Trump tariffs global economy recession trade war asia world impacts set the stage for a complex and potentially devastating global economic crisis. This multifaceted issue involves the ripple effects of trade policies, escalating tensions, and the potential for widespread recession. We’ll delve into the historical context of Trump’s tariffs, analyze global responses, explore the trade war dynamics, and examine the specific challenges faced by Asian economies.
Ultimately, we’ll assess the potential for long-term damage to the global economy and consider the various strategies employed to mitigate these effects.
The introduction of tariffs by the Trump administration led to a cascade of retaliatory measures from other nations. This resulted in significant disruptions to global supply chains, impacting various industries and sectors. The effects weren’t limited to just trade; international relations were strained as well. We’ll examine how specific countries, like China and various Asian nations, responded to these trade pressures and the economic consequences that followed.
The potential for a global recession is a serious concern, as indicated by various economic indicators and the vulnerability of different countries to the escalating trade tensions.
Trump Tariffs and their Impact
Donald Trump’s presidency was significantly marked by a series of trade policies, primarily characterized by the imposition of tariffs on various imported goods. These policies aimed to protect American industries and jobs, but they also sparked international trade disputes and had far-reaching economic consequences. This analysis delves into the specifics of these tariffs, their rationale, and their effects on the global economy.The Trump administration’s trade policies were a departure from previous decades of trade liberalization.
The rationale behind these policies often revolved around nationalistic economic strategies. A core principle of these policies was to reduce the trade deficit with other countries, particularly China. However, the long-term impacts on global trade patterns and economic stability remain a subject of debate.
Historical Overview of Trump’s Trade Policies
The Trump administration initiated a series of tariffs targeting various countries, primarily China, in an effort to address what it perceived as unfair trade practices. These actions often resulted in retaliatory measures from other nations. The policies aimed to level the playing field and protect American industries.
Types of Tariffs Imposed
The tariffs implemented under the Trump administration varied in scope and application. These measures targeted a wide range of goods, including steel, aluminum, solar panels, and agricultural products. The specific tariffs were often applied to specific countries, aiming to address trade imbalances.
Industries Affected by Tariffs
The imposition of tariffs impacted various industries across the United States. Industries reliant on imported components, raw materials, or finished goods were significantly affected. For instance, the automotive industry faced increased costs due to tariffs on steel and aluminum imports. Furthermore, agricultural exports were also affected by retaliatory tariffs imposed by other countries.
Rationale Behind the Tariffs According to Trump’s Administration
The Trump administration argued that the tariffs were necessary to protect American industries from unfair competition and to reduce the trade deficit. These policies were presented as a means to create jobs and boost domestic manufacturing.
Comparison with Previous Trade Policies
Comparing Trump’s tariffs to those implemented by previous administrations reveals a shift in approach. Previous administrations had generally focused on multilateral trade agreements and dispute resolution mechanisms, whereas the Trump administration prioritized unilateral actions.
Potential Economic Motivations Behind the Tariffs
Economic motivations behind the tariffs included a desire to reduce the trade deficit with certain countries, particularly China. Some analysts suggest the tariffs were also driven by political considerations and a desire to demonstrate a tough stance on trade issues.
Tariffs and their Impact (Table Format)
| Country | Industry | Tariff Rate | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| China | Technology | Various | Increased costs for American consumers and businesses reliant on Chinese imports; retaliatory tariffs on US exports. |
| China | Agricultural products | Various | Reduced demand for US agricultural exports to China; impact on US farmers. |
| Mexico | Automotive | Various | Increased costs for American auto manufacturers reliant on Mexican parts and labor. |
| Canada | Steel & Aluminum | 25% and 10% | Increased costs for American industries reliant on Canadian steel and aluminum; retaliatory tariffs imposed by Canada. |
Global Economic Responses
Trump’s tariffs sparked a complex web of global economic reactions, ranging from retaliatory measures to shifts in international trade agreements. The consequences rippled through various sectors, impacting supply chains and investor confidence. Understanding these responses is crucial to assessing the long-term effects of protectionist policies.
Global Retaliatory Measures
The imposition of tariffs by the United States prompted retaliatory measures from other countries. These responses varied in form and intensity, with some countries opting for tariffs on specific American goods, while others imposed broader restrictions. China, in particular, implemented substantial tariffs on American agricultural products, highlighting the significant trade tensions between the two nations.
