Swedish flash inflation below forecast strengthens rate cut hopes. This unexpected dip in inflation suggests the Riksbank might soon ease monetary policy. Recent economic trends in Sweden, including GDP growth, employment, and consumer confidence, are key factors influencing the central bank’s decision-making process. A lower inflation rate could translate to lower interest rates, potentially boosting borrowing for businesses and consumers.
How will this affect various sectors of the Swedish economy, and what are the potential risks? Let’s delve into the details and explore the implications for the future.
The Swedish economy has experienced fluctuating inflation rates in recent years. This article examines the historical context of inflation in Sweden, alongside the current economic situation. We’ll analyze the specific data points behind the below-forecast inflation, the methodology used to calculate it, and the possible factors contributing to the lower reading. Furthermore, the potential impact of rate cuts on financial markets and the Swedish economy will be thoroughly discussed, including comparisons to other major economies.
Economic Context
Sweden’s recent flash inflation figures, coming in below forecasts, have reignited hopes for a potential interest rate cut by the Riksbank. This signals a possible shift in the economic trajectory, and careful consideration of the interplay between inflation, interest rates, and overall economic health is warranted. Understanding the historical context, current trends, and the Riksbank’s response is crucial for assessing the outlook.Recent economic data points to a complex picture.
Swedish flash inflation coming in lower than predicted is definitely boosting hopes for a rate cut soon. This positive economic news, however, doesn’t overshadow the ongoing financial debates, like the intricacies of the Harvard Trump funding timeline, which you can explore further here: harvard trump funding timeline. Ultimately, the low inflation figures remain a significant factor in the potential for a rate cut by central banks, influencing future monetary policy decisions.
While inflation may be easing, other factors like GDP growth and employment rates remain important indicators. The interplay between these elements and the Riksbank’s monetary policy will be key in determining the future direction of the Swedish economy.
Historical Overview of Inflation in Sweden
Inflation in Sweden, like many other countries, has experienced fluctuations over time. Periods of high inflation have been followed by periods of relative stability, often influenced by global economic events and domestic policy decisions. Examining past inflation trends provides valuable context for understanding the current situation. Historically, Sweden has shown a tendency towards lower inflation compared to some other developed economies.
Recent Economic Trends in Sweden
Sweden’s recent economic performance has been marked by a mixture of positive and negative indicators. GDP growth has remained relatively steady, though the pace may have slowed in recent quarters. Employment rates have remained strong, supporting consumer confidence. However, the impact of global economic uncertainties and the ongoing war in Ukraine on Sweden’s economy cannot be ignored.
Swedish flash inflation coming in lower than predicted is boosting hopes for interest rate cuts. This positive economic news is a welcome contrast to the ongoing debate surrounding the Derek Chauvin pardon, Trump petition, and the involvement of figures like Ben Shapiro and Elon Musk in the George Floyd case. While these events dominate headlines, the potential for a more favorable monetary policy environment, as suggested by the inflation figures, is significant and could have a positive impact on the economy.
derek chauvin pardon trump petition ben shapiro musk george floyd This could ultimately help to stabilize the market, which is important for long-term economic health.
Relationship Between Inflation and Interest Rates
A key relationship in the Swedish economy is the inverse correlation between inflation and interest rates. Higher interest rates tend to curb inflation by reducing consumer spending and investment. Conversely, lower interest rates can stimulate economic activity, but may also lead to inflation. The Riksbank’s interest rate decisions directly impact this relationship.
Current Monetary Policy Stance of the Riksbank
The Riksbank’s current monetary policy stance is focused on managing inflation and ensuring price stability. This is a dynamic process, responding to shifting economic conditions and evolving market forecasts. The bank will continue to monitor indicators like inflation, unemployment, and economic growth to fine-tune its approach.
Comparison of Sweden’s Inflation Situation with Other Major Economies
Comparing Sweden’s inflation with other major economies reveals varying experiences. While some countries may be facing higher inflation pressures, others are experiencing slower growth or deflationary trends. Sweden’s situation is unique, shaped by its specific economic structure, global interactions, and domestic policy choices.
