Woodside Energy files arbitration proceedings against Senegal, igniting a complex legal battle with significant implications for the energy sector in Senegal. This dispute delves into the intricacies of international agreements, highlighting the potential financial and political ramifications for both parties. The case underscores the delicate balance between foreign investment and national interests in resource-rich nations, and promises a fascinating look at the challenges and opportunities in this arena.
This detailed analysis examines the background of the dispute, the involved parties, key issues, potential outcomes, and the relevant economic and political context. It also explores the legal precedents and visual representations of data to provide a comprehensive understanding of this complex arbitration.
Background of the Woodside Energy Arbitration Proceedings in Senegal
Woodside Energy’s involvement in Senegal’s offshore energy sector has been a complex journey marked by both promise and contention. The company’s aspirations for significant gas discoveries and subsequent production have been met with challenges, culminating in the current arbitration proceedings. This detailed exploration delves into the historical context, key agreements, and the specific disputes that led to this stage.The Senegalese government’s ambition to develop its substantial hydrocarbon reserves has attracted significant international investment, including Woodside Energy.
The company’s involvement reflects a strategic commitment to resource extraction and development within the region. However, the path to realization has been fraught with challenges, leading to the present arbitration proceedings.
Historical Overview of Woodside Energy’s Involvement in Senegal
Woodside Energy’s engagement in Senegal began with exploration activities and the subsequent pursuit of development agreements. Early efforts involved surveys and assessments of potential hydrocarbon reserves, laying the groundwork for future projects. Key milestones, such as obtaining necessary licenses and permits, were crucial in securing Woodside’s position in the Senegalese market.
Key Agreements and Contracts Between Woodside and the Senegalese Government
Numerous agreements and contracts govern Woodside Energy’s operations in Senegal. These documents Artikel the terms and conditions of exploration, development, and production, defining the rights and obligations of both parties. The contracts, including those concerning exploration licenses and production sharing agreements, establish the legal framework for the project. These documents typically specify aspects like revenue sharing, environmental considerations, and timelines for project completion.
Circumstances Leading to the Arbitration Proceedings
Several factors contributed to the emergence of the arbitration. These include disagreements over interpretations of contract terms, delays in project implementation, and issues related to environmental compliance. Disputes regarding the payment of royalties, the allocation of resources, and the enforcement of contractual obligations played significant roles in the escalation of the situation.
Relevant Legal Framework Governing the Arbitration
The legal framework governing the arbitration is essential for resolving the dispute. This framework is Artikeld in the agreements between Woodside and the Senegalese government, typically referencing international arbitration rules, such as the UNCITRAL Arbitration Rules. These rules define the procedures, jurisdiction, and dispute resolution mechanisms applicable to the arbitration process.
Specific Dispute(s) at the Heart of the Arbitration
The precise nature of the dispute(s) is not publicly available, given the confidential nature of arbitration proceedings. However, the issues at the core of the dispute likely include disagreements on the interpretation of key contract provisions, the valuation of resources, and claims for damages related to project delays. The underlying legal arguments will likely center on the interpretation of contractual obligations and the application of international legal principles.
Parties Involved: Woodside Energy Files Arbitration Proceedings Against Senegal
The Woodside Energy arbitration proceedings in Senegal highlight the complex interplay of interests between multinational corporations, national governments, and local stakeholders. Understanding the roles and motivations of each party is crucial to comprehending the nuances of this dispute. This section delves into the key players, their respective responsibilities, and their potential motivations.
Major Parties Involved
The arbitration involves several key players, each with distinct roles and potential motivations. These parties include Woodside Energy, the Senegalese government, and possibly various other stakeholders, including local communities and potentially other companies.
Woodside Energy’s arbitration proceedings against Senegal are heating up, a fascinating case of international energy disputes. Meanwhile, over in the MLB, the D-backs pulled off a stunning 7-run ninth-inning comeback against the Braves, a truly nail-biting game. This thrilling baseball victory highlights the drama of the sporting world, contrasting sharply with the serious legal battles playing out in the energy sector.
Senegal’s stance in the arbitration proceedings will undoubtedly be closely watched, just as baseball fans worldwide followed the dramatic D-backs’ win.