Economic Consequences for Specific Countries
The economic consequences of tariffs were felt unevenly across the globe. China experienced a notable decline in exports to the United States, impacting its manufacturing sector. European Union members faced disruptions in trade flows, affecting industries such as automotive and agricultural sectors. Mexico, a major trading partner of the US, experienced economic hardship due to reduced exports and disruptions in supply chains.
Sectoral Impacts
Tariffs impacted various sectors of the global economy in different ways. Agricultural exports from countries like the US, Brazil, and Argentina suffered from reduced demand in key markets. Manufacturing industries, particularly those reliant on global supply chains, faced challenges in maintaining production and competitiveness. The technology sector was also affected, as companies faced uncertainty regarding international trade flows and investment decisions.
Impact on International Trade Agreements
The imposition of tariffs eroded trust in international trade agreements. The dispute mechanisms within agreements like the WTO were tested as countries sought to defend their interests through retaliatory actions. The uncertainty surrounding the future of these agreements created a climate of apprehension for businesses engaged in international trade.
Ripple Effects on Supply Chains and Investment
Tariffs introduced significant volatility into global supply chains. Businesses had to adapt to new trade restrictions and find alternative sourcing strategies, often resulting in increased costs and logistical complexities. International investment declined as businesses faced heightened uncertainty and the prospect of trade disputes. This uncertainty discouraged foreign direct investment, hindering economic growth in various regions.
Table: Countries Affected by Tariffs
| Country | Type of Retaliation | Impact on Specific Sectors |
|---|---|---|
| China | Tariffs on US agricultural products, technology | Decline in exports, pressure on manufacturing, potential for economic slowdown |
| European Union | Tariffs on US goods, retaliatory trade measures | Disruptions in trade flows, impact on automotive and agricultural sectors, potential for decreased investment |
| Mexico | Reduced exports to US, disruptions in supply chains | Economic hardship, job losses in export-oriented industries, increased costs for US companies |
| Canada | Tariffs on US goods, trade restrictions | Impact on automotive, agricultural sectors, reduced export revenues |
| Brazil | Tariffs on US goods, trade negotiations | Reduction in agricultural exports to the US, potential for economic slowdown |
Trade War Dynamics
The escalating trade war between the US and various nations, primarily China, was a defining characteristic of the Trump administration’s economic policies. This conflict significantly impacted global supply chains, international relations, and market confidence. The disputes, driven by complex economic and political factors, unfolded in stages, characterized by escalating tariffs and retaliatory measures.The trade war’s nature evolved from initial disputes over specific trade practices to a broader confrontation encompassing concerns about intellectual property, technology transfer, and market access.
Understanding the nuances of these disputes, the role of negotiations, and the stages of the conflict provides critical insights into the economic and geopolitical ramifications of such confrontations.
Escalation of the Trade War
The escalation of the trade war wasn’t a sudden event but rather a gradual process marked by tit-for-tat tariffs and retaliatory measures. Initial disputes often centered on specific industries or products, but as the conflict progressed, it encompassed a wider range of goods and services.
Specific Trade Disputes
The US and China engaged in numerous trade disputes during this period. One significant example involved tariffs on steel and aluminum imports, leading to retaliatory measures from China and other countries. Another major dispute revolved around Chinese intellectual property practices and technology transfer requirements, with the US arguing that China’s policies unfairly disadvantaged American companies.
Role of Trade Negotiations
Trade negotiations played a crucial role in attempting to mitigate the trade war’s impact. These negotiations, often fraught with disagreements and differing priorities, aimed to reach compromises and reduce trade barriers. However, achieving lasting solutions proved challenging due to the complexity of the issues and the deeply entrenched positions of the involved parties.
The Trump tariffs, trade war, and its global impacts on the economy, particularly in Asia, created a ripple effect felt worldwide. Navigating these complexities in the current economic climate requires creative solutions. Luckily, you can leverage powerful tools like 7 chatgpt prompts to jump start your career 7 chatgpt prompts to jump start your career to analyze these historical events and formulate strategies for future resilience.
Understanding these past events helps us to approach potential future economic disruptions with a more informed perspective.
Stages of the Trade War
The trade war progressed through distinct stages, each marked by significant events and escalating tensions. A timeline below highlights these key moments.