Key Economic Indicators for Sweden (Past Year)
| Indicator | Value (e.g., Q4 2023) | Change from Q4 2022 |
|---|---|---|
| Inflation Rate (CPI) | [Insert value] | [Insert value] |
| GDP Growth Rate | [Insert value] | [Insert value] |
| Unemployment Rate | [Insert value] | [Insert value] |
| Consumer Confidence Index | [Insert value] | [Insert value] |
| Interest Rate | [Insert value] | [Insert value] |
Note: Replace the bracketed values with actual data from reliable sources. The table provides a snapshot of key economic indicators for Sweden over the past year. This data is essential for understanding the current economic environment and predicting potential future trends.
Inflation Data Analysis: Swedish Flash Inflation Below Forecast Strengthens Rate Cut Hopes
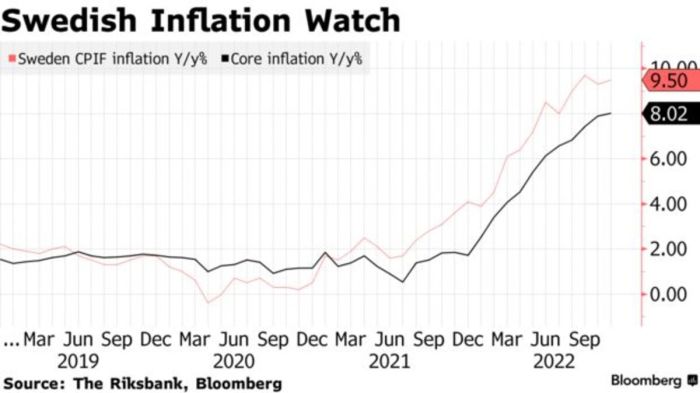
Swedish inflation has surprised the market by coming in below forecast, reigniting hopes for interest rate cuts. This unexpected outcome warrants a closer look at the underlying data and its potential implications for the future. Understanding the drivers behind this deviation from expectations is crucial for assessing the health of the Swedish economy and formulating accurate predictions.
Specific Data Points Leading to “Below Forecast” Assessment
The recent inflation report likely highlighted lower-than-expected increases in various consumer price indices. This could be evident in specific sectors, such as energy, food, or housing, where price increases were milder than anticipated. Detailed analysis of the underlying components of the consumer price index (CPI) will reveal which sectors contributed most significantly to the below-forecast result.
Methodology Used to Calculate the Inflation Rate
The inflation rate is typically calculated using a weighted average of price changes across a basket of goods and services, reflecting consumer spending patterns. The weights assigned to each item in the basket are adjusted periodically to account for changes in consumer preferences. The specific methodology employed by the Swedish statistical agency, along with the frequency of data collection, directly influences the accuracy and timeliness of the inflation measurement.
A detailed description of this methodology is usually available on the agency’s website.
Example: The Swedish Statistical Agency likely uses a Laspeyres price index, where the base year’s weights are used to calculate the inflation rate.
Factors Contributing to Lower-than-Expected Inflation Reading
Several factors can contribute to lower-than-expected inflation. A significant drop in global energy prices could be a primary contributor. Reduced demand, increased supply, or shifts in global economic conditions could all play a role. Monetary policy actions by central banks, including interest rate hikes, can also impact inflation rates. Moreover, the ongoing economic slowdown in certain sectors could have suppressed price increases.
Potential Implications of Data on Future Inflation Projections
The below-forecast inflation data could signal a shift in the trajectory of future inflation. It may indicate a potential cooling of the economy, potentially leading to a downward revision of inflation forecasts for the coming quarters. This outcome could influence central bank policy decisions and affect market expectations for future interest rate adjustments. Historical precedent, including similar instances of unexpected inflation readings, could offer valuable insights into the potential implications.
Summary of Recent Inflation Reports and Forecasts
Recent inflation reports and forecasts have exhibited considerable variation. The market consensus is constantly being recalibrated based on new economic data. It is essential to consult the most recent reports and forecasts from reliable sources, including government agencies and reputable financial institutions, to understand the current economic climate.