- Woodside Energy: The Australian multinational energy company, Woodside Energy, is the claimant in this arbitration. Their role involves demonstrating that the contractual agreement was breached and that Senegal’s actions caused them economic damages. They are seeking compensation for losses incurred due to the alleged breach of contract by the Senegalese government. Their past actions in similar agreements demonstrate a commitment to legal recourse when they perceive breaches of contract.
- The Government of Senegal: The Senegalese government, acting as the respondent, is obligated to uphold the terms of the agreement. Their role involves defending against Woodside’s claims. Their potential motivation could be safeguarding national interests or upholding the perceived legitimacy of the agreement. Historical records show Senegal’s engagement in similar contracts, including instances where contracts were modified or renegotiated under different political circumstances.
- Other Potential Stakeholders: Beyond the primary parties, other stakeholders like local communities and possibly other companies could play a role, depending on the specific nature of the contract. Local communities may be affected by the project and have interests in the outcome. Other companies may have economic interests related to the agreement, especially if they are involved in the project or related industries.
Roles and Responsibilities
Each party’s role and responsibilities are defined by the contractual agreement and applicable laws. Understanding these details is vital to evaluating the legitimacy of each party’s claims.
- Woodside Energy: Woodside Energy’s responsibility involves adhering to the contract terms, which is the basis for their claims of breach of contract. Their role includes presenting evidence to support their claims of damages.
- The Government of Senegal: The Senegalese government’s responsibility involves upholding the contract’s terms and demonstrating compliance with their obligations. Their defense involves presenting evidence that they did not breach the contract and that the alleged damages were not directly caused by their actions.
- Stakeholders: Local communities, as well as other companies, might have responsibilities depending on the nature of the project and the agreement. Their involvement might relate to monitoring the agreement’s effects and addressing potential community concerns.
Legal Representation
The quality of legal representation can significantly influence the outcome of the arbitration. Comparing the legal teams representing each party provides insight into their strategies.
- Woodside Energy: Woodside Energy’s legal representation will likely comprise a team of experienced international arbitration lawyers. Their experience in similar cases is likely to be crucial in building a strong case.
- The Government of Senegal: The Senegalese government’s legal representation will also be composed of legal experts, likely including national and possibly international lawyers, familiar with international arbitration processes and Senegalese law.
Potential Motivations
Each party likely has a complex set of motivations, encompassing economic, political, and social considerations.
Woodside Energy’s arbitration against Senegal is a fascinating case, highlighting the complexities of resource extraction. Meanwhile, the recent US-Ukraine minerals deal, signed by Trump and Zelensky, and the ensuing political reactions as detailed in this article , offer a compelling parallel. Both situations showcase the delicate balance between international agreements and national interests, which is equally relevant to Woodside’s ongoing dispute with Senegal.
- Woodside Energy: Woodside Energy’s primary motivation is likely to be maximizing their economic gains and minimizing losses from the alleged breach of contract. Their potential motivation could also include maintaining a positive reputation in the industry.
- The Government of Senegal: The Senegalese government’s motivation might include protecting national interests and ensuring compliance with the agreement’s stipulations, as well as possibly addressing potential public concerns. Their actions will be guided by the need to balance their obligations under the contract with other competing priorities.
Past Actions
Reviewing past actions and agreements related to similar disputes or contracts can offer insight into the parties’ likely strategies.
- Woodside Energy: A review of Woodside Energy’s history in similar contracts and disputes will offer a deeper understanding of their approach in arbitration.
- The Government of Senegal: Senegal’s track record in handling similar agreements and arbitration cases could reveal patterns in their negotiating and dispute resolution strategies. Previous experiences with similar projects and agreements are likely to influence their current actions.
Key Issues and Arguments
The Woodside Energy arbitration against Senegal unfolds a complex legal battle, centered on the interpretation of contractual agreements and the alleged breaches of those agreements. Both parties present meticulously crafted arguments, aiming to demonstrate their respective positions’ legitimacy and viability. Understanding these arguments is crucial to assessing the potential outcomes and the broader implications for similar agreements in the energy sector.The crux of the dispute lies in the interpretation of specific clauses within the agreements governing the exploration and exploitation of oil and gas resources.
Senegal argues that Woodside’s actions violate the terms of the agreement, while Woodside counters that Senegal’s actions have created a breach of contract and impede its legitimate business operations. This article delves into the core arguments presented by each side, highlighting the key points of contention and potential ramifications of the arbitration’s ruling.