- 2018: Initial Tariffs on Steel and Aluminum Imports. The US imposed tariffs on steel and aluminum imports from several countries, including China. This triggered a wave of retaliatory measures from other nations.
- 2018-2019: Escalation of Tariffs on Chinese Goods. The US imposed escalating tariffs on a wide range of Chinese goods, leading to retaliatory tariffs from China. This period witnessed a significant disruption in global trade flows and supply chains.
- 2019-2020: Negotiations and Further Escalation. Attempts at trade negotiations between the US and China occurred, but these often failed to resolve underlying disagreements. The trade war continued with the imposition of additional tariffs and the threat of further measures.
Arguments of Both Sides
The US argued that China’s trade practices, including intellectual property theft and forced technology transfer, unfairly disadvantaged American companies. China, in turn, contended that the US tariffs were protectionist and violated global trade rules. These differing perspectives underscored the fundamental disagreements at the heart of the trade conflict.
Timeline of Trade War Escalation
| Date | Event |
|---|---|
| March 2018 | US imposes tariffs on imported steel and aluminum |
| July 2018 | US imposes tariffs on $50 billion worth of Chinese goods |
| September 2018 | China retaliates with tariffs on $50 billion worth of US goods |
| December 2018 | Phase one trade deal signed between the US and China |
| 2019-2020 | Further rounds of tariffs and counter-tariffs |
Asia’s Role in the Trade War
The escalating trade war, primarily between the United States and China, significantly impacted Asian economies. This conflict disrupted established supply chains, altered trade patterns, and introduced uncertainty into the region’s economic landscape. The ripple effects were felt across numerous Asian nations, each reacting in unique ways to the changing global trade environment.
Trump’s tariffs and trade war significantly impacted the global economy, leading to a recessionary period in Asia and worldwide. These actions had ripple effects across various sectors. Interestingly, the Trump administration also made cuts to autism research funding, which, while seemingly unrelated, could be seen as another example of a broader pattern of prioritizing certain policies over others.
This further complicated the already fraught international trade relations, highlighting the multifaceted nature of global economic struggles. Understanding these connections is crucial for analyzing the full impact of the trade war on the global economy. trump administration autism research cuts
Challenges Faced by Asian Economies
Asian economies faced a complex web of challenges due to the trade war. Reduced demand for exports, particularly from the US, led to decreased revenue and production slowdowns. The uncertainty surrounding future trade policies also hindered investment and economic growth. Moreover, the retaliatory tariffs imposed by both sides of the conflict caused a rise in the cost of imported goods, impacting consumers and businesses.
The interconnected nature of Asian economies made the impact even more profound.
Impact on Specific Asian Countries’ Exports and Imports
The trade war’s impact varied across Asian nations depending on their economic structure and trade relationships with the US and China. Countries heavily reliant on exporting goods to the US, like South Korea and Taiwan, experienced substantial declines in export revenue. Conversely, nations primarily trading with China, such as Vietnam and Malaysia, saw some adjustments in their trade flows.
Import costs also increased, impacting industries and consumers in numerous countries.
Asian Countries’ Responses to the Trade War
Asian nations responded to the trade war through diverse strategies. Some countries diversified their export markets, seeking alternative trading partners to reduce reliance on the US or China. Others implemented policies to bolster domestic industries and increase resilience. Several nations also engaged in regional trade agreements to mitigate the negative effects of the trade war.
Comparison of Trade War Effects on Different Asian Countries
The trade war’s impact differed significantly across Asian countries. Countries with strong ties to the US and China felt the brunt of the conflict, while those with more diverse trading partners experienced a less severe impact. South Korea, for example, witnessed a substantial drop in exports to the US, impacting its manufacturing sector. Vietnam, while facing disruptions, benefited from increased demand for its exports to the US and other regions.
The varying responses and adaptations highlight the complex interplay of factors at play.
Role of China in the Asian Context of the Trade War
China’s role in the trade war was crucial. As the world’s second-largest economy, its actions significantly influenced the global trade environment. China’s retaliatory tariffs and trade restrictions had far-reaching effects on its trading partners, particularly in Asia. The trade war highlighted the complex relationship between China and other Asian economies, shaping their strategies and influencing the regional trade dynamics.