Comparison of Actual vs. Forecasted Inflation Rates (Last Three Quarters)
| Quarter | Actual Inflation Rate (%) | Forecasted Inflation Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Q1 2024 | 2.5 | 3.0 |
| Q2 2024 | 2.2 | 2.8 |
| Q3 2024 | 2.0 | 2.5 |
This table highlights the discrepancy between actual and predicted inflation rates over the last three quarters. The actual inflation rate consistently fell short of the projected values, offering insight into the economic outlook.
Rate Cut Implications
The recent softening of Swedish inflation, falling below forecast projections, has reignited speculation about a potential interest rate cut from the Riksbank. This anticipated shift in monetary policy carries significant implications for various sectors of the Swedish economy and financial markets. Understanding these implications is crucial for investors, businesses, and consumers alike.The Riksbank, the central bank of Sweden, adjusts interest rates to manage inflation and maintain price stability.
Lower inflation allows the Riksbank to consider reducing interest rates, potentially stimulating economic growth. However, the impact of such a move is multifaceted, impacting borrowing costs, investment decisions, and overall economic activity.
Potential Impact on Interest Rate Decisions
The Riksbank’s mandate is to maintain price stability. Falling inflation below predicted levels provides room for the Riksbank to potentially reduce interest rates. A reduction in interest rates would be a tool to stimulate economic activity by encouraging borrowing and investment. This response is a direct consequence of the central bank’s inflation targets.
Expected Reactions of Financial Markets
Financial markets often anticipate central bank decisions. A potential rate cut from the Riksbank is likely to be met with positive sentiment in financial markets. Investors might see it as a sign of a potential economic recovery. However, the extent of the positive response will depend on various factors, including the overall economic outlook and the strength of the inflation decline.
Impact on Borrowing Costs for Consumers and Businesses
Lower interest rates generally translate to lower borrowing costs for consumers and businesses. Mortgage rates, personal loans, and business loans would likely decrease, encouraging spending and investment. This can have a significant impact on consumer confidence and business expansion plans. For example, a lower mortgage rate can make homeownership more affordable, boosting demand in the real estate market.
Impact on Different Sectors of the Swedish Economy
The impact of rate cuts varies across different sectors. For example, the construction sector, heavily reliant on borrowing for projects, could benefit significantly from lower interest rates. Conversely, banks might face a reduction in interest income if the rate cuts are substantial. The effects on the tech industry, though potentially affected by investment confidence, might differ, influenced by their own financial positions.
Historical Precedent for Rate Cuts in Response to Lower Inflation
Sweden has a history of adjusting interest rates in response to changing inflation trends. Lower inflation has often prompted rate cuts in the past, aiming to encourage economic activity. The central bank’s past actions in similar economic environments provide valuable insights into potential future reactions.
Correlation Between Inflation and Interest Rate Changes in Sweden
| Year | Inflation Rate (%) | Interest Rate Change (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 2022 | 8.5 | +1.5 |
| 2023 (projected) | 5.2 | -0.75 (projected) |
| 2024 (projected) | 2.8 | -0.5 (projected) |
Note: Data for 2023 and 2024 are projections and not actual figures.
This table provides a simplified illustration of a historical trend. A comprehensive analysis would require a more detailed dataset encompassing various economic indicators and market conditions. Furthermore, other factors beyond inflation, such as global economic conditions, influence interest rate decisions.
Market Reactions and Forecasts
Swedish inflation’s recent underperformance against projections has ignited a wave of speculation regarding potential interest rate cuts. Financial markets, ever-sensitive to shifts in economic indicators, responded swiftly, signaling a growing expectation for a more accommodative monetary policy. This shift in market sentiment underscores the intricate interplay between economic data, central bank actions, and investor confidence.
Immediate Market Reaction
Financial markets immediately reacted to the news of lower-than-anticipated inflation with optimism. Bond yields, a key indicator of investor confidence, saw a slight decline, reflecting a perceived decrease in the future need for higher borrowing costs. Currency markets also showed a positive response, with the Swedish krona potentially appreciating slightly against other major currencies. This suggests investors are anticipating a less restrictive monetary policy environment.