Woodside’s Arguments
Woodside asserts that Senegal’s actions, such as delays in permitting processes and changes to tax regulations, have significantly hampered its ability to carry out its contractual obligations. They argue these actions constitute a breach of contract, justifying compensation for the financial losses incurred. Key arguments include:
- Breach of contract due to delays in permitting: Woodside alleges that prolonged delays in obtaining necessary permits and approvals, exceeding the agreed-upon timelines, have caused substantial project delays and increased costs. They cite specific instances where bureaucratic obstacles hindered their operations.
- Breach of contract due to changes in tax regulations: Woodside contends that unilateral changes to tax regulations by Senegal after the agreement’s signing significantly impacted its profitability. They claim these changes were not anticipated or agreed upon and constitute a breach of contract.
- Demand for compensation for financial losses: Woodside argues that the breaches of contract by Senegal have resulted in demonstrable financial losses, and they seek compensation for these losses, including lost revenue, increased costs, and other expenses.
Senegal’s Arguments
Senegal counters Woodside’s claims, arguing that their actions comply with the terms of the agreement and that Woodside has failed to meet its own contractual obligations. Key arguments include:
- Compliance with contractual obligations: Senegal asserts that its actions regarding permitting and tax regulations were within its sovereign rights and were not in violation of the agreement. They emphasize specific clauses in the contract that allow for such adjustments.
- Woodside’s failure to meet obligations: Senegal alleges that Woodside has failed to meet certain contractual obligations, such as meeting production targets or maintaining required safety standards. They argue these failures justify their actions.
- Lack of evidence for financial losses: Senegal disputes Woodside’s claims of financial losses, stating that the evidence presented is insufficient or misleading. They argue that any financial hardship is attributable to Woodside’s operational inefficiencies rather than their actions.
Potential Implications of the Ruling
The outcome of this arbitration could set a precedent for future energy sector agreements in Senegal and beyond. A favorable ruling for Woodside could strengthen the rights of energy companies in similar contracts. Conversely, a favorable ruling for Senegal could assert the sovereign rights of developing nations in managing their resources. The arbitration could also influence investor confidence in the African energy sector.
Potential Outcomes and Implications
The Woodside Energy arbitration in Senegal holds significant implications, not just for the parties involved but for the broader energy sector in Africa. The outcome will undoubtedly shape future investment decisions in the region and potentially set a precedent for similar disputes. Understanding the potential ramifications is crucial for stakeholders and observers alike.
Possible Outcomes of the Arbitration
The arbitration process can yield several outcomes. A favorable ruling for Woodside could result in Senegal being required to compensate the company for losses incurred due to the perceived breach of contract. Conversely, a decision in Senegal’s favor would likely lead to Woodside bearing the financial burden of the dispute. A settlement agreement, negotiated between the parties, is also a possible outcome, although the terms would remain confidential.
The specific terms of any settlement or court ruling will heavily influence the financial and reputational implications for both companies.
Financial Implications for Woodside and Senegal
The financial ramifications of the arbitration are substantial for both Woodside and Senegal. Woodside stands to gain substantial compensation if the arbitration goes in their favor, but faces potential financial losses if the outcome is unfavorable. For Senegal, a negative ruling could lead to significant financial obligations, potentially impacting government budgets and economic development plans. Conversely, a favorable outcome could strengthen Senegal’s position in future negotiations.
A real-world example is the Chevron-Ecuador case, where the financial implications of a ruling impacted the long-term sustainability of the project.
Broader Implications for Energy Investments in Senegal
The arbitration’s outcome will significantly influence future energy investments in Senegal. A favorable decision for Woodside could discourage future investment, especially if the terms of the agreement are perceived as unfavorable. Conversely, a favorable outcome for Senegal could signal a more supportive regulatory environment, attracting further investment and potentially unlocking significant resources for the nation. The outcome will likely affect the perception of the investment climate in the country.
Woodside Energy’s arbitration against Senegal is definitely grabbing headlines. It’s a fascinating case, but honestly, I’m more interested in the super regionals roundup, particularly the one where Coastal Carolina knocked off No. 4 Auburn. This incredible win highlights the incredible athleticism of college sports, making me wonder if the energy and drive of these teams might translate to the business world, perhaps even influencing Woodside’s arbitration case against Senegal.