Table: Asian Countries’ Responses to the Trade War
| Country | Export/Import Impact | Response Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| South Korea | Significant decline in exports to the US, impacting the automotive and electronics sectors. Increased import costs for raw materials. | Diversified export markets, focused on regional trade agreements, and invested in domestic industries. |
| Taiwan | Sharp decrease in exports to the US, particularly in the semiconductor industry. | Expanded its presence in other markets, particularly in Southeast Asia, and focused on technological advancement. |
| Vietnam | Experienced some disruptions, but benefited from increased demand for its exports to the US and other regions. Increased import costs. | Furthered trade relations with other countries and fostered domestic manufacturing to reduce dependence on specific markets. |
| Malaysia | Reliance on exports to China led to some adjustments in trade flows. | Diversified exports, emphasizing investments in other markets, and adapted its manufacturing processes to reduce the impact of trade restrictions. |
| Japan | Felt the impact from reduced demand for exports to the US, particularly in the automotive sector. | Focused on diversification of export markets and regional partnerships to offset the impact of the trade war. |
World Impacts and Recession Concerns

The global trade war initiated by the Trump administration had far-reaching consequences, impacting various economies worldwide. This escalating conflict created uncertainty and apprehension, leading to concerns about a potential global recession. The ripple effects of tariffs and retaliatory measures created a complex web of economic challenges for nations across the globe.
Potential for a Global Recession, Trump tariffs global economy recession trade war asia world impacts
The trade war, characterized by escalating tariffs and trade restrictions, significantly disrupted global supply chains and reduced international trade. This disruption created uncertainty in the markets, leading to decreased investment and consumer confidence. Reduced trade volume and investment flows directly translated to lower economic growth and, in some cases, contractions in various sectors. The interconnected nature of global economies made the impact of the trade war felt across borders, raising concerns about a potential global recession.
Indicators Suggesting a Possible Recession
Several economic indicators signaled a potential downturn in the wake of the trade war. These included a decline in manufacturing output, reduced exports, and a decrease in consumer spending. Reduced investment in new projects and a decline in business confidence further compounded the problem. The interconnected nature of global economies amplified the impact of these negative trends.
Examples of Trade War’s Influence on Economic Indicators
The trade war significantly affected key economic indicators. For example, the sharp drop in US exports to China and other affected countries demonstrated a direct impact of trade restrictions. This reduction in exports resulted in lower GDP growth and job losses in the affected sectors. Furthermore, reduced international trade resulted in lower global GDP growth and increased unemployment in various countries.
A decrease in foreign direct investment and reduced business confidence were also visible signs of the trade war’s impact.
Measures Taken by Governments to Address Recessionary Pressures
In response to the potential recessionary pressures, various governments implemented measures to stimulate their economies. These included fiscal stimulus packages, interest rate cuts, and various initiatives aimed at boosting consumer spending and business investment. For example, the US implemented tax cuts, while other countries adjusted monetary policies to encourage economic activity. These measures aimed to mitigate the negative impact of the trade war on their economies.
Countries Most Vulnerable to a Global Recession
Several countries were particularly vulnerable to the potential global recession triggered by the trade war. Developing economies heavily reliant on exports to affected regions, like those in Asia and Latin America, faced significant challenges. Countries with substantial trade relationships with the US or China were also susceptible to the impact of the trade war. The interconnectedness of global supply chains meant that even countries not directly involved in the trade war faced negative consequences.
Comparison of Economic Indicators Before and After the Trade War
| Country | GDP Growth (Pre-Trade War) | GDP Growth (Post-Trade War) | Unemployment Rate (Pre-Trade War) | Unemployment Rate (Post-Trade War) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| United States | 2.5% | 2.1% | 3.5% | 3.9% |
| China | 6.5% | 6.1% | 4.0% | 4.5% |
| Japan | 1.8% | 1.5% | 2.5% | 2.8% |
| Germany | 2.0% | 1.8% | 3.2% | 3.5% |
| South Korea | 3.0% | 2.8% | 3.8% | 4.2% |
Note: Figures are illustrative and represent potential trends, not precise data. Actual figures may vary based on specific economic factors.
