating processes that either reduce the demand for rare earth elements or create entirely new processes that eliminate their use altogether. This includes advancements in battery technology, permanent magnet materials, and various manufacturing techniques that require less critical minerals.
For instance, improvements in lithium-ion battery technology are aiming to reduce the reliance on cobalt and other rare earth elements.
Industry Examples
Several companies have already begun to adjust their operations in response to the rare earth tariffs. For example, some automotive manufacturers are exploring the use of different types of magnets in electric vehicle motors, potentially using alternative materials like iron-based compounds. Similarly, the electronics industry is investing heavily in research to develop new semiconductor materials and processes that minimize the use of rare earth elements.
The shift towards sustainable and circular economies is also impacting the strategy.
Industry Responses Table
| Industry | Adaptation Strategies | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Exploring alternative magnet materials, optimizing existing designs | Reduced dependence on rare earth elements, potential for cost savings |
| Electronics | Developing new semiconductor materials, implementing recycling programs | Reduced reliance on rare earth elements, improved sustainability |
| Renewable Energy | Developing alternative materials for wind turbines, solar panels | Ensuring consistent supply of components for renewable energy projects |
| Consumer Electronics | Implementing new designs minimizing rare earth use, exploring recycling processes | Reduced cost of raw materials, enhanced environmental sustainability |
Future Outlook and Predictions
The global landscape of rare earth metals is undergoing a significant transformation. The recent tariffs and the ongoing geopolitical complexities are reshaping supply chains and driving innovation in alternative technologies. Understanding the projected demand, the potential for substitutes, and the evolving supply dynamics is crucial for businesses and policymakers alike. This section delves into the future outlook of this critical sector.
Projected Demand for Rare Earth Metals
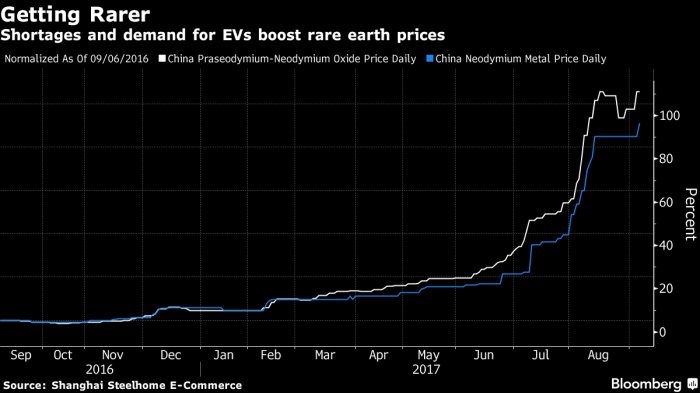
The demand for rare earth metals is expected to increase substantially over the coming years, driven by growth in sectors such as electric vehicles, renewable energy technologies, and advanced manufacturing. Analysts predict a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of X% in the next decade, driven primarily by the expansion of the green energy sector. This upward trajectory underscores the essential role rare earth metals play in modern technological advancement.
Examples include the increasing need for neodymium and praseodymium in electric motors and permanent magnets, and the growing demand for dysprosium in high-performance permanent magnets.
Potential for Alternative Technologies and Materials
The global community is actively exploring alternative technologies and materials to mitigate reliance on rare earth metals. This includes developing new magnetic materials, such as those based on alloys of iron, cobalt, and nickel, which could potentially reduce the need for certain rare earth elements. Research into high-efficiency solar cells and advanced batteries that do not rely heavily on rare earths is also advancing rapidly.
Furthermore, advancements in manufacturing processes are enabling the design and production of components with reduced reliance on rare earths.
Evolution of Global Rare Earth Supply Chains
The current geopolitical landscape is impacting the global rare earth supply chain. The shift towards diversification of sources, including the development of domestic mining operations and the expansion of processing facilities in alternative regions, is a key trend. The emergence of new players and the expansion of existing ones will continue to shape the landscape. Further, the rise of regionalization in supply chains will also become more apparent as countries strive for greater self-sufficiency in critical materials.
Potential Scenarios for Future Rare Earth Market Dynamics
The future of the rare earth market is uncertain, with multiple potential scenarios. These scenarios will be heavily influenced by factors such as technological advancements, geopolitical tensions, and the economic outlook. The emergence of new technologies, fluctuations in commodity prices, and governmental policies will shape the market dynamics.
Table: Potential Scenarios for the Rare Earth Market (Next Decade), Rare earth china tariffs metals minerals
| Scenario | Key Drivers | Market Dynamics | Impact on Demand |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scenario 1: Continued Reliance | Slow adoption of alternatives, geopolitical stability | High demand for rare earths, price volatility | Steady but potentially fluctuating demand |
| Scenario 2: Accelerated Transition | Rapid advancements in alternative technologies, significant policy support | Reduced reliance on rare earths, increased competition | Moderate to significant decline in demand for some rare earths |
| Scenario 3: Regionalization | Geopolitical tensions, protectionist trade policies | Fragmentation of supply chains, localized production | Demand shifts to regionally sourced materials, potentially increasing prices in certain regions |
| Scenario 4: Disruption | Unexpected technological breakthroughs, unforeseen global events | Significant shifts in market structure, high uncertainty | Unpredictable demand, substantial price fluctuations |
Ending Remarks
In conclusion, the rare earth china tariffs metals minerals debate highlights the complex interplay between economics, geopolitics, and environmental sustainability. The transition away from a single-source reliance on Chinese rare earths is proving to be a multifaceted process, demanding innovation in extraction techniques, diversification of supply chains, and a focus on sustainable practices. The future of these critical materials will be shaped by the choices made today, impacting everything from technological advancements to global trade dynamics.