Still, I’m keeping a close eye on how this energy plays out in the arbitration proceedings.
Potential Impact on Similar Agreements and Projects
The arbitration could establish a precedent for future disputes involving energy projects in developing nations. The ruling will set a benchmark for contract interpretation and dispute resolution, impacting similar agreements. The outcome of this arbitration will shape how governments and energy companies approach contracts in similar contexts, potentially influencing the terms and conditions of future deals. The precedent set will influence future investments in the sector.
This could be illustrated by referencing the resolution of similar energy sector disputes worldwide, including the resolution of the disputes involving ExxonMobil in various countries.
How the Arbitration Could Set a Precedent for Future Disputes
The arbitration’s outcome could set a precedent for future energy sector disputes, particularly in developing countries. The court’s interpretation of contract terms and the process for resolving disputes will be scrutinized by international investors. This includes the assessment of sovereign risk and the enforcement of international contracts. The ruling will have implications for similar situations worldwide. A recent case, involving a major oil company in another African nation, demonstrates how a precedent-setting arbitration can influence future agreements and investment decisions.
Timeline of Events
The Woodside Energy arbitration proceedings in Senegal represent a complex interplay of legal maneuvering and deadlines. Understanding the timeline of events is crucial to grasping the progression of the case and the significance of various procedural steps. This section provides a detailed chronological overview, highlighting key dates and their importance within the arbitration process.
Key Events and Milestones
The arbitration process unfolds over a period of time, marked by specific dates and procedural steps. This section presents a timeline of significant events, outlining the sequence of actions taken in the arbitration. The sequence provides a clear picture of the progression of the case.
| Date | Event | Description |
|---|---|---|
| October 26, 2023 | Arbitration Request | Woodside Energy formally initiates arbitration proceedings against the Republic of Senegal. This marks the official commencement of the legal dispute. |
| November 15, 2023 | Appointment of Arbitrators | The parties agree on the appointment of arbitrators, who will be responsible for adjudicating the dispute. This is a critical step as it establishes the decision-making body. |
| December 10, 2023 | Initial Submissions | Both parties submit initial written arguments, setting the stage for the legal arguments and evidence to be presented. These initial filings are foundational to the arbitration. |
| January 15, 2024 | Pre-hearing Conference | A pre-hearing conference is scheduled to discuss procedural matters, clarify issues, and potentially narrow the scope of the dispute. This helps streamline the proceedings. |
| February 28, 2024 | Witness Testimony | Witness testimony is scheduled, allowing both sides to present evidence directly from individuals involved in the case. This is a critical stage in establishing facts. |
| March 15, 2024 | Closing Arguments | The parties present their final arguments, summarizing their positions and evidence. This marks a crucial point in the arbitration. |
| April 5, 2024 | Arbitral Award | The arbitral tribunal issues its final award, resolving the dispute and outlining the legal determination. This is the culmination of the arbitration process. |
Importance of Specific Dates and Deadlines
Specific dates and deadlines play a crucial role in arbitration proceedings. These deadlines ensure that the process moves forward efficiently and prevents delays. Failure to adhere to deadlines can have significant consequences.
- October 26, 2023: The date of the arbitration request is important because it officially initiates the dispute resolution process. This date sets the legal clock for the case.
- Arbitrator appointments: The timely appointment of arbitrators is crucial, as this step establishes the decision-making body for the case. Delays can impact the overall timeline.
- Pre-hearing Conference: The pre-hearing conference is important because it allows for clarification of issues, narrowing the scope of the dispute, and streamlining the subsequent proceedings.
- Witness Testimony and Closing Arguments: These are pivotal stages in presenting evidence and arguments. The dates of these events determine the flow of the proceedings.
- Arbitral Award: The date of the arbitral award marks the conclusion of the case. This final step determines the outcome of the dispute.
Economic and Political Context
The Woodside Energy arbitration in Senegal unfolds against a backdrop of complex economic and political realities. Understanding these factors is crucial to comprehending the potential outcomes and implications of the case. Senegal’s trajectory, both economically and politically, significantly influences the arbitration process and its ultimate resolution. International relations also play a crucial role in shaping the environment surrounding the dispute.