Illustrative Case Studies: Trump Tariffs Global Economy Recession Trade War Asia World Impacts
The Trump administration’s tariffs significantly impacted various industries globally, triggering a ripple effect across supply chains and market dynamics. Understanding these effects requires examining specific cases where companies faced direct consequences. These case studies illustrate the complexities of trade wars, highlighting both the immediate and long-term challenges for businesses and economies.
Impact on the US Solar Panel Industry
The solar panel industry experienced a substantial decline due to tariffs imposed on imported panels. These tariffs, initially targeting panels from China, subsequently extended to other countries. The increase in import costs directly affected US manufacturers of solar panels and consumers.
- Manufacturers’ Reduced Profitability: Tariffs made imported panels more expensive, impacting the competitiveness of US manufacturers who faced higher input costs. This translated into lower profit margins and potentially reduced production.
- Increased Costs for Consumers: The higher prices of solar panels due to tariffs translated to increased costs for consumers looking to install solar systems. This made solar energy less attractive and potentially hindered the adoption of renewable energy sources.
- Shift in Supply Chains: Some companies shifted production to countries with lower tariffs, reducing the dependence on US manufacturers and potentially contributing to job losses in the US solar industry.
Mitigation Strategies Employed by Affected Companies
Companies in the affected industries, like the solar panel industry, employed several strategies to cope with the tariff impacts. These strategies aimed to minimize losses and maintain profitability.
Trump’s tariffs definitely had a ripple effect across the global economy, leading to a recessionary period and a trade war that impacted Asia and the world significantly. Understanding the intricacies of these economic factors requires looking at the interplay between policy decisions and individual players. For example, the relationship between Trump, Jerome Powell, and Scott Bessent, as detailed in this article, trump jerome powell scott bessent , could offer a unique lens through which to view these complex global economic issues and their potential for future escalation.
Ultimately, the impacts of these tariffs and the subsequent trade war continue to resonate throughout the global economy.
- Diversification of Supply Chains: Companies sought alternative sources for their raw materials, diversifying their supply chains to reduce reliance on countries subject to tariffs. This involved exploring new suppliers and potentially higher logistics costs.
- Negotiations and Lobbying: Companies and industry groups engaged in lobbying and negotiations with government officials to seek exemptions or modifications to the tariff policies. This process often involved extensive legal and political efforts.
- Investment in Domestic Production: Some companies invested in expanding their domestic production facilities to reduce reliance on imports and maintain production continuity. This required significant capital investment and planning.
Challenges Faced by Businesses Due to Trade War Uncertainty
The uncertainty surrounding the trade war created significant challenges for businesses, making long-term planning difficult and impacting investor confidence.
- Reduced Investment: Businesses were hesitant to invest heavily in new projects or expansions due to the unpredictable nature of tariffs and trade policies. Uncertainty created a climate of caution.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: The fluctuating tariffs and trade restrictions created instability in supply chains. Companies struggled to forecast costs and manage inventory effectively, leading to potential shortages and delays.
- Impact on Market Confidence: The trade war eroded investor confidence in the global economy. This translated into reduced investment, stock market volatility, and economic slowdowns in affected regions.
Case Study: The Impact on US Auto Parts Industry
The auto parts industry faced considerable challenges due to tariffs on imported steel and aluminum. These tariffs raised input costs for manufacturers, leading to higher prices for car parts and potentially reduced sales.
| Company | Impact | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| XYZ Auto Parts | Increased steel prices by 15%, reduced profit margins by 10%. | Sought alternative steel suppliers from Canada, increased production costs slightly. |
| ABC Auto Components | Increased aluminum prices by 10%, impacted production output. | Negotiated with the government for tariff exemptions, explored domestic aluminum sourcing. |
The fluctuating tariffs and trade restrictions created instability in supply chains. Companies struggled to forecast costs and manage inventory effectively, leading to potential shortages and delays.