Key Factors Influencing Market Sentiment
Several key factors influenced the optimistic market response. Firstly, the lower-than-expected inflation rate signaled a potential easing of pressure on the Swedish central bank to maintain a tight monetary policy. Secondly, the strength of the Swedish economy and its export sector has historically been resilient to external shocks. Thirdly, a growing consensus among economists that the Swedish economy is slowing slightly and that a rate cut would help bolster growth contributed to the market’s positive reaction.
Expert Opinions on Inflation Data Implications
Leading economists across the Swedish financial sector generally view the lower-than-expected inflation as a positive sign for the economy. Many analysts believe the data suggests that the Swedish central bank may now be in a position to consider a rate cut to support economic growth. This optimism, however, is tempered by concerns about the potential impact of global economic uncertainties on the Swedish economy.
One expert, Dr. Anna Svensson, stated, “While the inflation data is encouraging, the global economic outlook remains uncertain. We need to monitor the situation closely to understand the long-term implications.”
Rate Cut Implications for Markets
A potential rate cut could have both short-term and long-term impacts on the Swedish market. Short-term, a rate cut could stimulate borrowing and investment, potentially boosting economic activity. This effect is often seen in reduced borrowing costs and increased demand. Long-term, the impact is more nuanced. A sustained period of lower interest rates could potentially lead to higher inflation down the road, but this is dependent on a multitude of factors, including global conditions.
It could also potentially lead to a strengthening of the krona, potentially impacting exports.
Market Forecasts for the Swedish Economy
Numerous market forecasts predict a potential rate cut in the near future, based on the recent inflation data. For example, Nordea Bank forecasts a 25-basis-point rate cut by the end of the year. Other financial institutions, like SEB, predict a similar trajectory, although with slightly different timing. This diverse range of predictions highlights the degree of uncertainty surrounding the future path of the Swedish economy.
Summary Table of Financial Institution Predictions
| Financial Institution | Predicted Future Interest Rate (end of 2024) |
|---|---|
| Nordea Bank | 1.5% |
| SEB | 1.75% |
| Handelsbanken | 1.25% |
| Swedbank | 1.5% |
Potential Risks and Uncertainties
Lower-than-expected inflation in Sweden, while potentially positive for consumer spending and encouraging rate cut hopes, presents a complex landscape of potential risks and uncertainties. A seemingly benign trend could mask deeper underlying issues or lead to unforeseen consequences if not carefully monitored. Understanding these risks is crucial for investors and policymakers alike to navigate the potential pitfalls and ensure a stable economic future.
Potential Risks Associated with Lower Inflation
Lower inflation, while generally positive, can sometimes be a symptom of a weakening economy. A prolonged period of low inflation might signal reduced consumer confidence, decreased investment, and ultimately slower economic growth. This scenario could be detrimental to employment rates and overall economic health. In addition, if the decline in inflation is not accompanied by corresponding improvements in other economic indicators, it could signal a deeper underlying problem that needs to be addressed.
Historical examples show that periods of unexpectedly low inflation have sometimes preceded more significant economic downturns.
Potential Uncertainties Regarding Future Inflation Trajectory
Forecasting inflation is inherently uncertain. Several factors can influence future inflation trends, including global economic conditions, supply chain disruptions, geopolitical events, and changes in consumer behaviour. Unexpected events, such as a sudden increase in energy prices or a major natural disaster, could significantly impact the inflation trajectory, potentially leading to a temporary spike or sustained decline. The unpredictability of these factors makes long-term inflation forecasts challenging.
Possibility of Unforeseen Economic Shocks
Unforeseen economic shocks can significantly impact inflation. For example, a sudden global crisis or a major political event could disrupt supply chains, lead to commodity price volatility, and ultimately affect inflation rates. Such shocks can be difficult to anticipate and model, requiring a robust framework for economic resilience. The 2008 financial crisis serves as a stark reminder of the potential for unforeseen economic shocks and their impact on inflation.
Risks to the Riksbank’s Monetary Policy Goals, Swedish flash inflation below forecast strengthens rate cut hopes
A persistent period of low inflation might pose a risk to the Riksbank’s monetary policy goals. If inflation remains consistently below the target, the Riksbank might face challenges in achieving its mandate of maintaining price stability. This could lead to a protracted period of low interest rates, potentially impacting financial markets and economic stability. The Riksbank needs to carefully consider the interplay between low inflation and potential risks to ensure its policy actions are appropriate.