Economic Situation in Senegal
Senegal’s economy is predominantly service-oriented, with agriculture and fishing playing important, though less prominent, roles. Significant challenges include infrastructure limitations, which impact the ease of doing business. High levels of youth unemployment also contribute to socio-economic instability. Recent economic growth has been spurred by investments in the energy sector, particularly with the increasing presence of oil and gas projects.
However, this growth is not evenly distributed, leading to disparities in wealth and opportunity.
Political Climate in Senegal
Senegal boasts a relatively stable democratic political system, but challenges remain in ensuring equitable access to resources and opportunities for all citizens. Political stability is vital to attracting foreign investment and ensuring the successful execution of major projects like the one involving Woodside Energy. Recent political developments and their potential impact on the arbitration process are critical considerations.
The government’s stance on foreign investment and its adherence to established legal frameworks are key factors in this case.
International Relations Considerations
Senegal’s international relations are diverse and multifaceted. The country maintains strong ties with several international organizations and its approach to foreign investment is influenced by its relationships with key partners. Potential diplomatic or international pressures could influence the arbitration’s course. For example, the country’s role in regional organizations could impact the involvement of external actors in the arbitration.
Energy Sector Overview
Senegal’s energy sector is undergoing a period of significant development, driven by the discovery of substantial hydrocarbon resources. This has created opportunities for growth but also presented challenges regarding environmental protection and equitable distribution of benefits. The energy sector’s expansion also intersects with broader economic development plans, highlighting its strategic importance. Foreign investment in the energy sector is vital for Senegal’s long-term energy security and economic advancement.
Economic Factors Impacting the Arbitration, Woodside energy files arbitration proceedings against senegal
| Economic Factor | Impact on Arbitration |
|---|---|
| GDP Growth Rate | A declining GDP growth rate could indicate economic hardship, impacting the government’s ability to fulfill its contractual obligations and potentially influencing the arbitration’s outcome. |
| Inflation Rate | High inflation erodes the purchasing power of currency, which could impact the financial implications of the arbitration. |
| Foreign Investment Climate | A hostile or uncertain foreign investment climate could dissuade future investors, potentially impacting the overall economic stability of the country. |
| Government Revenue | Changes in government revenue can affect the state’s ability to support projects like the one in question, influencing the arbitration’s outcome. |
| Infrastructure Development | Improved infrastructure can facilitate economic growth, potentially supporting the company’s operations and influencing the arbitration. |
Legal Precedents and Analysis

The Woodside Energy arbitration in Senegal hinges on a complex interplay of international law, national regulations, and contractual obligations. Understanding the legal precedents relevant to similar disputes is crucial for evaluating the potential outcomes. This analysis examines the applicable international legal framework, explores key legal arguments from both sides, and highlights the specific laws and regulations involved.
Relevant Legal Precedents
Numerous international investment agreements (IIAs) and arbitral awards provide precedents for disputes involving foreign investment and expropriation. These precedents establish the standards for assessing the legality of government actions and the remedies available to investors. A key consideration is whether the actions taken by the Senegalese government constitute a breach of its obligations under these agreements.
International Legal Framework
The applicable international legal framework encompasses treaties, conventions, and customary international law. The relevant provisions address issues such as fair and equitable treatment, full protection and security, and the prohibition of arbitrary or discriminatory measures. Specifically, the relevant agreements might include provisions related to the treatment of foreign investment and the mechanisms for resolving disputes. The specific framework applicable depends on the relevant IIAs, bilateral investment treaties (BITs), and other agreements between Senegal and the investor’s home country.
Comparison with Similar Disputes
Analyzing previous cases involving similar issues of investment disputes, expropriation, and contract breaches is essential for understanding the strengths and weaknesses of both sides’ arguments. Such comparisons help anticipate potential challenges and identify potential precedents for legal arguments. For instance, analyzing previous cases of expropriation in similar contexts can provide insights into the potential for successful legal claims.