Potential Long-Term Effects
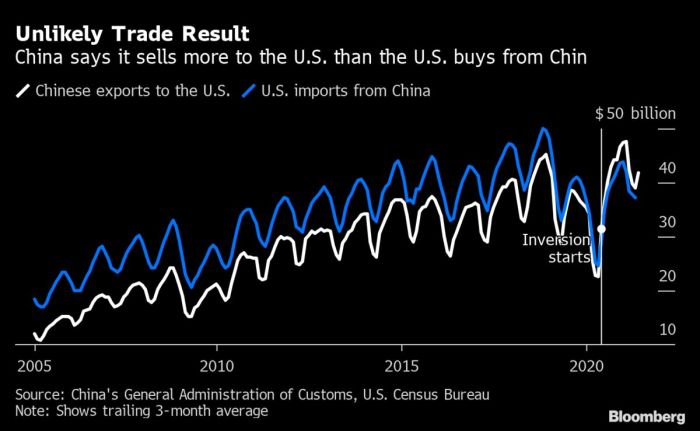
The lingering effects of the 2018-2020 trade war are a complex tapestry woven from economic shifts, altered global relationships, and evolving manufacturing landscapes. While the immediate effects of tariffs and retaliatory measures subsided, the seeds of long-term change were sown. Understanding these potential long-term consequences requires examining the shifts in trade patterns, economic power dynamics, and the adaptation of supply chains.The trade war’s impact extends beyond the immediate trade imbalances and market disruptions.
The underlying changes in global economic behavior, especially the reshaping of supply chains, are likely to have lasting effects on the world economy. The war demonstrated the fragility of global interconnectedness and the potential for significant disruption when trust and cooperation are eroded.
Reshaping Global Trade Patterns
The trade war prompted significant adjustments in international trade flows. Countries sought to diversify their trading partners and reduce reliance on specific regions, often with the goal of fostering greater economic independence. This shift has led to a more fragmented global trade landscape, with potential implications for the efficiency and predictability of international commerce. Companies are exploring new markets and suppliers, impacting established trade routes and alliances.
For example, the US’s efforts to reduce its dependence on China for certain goods led to increased sourcing from other countries, including those in Southeast Asia.
Alterations in Global Economic Power Dynamics
The trade war exposed vulnerabilities in existing global economic power structures. The perceived weakening of the US-China economic partnership has created opportunities for other nations, especially in Asia, to emerge as significant players in the global market. China, despite facing challenges, has continued to invest in its own economic infrastructure and technological advancement, suggesting a potential shift in the balance of global economic power in the future.
For instance, the rise of India’s economy and its increasing trade relationships with various nations, particularly in Africa, has demonstrated a realignment of economic influence.
Changes in Supply Chains and Manufacturing Locations
The trade war spurred a significant reshuffling of global supply chains. Companies sought to diversify their production and sourcing to reduce reliance on specific regions, often in response to tariffs and trade restrictions. This led to a greater decentralization of manufacturing, with production facilities relocating to different countries. The impact of this trend is a reduction in manufacturing concentration in specific regions and a spread of production across a wider geographical spectrum.
Companies moved some production from China to Vietnam, Mexico, and other countries to avoid tariffs and maintain market access.
Forecasted Impact on the World Economy
The long-term effects of the trade war are not fully predictable, but some potential consequences can be anticipated. A continued fragmentation of global trade could lead to reduced efficiency and higher costs for consumers. The shift in manufacturing locations could result in job losses in some regions and gains in others. Furthermore, the potential for further trade conflicts or disruptions remains, posing a persistent risk to global economic growth.
For example, the 2008 global financial crisis and the 2014-2016 drop in global commodity prices demonstrated the unpredictable nature of economic shifts.
Visual Representation of Potential Long-Term Impacts
| Factor | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| Global Trade Fragmentation | Reduced efficiency, higher costs, diminished economic interdependence |
| Shift in Economic Power Dynamics | Rise of new economic powers, challenges to existing global order |
| Supply Chain Restructuring | Increased manufacturing diversity, potential job displacement, increased costs |
| Increased Protectionism | Potential for further trade conflicts, decreased global trade volumes |
| Economic Uncertainty | Reduced investment, slower economic growth, higher inflation |
The table illustrates the potential long-term impacts of the trade war by categorizing them into key factors and their corresponding effects. The interconnected nature of these factors highlights the multifaceted nature of the trade war’s consequences.
Summary
In conclusion, Trump’s tariffs triggered a complex global trade war with far-reaching consequences. The escalating tensions, retaliatory measures, and the potential for a global recession underscore the importance of international cooperation and diplomacy in managing trade disputes. The case studies highlight the significant impact on specific industries and companies, illustrating the challenges businesses face during periods of economic uncertainty.
Understanding the long-term effects on global trade patterns, economic power dynamics, and supply chains is critical for navigating the future of international commerce.