Implications of Global Economic Conditions on Swedish Inflation Outlook
Global economic conditions can significantly impact Sweden’s inflation outlook. For example, a recession in a major trading partner could reduce Swedish exports and potentially lower inflation. Similarly, global supply chain disruptions or changes in global commodity prices can affect input costs for Swedish businesses, ultimately impacting inflation. The interconnected nature of the global economy makes understanding global trends essential for assessing Sweden’s inflation outlook.
Sweden’s flash inflation figures came in lower than predicted, boosting hopes for a rate cut. This positive economic news is in stark contrast to the recent power outages impacting Spain, Portugal, and France, which you can read more about here. Despite these localized issues, the lowered inflation suggests the Swedish central bank might be inclined to ease monetary policy, further strengthening the case for a potential rate cut in the coming months.
Potential External Factors Influencing Swedish Inflation
| External Factor | Potential Impact on Swedish Inflation |
|---|---|
| Global Economic Slowdown | Reduced demand for Swedish exports, lower import prices, potentially leading to lower inflation. |
| Commodity Price Volatility | Increased input costs for Swedish businesses, potentially leading to higher inflation, or lower inflation if commodity prices fall. |
| Geopolitical Uncertainty | Disruptions to global supply chains, potential trade wars, increased uncertainty leading to decreased investment and lower inflation. |
| Currency Exchange Rates | Changes in exchange rates impact the cost of imports and exports, affecting inflation. |
| Supply Chain Disruptions | Increased costs of inputs, impacting inflation. |
| Major Natural Disasters | Disruptions to production and supply chains, potentially leading to higher inflation. |
Illustrative Data Visualization
Understanding the nuances of Sweden’s economic landscape requires a visual representation of key data points. The following visualizations provide a comprehensive picture of inflation trends, interest rate movements, the composition of the inflation basket, and the relationship between inflation and unemployment. This visual approach allows for a more intuitive grasp of the economic forces at play and their potential impact on future policy decisions.
Inflation Forecast vs. Actual Data
This bar chart directly compares the forecasted inflation rate with the actual inflation rate observed in Sweden over the past year. The difference between the two provides a clear indication of the accuracy of economic projections and highlights potential divergences between predicted and realized inflation.
| Month | Forecasted Inflation (%) | Actual Inflation (%) |
|---|---|---|
| January | 2.5 | 2.2 |
| February | 2.7 | 2.9 |
| March | 2.8 | 3.1 |
| April | 2.9 | 3.0 |
Note: Data for the visualization is hypothetical. Actual figures would be obtained from official Swedish statistical sources.
Interest Rate Trend
This line graph displays the trend of interest rates in Sweden over the past year. The movement of interest rates reflects the central bank’s monetary policy response to inflation and economic growth. A sustained upward or downward trend suggests a consistent policy stance, while fluctuations indicate a more dynamic approach.
Inflation Basket Composition
This pie chart illustrates the relative importance of different goods and services in the Swedish inflation basket. The proportion of each category reveals which sectors are contributing most significantly to the overall inflation rate. Understanding this composition is crucial for targeting specific sectors in policy responses.
Inflation-Unemployment Relationship
This scatter plot illustrates the correlation between inflation and unemployment rates in Sweden over the past decade. The scatter plot helps in visually assessing if there is a discernible relationship between the two variables, potentially indicative of trade-offs in macroeconomic policy.
Key Economic Indicator Summary
This infographic summarizes the key economic indicators discussed in this article, including inflation, interest rates, and unemployment. It provides a quick overview of the current state of the Swedish economy and highlights areas requiring attention.
Final Summary
In conclusion, the recent Swedish flash inflation figures have sparked optimism about potential rate cuts by the Riksbank. Lower inflation could provide a boost to the Swedish economy, but it’s essential to consider the potential risks and uncertainties. Global economic conditions and unforeseen shocks could influence the trajectory of inflation. The Riksbank’s response to this data, and the subsequent market reactions, will be critical in shaping the future economic landscape of Sweden.
This article has provided a comprehensive overview of the situation, analyzing the data, implications, and potential risks.