Legal Arguments of the Parties
| Party | Argument |
|---|---|
| Woodside Energy | Woodside Energy will likely argue that the Senegalese government’s actions, including [specific government actions, e.g., changes in regulations, or delays in permits], violate the fair and equitable treatment provisions of the relevant agreements. The company will emphasize the contractual obligations and the economic losses suffered due to these actions. |
| Senegal | Senegal will likely argue that its actions were justified under national law and public interest considerations. The government might claim that the actions taken were within their rights to regulate and manage natural resources. Senegal might also emphasize the sovereign right to regulate, the existence of necessary permits, and compliance with local laws. They may highlight specific legal justifications for the changes in regulations. |
Applicable Laws and Regulations
Senegal’s domestic laws and regulations governing energy exploration and exploitation are crucial to the case. These laws will be examined to determine if the government’s actions are in compliance with national laws. Furthermore, the laws of the investor’s home country may also play a role if the investor is bound by those laws. Both sides’ arguments must demonstrate compliance or non-compliance with relevant legal requirements, including environmental and labor laws.
Visual Representation of Data
Dissecting the Woodside Energy arbitration proceedings against Senegal requires a visual approach to comprehend the intricate financial, temporal, and relational aspects. These visualizations will offer a clear picture of the potential outcomes, timeline, party relationships, project location, and legal arguments involved in this complex case.
Financial Implications of Potential Outcomes
Understanding the potential financial ramifications is crucial for stakeholders. The table below illustrates the estimated financial impacts of different arbitration outcomes, categorized by potential award amounts and the resulting impact on Woodside Energy’s projected profits.
| Arbitration Outcome | Estimated Award (USD millions) | Impact on Woodside Energy Projected Profits (USD millions) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Favorable to Woodside | 150-300 | +150-300 | Woodside receives a substantial award, boosting projected profits significantly. |
| Neutral | 0-50 | 0-50 | The award is negligible, with minimal impact on projected profits. |
| Unfavorable to Woodside | -100-200 | -100-200 | Woodside incurs significant financial losses, impacting projected profits substantially. This outcome is highly dependent on the cost of litigation. |
Note: These figures are estimations based on the case’s complexity and various factors. They are not definitive predictions but serve as a guide to potential financial consequences.
Timeline of Events
Visualizing the timeline helps to grasp the progression of the arbitration process. This chart Artikels key milestones, from the initial dispute to the potential final award.
The timeline is represented by a bar chart, with each bar representing a key event and the length corresponding to the duration. Dates are approximate and subject to change based on court proceedings.
Relationships Between Parties
A clear understanding of the relationships between the parties involved is vital. This diagram displays the interconnections between Woodside Energy, Senegal, the arbitration tribunal, and other relevant parties.
The diagram uses various shapes to represent each entity and connecting lines to illustrate their interactions. This visualization clarifies the complex network of participants in the arbitration process.
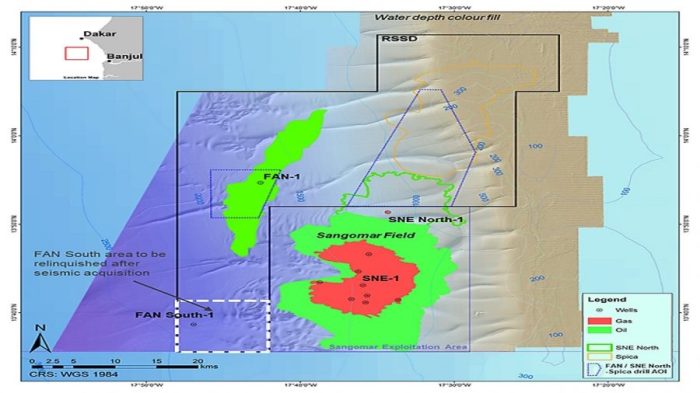
Location of the Project
Visualizing the location of the project provides geographical context. This map highlights the area where the disputed energy project is situated.
The map is crucial for understanding the geographical factors that might influence the arbitration outcome.
Legal Arguments
The legal arguments are complex and multifaceted. This graphic Artikels the key arguments presented by both sides, visually representing the core issues in contention.
The graphic displays the arguments in a clear and concise manner, providing a visual summary of the legal points at issue.
Last Point
In conclusion, the Woodside Energy arbitration against Senegal presents a compelling case study of international legal disputes in the energy sector. The intricacies of the agreements, the motivations of the parties, and the potential outcomes highlight the complexities of international relations and the importance of careful legal maneuvering. This case will undoubtedly have far-reaching implications for future investments in Senegal’s energy sector, and serves as a critical benchmark for similar agreements globally.

